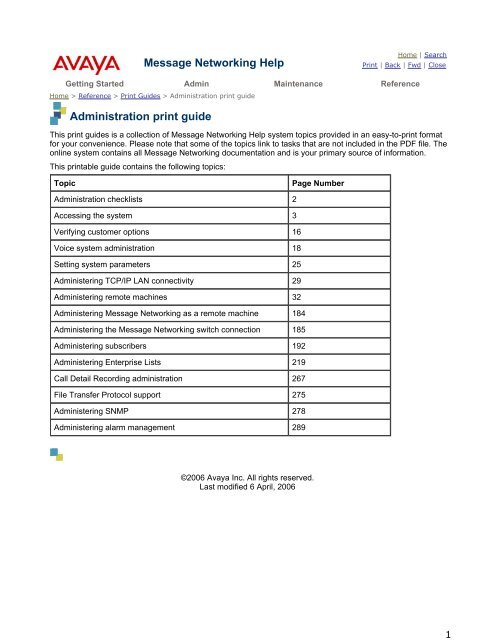
Administration printable guide - Avaya Support
Administration printable guide - Avaya Support
Administration printable guide - Avaya Support
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
6Overview of passwordsAccess to the Message Networking system is controlled by a set of passwords that provide different accesslevels. The following passwords are provided with the system for system installers, administrators, and supportpersonnel:! sa: The sa login is for use by the customer's system administrators either from the console or via anothercomputer on the customer's LAN.! craft: The craft login is for use by <strong>Avaya</strong> personnel performing system installation, administration, ormaintenance on the customer site, either from the console or via another computer on the customer'sLAN.! dadmin: The dadmin login is for use by <strong>Avaya</strong> Business Partners performing administration ormaintenance on the customer site, either from the console or via another computer on the customer'sLAN. The customer must use the craft login to activate the dadmin login and grant permission. Thedadmin login has the same permissions as the craft login.! icftp: The icftp login is for use with Message Networking's FTP feature. The FTP feature enables fileimporting and exporting.! sappp: The sappp login is for use by a system administrator performing system administration andmaintenance remotely via dial up. You must set up the sappp password to allow the remote administratorto dial in to the system.! craftppp: The craftppp login is for use by remote <strong>Avaya</strong> personnel performing system installation,administration, or maintenance via dial up. You must set up the craftppp password to allow the remote<strong>Avaya</strong> personnel to dial in to the system.When your system is installed, the sa and icftp logins come with default passwords. You must change thesepasswords immediately to ensure system security following minimum password standards. You should also setup the system's ppp passwords, to allow a remote service center to dial in to the system to performtroubleshooting or system maintenance. See Administering logins and passwords for information on setting upadditional logins.Additionally, you can administer several parameters of the password aging feature that will enhance the level ofsecurity the system maintains.Note: You can administer the Access Security Gateway (ASG) on the Message Networking system to provideadditional security. The ASG provides the newest generation of strong authentication for the MessageNetworking system logins by challenging each potential dial-up session user when the authentication type for aparticular login is set to ASG. To respond to the ASG challenge, the user must have a handheld device, calledthe ASG Key, which must be set with an ASG secret key number that matches that of the user's ASG secret keynumber in the Message Networking system.Guidelines for passwordsTo minimize the risk of unauthorized people using the Message Networking system, follow these <strong>guide</strong>lines forsystem administrator passwords.! Establish a new password as soon as the Message Networking system is installed.! Use a password containing 6–8 alphanumeric characters.! Never use obvious passwords, such as a telephone extension, room number, employee identificationnumber, social security number, or easily guessed numeric or letter combinations (for example, denver oraudix).! Do not post, share, print, or write down passwords.! Do not put the password on a programmable function key.! Change the password at least once per month. You can administer your system to age the password andnotify you that a new password is required. See Setting administrator password aging for moreinformation.
7! If you suspect that the security of any password has been compromised, notify your project manager orsystem administrator.Changing passwordsYou should immediately change the password for the sa, icftp, craft, and dadmin logins after your system isinstalled. Once a new password is established, you should also establish a regular schedule for changing thepassword, for example, at least monthly. Be sure to alert any other Message Networking administrators orsystem administrators to the change in the passwords.The passwords for which you can set Password Aging depend on your login. For example, when you are loggedin with the sa password, you can set Password Aging for the sa, icftp, and sappp passwords.To change the password for the sa login:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Password<strong>Administration</strong> > Assign/Change Password.The system displays the Assign/Change Password page. For information about the fields on this page,click Help.2. At the Login drop-down box, select the login for the password you want to change.3. In the New Password field, type a new password containing 6–8 alphanumeric characters.4. In the Reenter New Password field, type the new password again for verification.5. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Setting Administrator Password AgingYou can determine how often the system's passwords have to be changed by setting the Password Aging. Thepasswords for which you can set Password Aging depend on your login. For example, when you are logged inwith the sa password, you can set Password Aging for the sa, icftp, and sappp passwords. It is stronglyrecommended that you set Password Aging for administrator passwords to help maintain a high level of systemsecurity. However, the sa login can disable the Password Aging feature for the sa login.To set administrator Password Aging:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Password<strong>Administration</strong> > Assign/Change Password Aging.2. At the Login drop-down box, select the login for which you want to change aging.3. Click Save.The system displays the Change Password Aging page. For information about the fields on this page,click Help.4. Designate the attributes for this login password by selecting Yes/No, and type the number of days.For additional information on any field, click the field name.5. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.6. To change the aging attributes for other logins, click Back (on the browser toolbar) twice, and reselect alogin.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
8Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG)Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG)The Access Security Gateway (ASG) provides the newest generation of strong authentication for the MessageNetworking system logins. ASG protects the Message Networking system by challenging each potential dial-upsession user when the authentication type is set to ASG for that particular login (such as sa). The following tablelists the types of authentication supported on the system and the access ID required for each authenticationtype.Authentication typeASGPasswordBlockedAccess ID requiredASG challenge/responseSystem passwordno access allowedIn order to respond to the ASG challenge, the user must have a handheld device, called the ASG Key. The ASGKey must be set with an ASG secret key number that matches that of the user's ASG secret key number in theMessage Networking system.This topic includes the following information:! Logging in with ASG! Maintaining ASG login IDs" Adding an ASG login" Blocking or reinstating access privileges for an ASG login" Changing the ASG secret key number for an ASG login" Displaying ASG login information" Disabling ASG authentication! Setting and resolving violation warningsTop of page" Setting notification limits" Resolving ASG security violation warningsMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Logging in withASGLogging in with ASGWhen you begin a remote session with an Message Networking system that has the ASG feature activated, thesystem prompts you with a challenge.
9To log in to a system that has ASG activated for your login:1. Enter your login ID at the login: prompt.The terminal screen displays the following message:Challenge: xxxxxxxResponse:2. Press Enter on the ASG Key to start the ASG Key.The ASG Key displays the following message:PIN:3. On the ASG Key, type your PIN, and press Enter.4. On the ASG Key, type the challenge number that is displayed on the terminal screen, and press Enter.The ASG Key displays the unique, 7-digit response number that corresponds to the challenge numberyou entered. The challenge and response numbers are valid for this session only.5. On the terminal screen at the Response: prompt, enter the response number that is displayed on theASG Key.If the authentication process is successful, the system displays the <strong>Administration</strong> main menu for the salogin. If the authentication process fails, the system makes an entry in the system History Log anddisplays the following message:INVALID LOGINAfter a certain number of unsuccessful attempts, which is set in the Login Security Violation Warning<strong>Administration</strong> page, a warning alarm is generated.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Maintaining ASGlogin IDsMaintaining ASG login IDsOnce you establish an ASG login for a Login ID, anyone with that login who attempts to access your systemremotely through a protected port is prompted for the challenge response number.Maintaining ASG login IDs involves the following tasks:! Adding an ASG login! Blocking or reinstating access privileges for an ASG login! Changing the ASG secret key number for an ASG login! Displaying ASG login information! Disabling ASG authenticationTop of page
10Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Adding an ASGloginAdding an ASG loginThis topic provides information on adding an ASG login to the system.Note: The default authentication type for sa is password, which requires the usual login and password. Youmust be logged in as sa to add an ASG login for sa.To add a new ASG login to your system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong> > ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong> page. For information about the fields on thispage, click Help.2. Select the login from the Login ID: drop-down menu.3. Select ASG from the Authentication Type? drop-down menu to activate ASG authentication.Note: If you select Password from the Authentication Type? drop-down menu, the system uses regularMessage Networking password protection. See Guidelines for Passwords for more information.4. Do one of the following in the System Generated Secret Key field:" Select Yes to have the system randomly generate an ASG secret key number. Then leave theSecret Key: field blank." Select No if you want to enter the secret key that the system uses to generate ASG responses.Then type the secret key in the Secret Key: field." Do not make a selection for the System Generated Secret Key field if you selected Password inthe Authentication Type? field. Then leave the Secret Key: field blank, also.5. Click Save to make the changes.6. A confirmation page displays the ASG secret key number that must match the ASG Key when a userattempts to log in. The ASG secret key number must be entered into the ASG Key as Key1 or Key2.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Blocking orreinstating access privileges for an ASG loginBlocking or reinstating access privileges for an ASG loginYou can block ASG login access temporarily if necessary.To block or reinstate access for the ASG login:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong> > ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong> page. For information about the fields on thispage, click Help.
112. Select the Login ID (User ID) that you want to block or reinstate. You can choose only from the IDs in thelist. You cannot create new IDs.3. To block the user's access to the system, select Blocked from the Authentication Type? drop-downmenu.4. To reinstate the user's access to the system, select ASG from the Authentication Type? drop-downmenu.5. Click Save to accept the page settings.A confirmation page displays.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Changing the ASGsecret key number for an ASG loginChanging the ASG secret key number for an ASG loginThe ASG secret key number is used by the system and by the ASG Key handheld device to create challengeresponse pairs of numbers. If an ASG secret key number is lost or compromised, it must be changed in thesystem and in all associated ASG Key handheld devices.To change the ASG secret key number:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong>> ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong> page. For information about the fields on thispage, click Help.2. Select the ASG login ID from the Login ID: drop-down menu.3. Select Yes in the System Generated Secret? field if you want the system to generate a unique secret keynumber, or select No in the System Generated Secret? field if you want to enter your own secret keynumber.4. Complete the Secret Key: field if you selected No from the System Generated Secret? drop-down menu.5. Click Save to accept the page settings.6. A confirmation page displays the ASG secret key number that must be entered into the ASG Keyhandheld device.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
12Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Displaying ASGlogin informationDisplaying ASG login informationYou can check the status of an ASG login if necessary.To display ASG login information:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong> > ASG Security Logins Display.The system displays the Display ASG Security Login Information page.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Disabling ASGauthenticationDisabling ASG authenticationIf you want to discontinue ASG protection for a particular login, change the Authentication Type to Password.This will allow access to the Message Networking system with just the login ID and password.To disable ASG authentication:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong> > ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the ASG Security Login <strong>Administration</strong> page. For information about the fields on thispage, click Help.2. Select the Login ID (User ID) for which you want to disable ASG authentication from the Login ID dropdownmenu.3. Select Password from the Authentication Type? drop-down menu.4. Click Save to accept the page settings.A confirmation page displays.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
13Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Setting andresolving violation warningsSetting and resolving violation warningsASG tracks the number of unsuccessful login attempts and the time between unsuccessful login attempts. Ifsomeone exceeds the allowed number of failed login attempts, a warning is added to the Alarm Log.The following tasks are associated with setting and resolving violation warnings:! Setting notification limits! Resolving violation warningsTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the Access Security Gateway (ASG) > Setting notificationlimitsSetting notification limitsThis topic provides information on setting notification limits for ASG login warnings.To set notification limits for ASG logins:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong> > ASG Login Security Violation Warning <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the Login Security Violation Warning <strong>Administration</strong> page. For information about thefields on this page, click Help.2. Type a new value in the Number of failed login attempts: field, if necessary.3. Type a new value in the Failed login measurement window: field, if necessary.4. Click Save to accept the page settings.5. Specify whether you want to resolve an active ASG warning alarm in the Resolve existing alarm? field.Select Yes to specify that you want to resolve an active ASG warning alarm. Select No to specify thatyou do not want to change the status of any active alarms.A confirmation page displays.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance Reference
14Home > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Administering the access security gateway (ASG) > Resolving ASGsecurity violation warningsResolving ASG security violation warningsThis topic provides information on resolving an ASG security violation warning:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu and select Basic Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> > Access SecurityGateway (ASG) Security <strong>Administration</strong> > ASG Login Security Violation Warning <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the Login Security Violation Warning <strong>Administration</strong> page. For information about thefields on this page, click Help.2. Select Yes from the Resolve existing alarm? menu.3. Click Save to accept the page settings.A confirmation page displays.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Accessing the system > Setting up remote access to the systemSetting up remote access to the systemComplete the following procedures to set up remote access to the Message Networking system. Theseprocedures allow a remote service center to dial in to the server to perform troubleshooting or systemmaintenance:! Administer logins and passwords! Configure the PPP server! Activate the RMB modem (external modems only)Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Setting up remote access to the system > Administering logins and passwordsAdministering logins and passwordsYou might be required to set up additional logins, such as the dadmin login that <strong>Avaya</strong> Business Partners use toperform administration or maintenance on the system, either from the console or via another computer on thecustomer's LAN. You can use the craft login to activate dadmin or other required logins and grant permission.You must administer logins and passwords for all INADS-supported systems to support remote maintenance.
15See the Message Networking planning forms on the Documentation CD-ROM for a list of required logins andpasswords.To administer additional logins:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Password<strong>Administration</strong> > Assign/Change Password.The Assign/Change Password page displays. For information about the fields on this page, click Help.2. At the Login drop-down box, select the login that you want to administer (for example, dadmin orcraftppp).3. In the New Password field, enter the appropriate password.4. In the Re-enter New Password field, type the new password again for verification.5. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.6. Click the Back button on the Web browser to return to the Assign/Change Password page.7. Repeat Steps 2 through 6 for each additional login you need to administer.8. When finished, click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering TCP/IP LAN Connectivity > Configuring the PPP serverConfiguring the PPP serverThis topic provides information on identifying the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) servers. You must identify thelocal and remote IP addresses that are required for PPP remote access to the system. PPP connections allowinternal and external support teams to connect to the Message Networking system through a dial-up connection.To set up PPP service on this machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > TCP/IP <strong>Administration</strong> >PPP Server Configuration.The PPP Server Configuration page displays.2. For each login that you must administer, enter the following information. See the Message Networkingplanning forms on the Documentation CD-ROM for a list of required logins and passwords. Forinformation on completing the fields, click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page:a. For Local IP Address, type the customer-provided IP address for the PPP access through theMessage Networking system modem.b. For the Remote IP Address, type the IP address provided by the customer or remote support forthe remote device that will connect to this Message Networking system.3. Repeat step 2 for each of the PPP logins you need to set up.4. When finished, click Save.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
16Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Setting up remote access to the system > Activating the RMB modem (external modems only)Activating the RMB modem (external modems only)The system automatically activates the on-board modem for the type of RMB installed in the United States.However, international users must activate the external modem that connects to the RMB on the server. Thismodem is used to report alarms, and to allow remote support personnel to dial in to the server.To activate the modem for an external RMB board:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Modem and Terminal<strong>Administration</strong> > Install Modem/Terminal software.The Install Modem/Terminal Software page displays.2. Locate Device Type RMB and update the fields for the modem you are using. Click Help for informationabout completing each field.3. When finished, click Save.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Verifying customer optionsVerifying customer optionsThe Message Networking system has a variety of optional features. If you purchase an optional feature, you canverify that it is enabled (turned on) by checking its status on the Customer Options page. All available optionsare activated on the S3400-H server.Only certified <strong>Avaya</strong> personnel can change options on this page, but the page can be displayed for informationalpurposes. If an option is turned off, it will not function.Note: If you require changes to the right-to-use features activated on the system, you must contact <strong>Avaya</strong>technical support. Right-to-use activations are only completed Monday through Friday between the hours of 8a.m. and 7 p.m., EST. Make sure you have the following information available:! Business Partner name, if applicable! Order Number for Message Networking. If SMTP/MIME is purchased through Modular Messaging, youalso need Order Number for Modular Messaging! Remote log-in informationTo verify feature options:1. Log on to Message Networking.The system displays the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.2. Select Global <strong>Administration</strong> > Customer Options.
17The system displays the Customer Options (Read Only) page. The following table describes the featureoptions that apply to the Message Networking system.3. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Feature option Current MaximumAMIS NodesAria Digital PortsCall Detail Recording(CDR)Digital NodesEnterprise List<strong>Administration</strong>Number of BridgedNodesOctel Analog NodesON or OFF; indicates whether remote AMIS Analogmachines can be connected to the Message Networkingsystem.If this field is set to YES, a maximum of 500 AMIS Analognodes can be connected to the Message Networkingsystem. Note that the total number of nodes betweenOctel nodes, AMIS nodes, and Digital nodes cannotexceed 500.Number of simultaneous Aria Digital sessions support onthe Message Networking system. This is always set to 4for the 3S210/S3210R and to 16 for the S3400-H.Indicates whether CDR is activated.ON or OFF; indicates whether remote digital machinescan be connected to the Message Networking system.If this field is set to YES, a maximum of 500 digital nodescan be connected to the Message Networking system.Note that the total number of nodes between Octel nodes,AMIS nodes, and Digital nodes cannot exceed 500.ON or OFF; indicates whether the Enterprise List featureis enabled on the Message Networking system.Note: The Enterprise List feature is only available on theS3400-H server.Indicates whether the Message Networking system isusing a hub-and-spoke or bridging configuration. Whenthis parameter is set to 500 (the maximum), MessageNetworking is being used in a hub-and-spokeconfiguration. When this parameter is set to any numberbelow 500, a bridging configuration is being used and thisparameter specifies the number of remote machines thatcan be designated as a bridged machine.For the S3210/S3210R server, the default for this field is1. For the S3400-H server, the default for this field is 500.Note: If the number of systems administered as bridgedmachines equals the Number of Bridged Nodes on theCustomer Options page, you must not modify the Numberof Bridged Nodes parameter to reduce the number ofbridged nodes. If you do, the system removes the bridgingfrom the first system you administered as a bridgedmachine.ON or OFF; indicates whether remote Octel AnalogNetworking machines can be connected to the MessageNetworking system.If this field is set to ON, a maximum of 500 Octel AnalogNetworking nodes can be connected to the MessageON/OFF4 or 16ON/OFFON/OFFON/OFF500ON/OFF
18SMTP PortsSNMPSerenade Digital PortsTCP/IP digital portsvoice_portsNetworking system. Note that the total number of nodesbetween Octel nodes, AMIS nodes, and Digital nodescannot exceed 500.Indicates the number of simultaneous SMTP sessionssupported on the Message Networking system. Thesesessions are shared by the SMTP/MIME and VPIMprotocols.0 or 8 for the S3210/S3210R; 20 for the S3400-HON or OFF; indicates whether SNMP is supported on theMessage Networking system.If this field is set to ON, you can administer SNMP on theMessage Networking system to provide alarm informationto a remote network management system.Indicates the number of simultaneous Serenade Digitalsessions supported on the Message Networking system.This feature is always set to 4 for the S3210/S3210R andto 16 for the S3400-H.Indicates the number of simultaneous AUDIX digitalsessions supported. This feature is always set to 4 for theS3210/S3210R and to 12 for the S3400-HIndicates the number of analog ports on the MessageNetworking system. This feature can be set to 0, 4, 8, or12 for the S3210/S3210R. This feature can be set to 0, 4,8, 12, 16, or 24 or for the S3400-H.8 or 20ON or OFF4 or 164 or 1212 or 24Note: When referring to digital communication, the number of ports supported refers to the simultaneousTCP/IP sessions supported. For example, support for 12 SMTP ports indicates that the system supports amaximum of 12 simultaneous sessions shared by the SMTP/MIME and VPIM protocols. All digitalcommunication on the Message Networking system is supported by the installed LAN card/connector.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing voice system administrationPerforming voice system administrationThis procedure provides information on administering the voice system. Voice system administration includesthe following tasks:! Voice equipment administration! Number services administration! Call transfer administrationTop of page
19Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing voice system administration > Administering voice equipmentAdministering voice equipmentThis procedure provides information on voice equipment administration. Voice equipment administrationinvolves the following tasks:! Assign channels to groups! Assign PBX extensions to channels! Assign services to channels! Change state of voice equipment! Renumber voice system! Unassign channels from groups! Unassign PBX extension from a channel! Unassign services from channelsNote: These procedures are only required for Message Networking systems supporting analog.To assign channels to groups:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > Channels to Groups.The Assign Channels to Groups page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To assign PBX extensions to channels:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > PBX Extensions to Channels.The PBX Extensions to Channels page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page as follows. For information on completing the fields, click the field namesor Help on the Web-based administration page.3. Make the following field settings, as specified by the customer:" Starting PBX Extension: enter the phone number for the first channel" Starting Channel Number: 0 - start at channel 0" Ending Channel Number: 3 - enter the last channel number (on a 4-port system the number is 3,on an 8-port system the number is 7)4. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.
20To assign services to channels:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > Services to Channels.The Services to Channels page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page using the following settings. For information on completing the fields,click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page.3. Make the following field settings:" Channel Numbers: all" Service Name: acr4. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the state of the voice equipment:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > State of Voice Equipment.The State of Voice Equipment page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page using the following settings. For information on completing the fields,click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page.Make the following field settings:" New State: inserv" Equipment: Card" Equipment Number: all" Change Immediately?: Yes3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To renumber the voice system:Note: Use the Renumber Voice System page to remove all NONEX cards from the voice equipment table.Warning: This command brings down the voice system immediately! Any options or script assignments thatmight have been made to these NONEX cards and their channels are permanently lost! In addition, thiscommand reorders the voice equipment table so that all existing T1s are followed by TRs and then by SPs. Thisreordering results in the channel numbers on some of the cards changing. All user-defined characteristics(options, attributes, script assignments) of a channel remain intact, regardless of the reordering. If a card isdiscovered in the system that was not in the voice equipment table, it is then added in its correct position withdefault settings.1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > Renumber.The Renumber Voice Equipment page displays.2. Click Continue to renumber the voice equipment, or click Quit to return to the previous page withoutrenumbering.3. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To unassign channels from groups:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment
21<strong>Administration</strong> > Channels from Groups.The Unassign Channels from Groups page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To unassign a PBX extension from a channel:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > PBX Extension from Channel.The Unassign PBX Extension from a Channel page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To unassign services to channels:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Voice Equipment<strong>Administration</strong> > Services from Channels.The Unassign Services from Channels page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing voice system administration > Administering number serviceAdministering number serviceThis procedure provides information on administering number service. When a call comes into the MessageNetworking system, it passes the call to a service based on the best match between the called and/or callingnumbers of the call and the list of called and/or calling numbers of the installed services.
22When an incoming call arrives, the system finds the most specific range of called numbers that includes thecalled number for the call. If the system finds more than one range of called numbers that includes the callednumber, the system continues to look for the most specific range of calling numbers that includes the callingnumber of the caller. When there is a most specific match on called and calling numbers, the servicecorresponding to that match handles the call. If there is no match, the call is handled by the servicecorresponding to "any" called or "any" calling number. To ensure that all calls are answered, it is important toassign a service to a called number of "any" and a calling number of "any."Number service administration involves the following tasks:! Assign service! Display services! Unassign serviceTo assign number service, which specifies the called and calling numbers assigned to each installed service:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Number Services<strong>Administration</strong> > Assign Service.The Assign Number Service page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To display the currently assigned services:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Number Services<strong>Administration</strong> > Display Services .The Display Services page displays.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To assign number service:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Number Services<strong>Administration</strong> > Unassign Service.The Unassign Number Services page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page using the following settings. For information on completing the fields,click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page.3. Make the following field settings:" Channel Numbers: all" Service Name: acr4. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
23Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing voice system administration > Administering call transfer numbersAdministering call transfer numbersThis procedure provides information on call transfer administration. Call transfer administration involves thefollowing tasks:! Adding allowed transfer numbers! Deleting allowed transfer numbers! Displaying allowed transfer numbers! Adding denied transfer numbers! Deleting denied transfer numbers! Displaying denied transfer numbersTo add allowed transfer numbers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Call Transfer<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Allowed Numbers.The Add Allowed Transfer Numbers page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete allowed transfer numbers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Call Transfer<strong>Administration</strong> > Delete Allowed Numbers.The Delete Allowed Transfer Numbers page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To display allowed transfer numbers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Call Transfer<strong>Administration</strong> > Display Allowed Numbers.The Display Allowed Transfer Numbers page displays.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To add denied transfer numbers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Call Transfer<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Denied Numbers.The Add Denied Transfer Numbers page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help
24on the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete denied transfer numbers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Call Transfer<strong>Administration</strong> > Delete Denied Numbers.The Delete Denied Transfer Numbers page displays.2. Complete the fields on this page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To display denied transfer numbers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Voice System <strong>Administration</strong> > Call Transfer<strong>Administration</strong> > Display Denied Numbers.The Display Denied Transfer Numbers page displays.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
25Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Setting system parametersSetting system parametersThe System Parameters menu allows you to define the following Message Networking system settings:! General parameters! Reschedule parameters! AMIS Analog parameters! AMIS Analog timing parameters! Serenade Digital parametersSet system parameters only once for each Message Networking system in your network.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong>> Setting system parameters > Administering general system parametersAdministering general system parametersThis topic provides information on administering the general system parameters. Before you complete thisprocedure, make sure that you configure network addressing.To administer the general system parameters:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > SystemParameters > General Parameters.The system displays the General Parameters page.2. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.Important! If you want to change the Network Address Length field after initial system installation, seeChanging the system's network address length.3. Click Save.4. Click Back to return to the System Parameters page or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | Close
26Getting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong>> Setting system parameters > Administering rescheduling parametersAdministering rescheduling parametersUse this page to optionally change the increments at which the system reschedules unsuccessfully sentmessages. If you do not modify this page, the system uses the default rescheduling increments.To set the rescheduling increments for unsuccessful message delivery:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > SystemParameters > Rescheduling Parameters.The system displays the Rescheduling Parameters page.2. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.3. Click Save.4. Click Back to return to the System Parameters page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong>> Setting system parameters > Administering AMIS Analog parametersAdministering AMIS Analog parametersUse this page to identify the telephone number to use for protocol exchanges with AMIS Analog remotemachines.To administer the parameters to be used by AMIS Analog on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Administer Message Networking > System Parameters >AMIS Analog Parameters.The system displays the AMIS Analog Parameters page.2. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.3. Click Save.4. Click Back to return to the System Parameters page or click Return to Main.Top of page
27Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering system parameters > Administering AMIS Analog timing parametersAdministering AMIS Analog timing parametersThis topic provides information on defining the timing parameters used by the AMIS Analog protocol.Administering AMIS Analog timing parameters involves the following tasks:! Adding a new AMIS Analog timing definition! Changing an existing AMIS Analog timing definition! Deleting an AMIS Analog timing definitionTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering system parameters > Administering AMIS Analog timing parameters > Adding anew AMIS Analog timing definitionAdding a new AMIS Analog timing definitionThis topic provides information on adding a new AMIS Analog timing definition. Message Networking's AMISAnalog timing parameters define the timing used by the AMIS Analog protocol.To add a new AMIS Analog timing definition:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > SystemParameters > AMIS Analog Timing Parameter Definition.The system displays the AMIS Analog Timing Parameter Definition page, which displays the currenttiming definitions.2. To add a new timing definition, click Add A New Timing Definition.The system displays the Add New AMIS Timing Definition page.3. Complete the fields on the page.4. Click Add.A message displays that the new timing definition has been added.5. Click OK.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
28Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering system parameters > Administering AMIS Analog timing > Changing an existingAMIS Analog timing definitionChanging an existing AMIS Analog timing definitionThis topic provides information on changing an existing AMIS Analog timing definition. Message Networking'sAMIS Analog timing parameters define the timing used by the AMIS Analog protocol.To change an AMIS Analog timing definition:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > SystemParameters > AMIS Analog Timing Parameter Definition.The system displays the AMIS Analog Timing Parameter Definition page, which displays the currenttiming definitions. Use the scroll bar to view the entire list of definitions.2. To modify an existing timing definition, select the timing definition that you want to change, and clickChange A Selected Timing Definition.The system prompts whether you want to change the selected timing definition.3. Click Yes.4. The system displays the Change An AMIS Timing Definition page.5. Modify the fields on the page.6. Click Change.A message displays that the timing definition has been changed.7. Click OK.8. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering system parameters > Administering AMIS Analog timing > Deleting an AMISAnalog timing definitionDeleting an AMIS Analog timing definitionThis topic provides information on deleting an AMIS Analog timing definition. Message Networking's AMISAnalog timing parameters define the timing used by the AMIS Analog protocol.To delete an AMIS Analog timing definition:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > SystemParameters > AMIS Analog Timing Parameter Definition.The system displays the AMIS Analog Timing Parameter Definition page, which displays the currenttiming definitions. Use the scroll bar to view the entire list of definitions.2. To delete a timing definition, select the timing definition that you want to delete and click Delete ASelected Timing Definition.The system prompts whether you want to delete the selected timing definition.
293. Click OK.A message display that the timing definition has been deleted.4. Click OK.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong>> Setting system parameters > Administering Serenade Digital parametersAdministering Serenade Digital parametersUse this page to administer the Serenade Digital parameters.To administer the parameters to be used by Serenade Digital on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > SystemParameters > Serenade Digital Parameters.The system displays the Serenade Digital Parameters page.2. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.3. Click Save.4. Click Back to return to the System Parameters page or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering TCP/IP LAN connectivityAdministering TCP/IP LAN connectivityThe following procedures establish addresses for the Message Networking system to use to send and receiveinformation over the customer's LAN. You complete the procedures initially during system installation.! Configure network addressing! Configure the PPP server (optional; for remote support)! Enable/disable the default router ping! Connecting the Message Networking to the LAN (completed during server installation)Before you begin these procedures, determine if the LAN is administered for the system or if you need to notify
30the LAN administrator and arrange for LAN administration for the system.Caution! <strong>Avaya</strong> is not responsible for the installation, administration, or testing of the LAN. Seek service asdirected by your LAN administrator to resolve LAN problems. Some LANs can be administered prior to yourarrival on site. Other LANs require that the administration for a new machine be done at the time of installationbecause an open connection could cause the LAN to fail.If you modify TCP/IP settings, you should test the digital networking and TCP/IP connection to ensure that it isworking properly.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering TCP/IP LAN Connectivity > Configuring network addressingConfiguring network addressingThis topic provides information on configuring the TCP/IP interface.To set up the Message Networking server to work correctly on the corporate LAN:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > TCP/IP <strong>Administration</strong> >Network Addressing.The system displays the Network Addressing page.2. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.Note: It is strongly recommended that you do you not use hyphens or underscores in the Host Name fieldand the Primary Name + Domain field. It is also strongly recommended that the entry in the Host Namefield and the Primary Name in the Primary Name + Domain field match.3. Click Save to accept the page settings.4. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > System Parameters >General Parameters to open the General Parameters page, and then click Save.5. If you change the Host Name after installation, a dialog box informs you that the browser must berestarted:a. Click OK to continue. A results page displays.b. Click Logoff to restart the browser.c. Wait one minute, and then log back into the system.Important! If you modify the Domain Name or IP address field after initial administration, it is critical that youthen open the General Parameters page to verify that the updated Domain Name or IP Address displayscorrectly on the General Parameters page. Failure to verify the change on the General Parameters page cancause Message Networking to stop functioning properly.When the LAN is administered for the system, you should test the TCP/IP LAN connectivity.Top of page
31Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering TCP/IP LAN Connectivity > Configuring the PPP serverConfiguring the PPP serverThis topic provides information on identifying the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) servers. You must identify thelocal and remote IP addresses that are required for PPP remote access to the system. PPP connections allowinternal and external support teams to connect to the Message Networking system through a dial-up connection.To set up PPP service on this machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > TCP/IP <strong>Administration</strong> >PPP Server Configuration.The PPP Server Configuration page displays.2. For each login that you must administer, enter the following information. See the Message Networkingplanning forms on the Documentation CD-ROM for a list of required logins and passwords. Forinformation on completing the fields, click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page:a. For Local IP Address, type the customer-provided IP address for the PPP access through theMessage Networking system modem.b. For the Remote IP Address, type the IP address provided by the customer or remote support forthe remote device that will connect to this Message Networking system.3. Repeat step 2 for each of the PPP logins you need to set up.4. When finished, click Save.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > Getting Started > Installation > Installing the system hardware > Installing the servers > Connecting theMessage Networking server to the LANConnecting the Message Networking server to the LANThis topic provides information on connecting the Message Networking servers to the customer's LAN.Note: Typically, you perform this task during system installation, in which case the system will not yet berunning. If you need to perform this task after initial system installation, make sure that you first shut down thesystem.Connecting the S3210 and S3210R servers to the LANTo connect an S3210 or S3210R server to the corporate LAN:1. Connect one end of the standard Ethernet cable to the RJ45 connector on the back of the server.See S3210R and S3210 back views if you need to locate the LAN connection on the back of the server.2. The other end of this cable should be connected to an Ethernet interface on the corporate LAN.
32The entity that is responsible for maintaining the corporate LAN should make this connection (see thecustomer contract or the statement of work).3. Continue with Connecting the modem.Connecting an S3400-H to the LANTo connect an S3400-H to the corporate LAN:1. Connect one end of the standard Ethernet cable to the appropriate RJ45 connector on the back of theserver:" Integrated video and LAN: Use the NIC1 (1 Ggit) connector next to the video connector." Nonintegrated video and LAN: Use the RJ45 jack on the NIC.See S3400-H back views for examples.2. The other end of this cable must be connected to an Ethernet interface on the corporate LAN.The organization that is responsible for maintaining the corporate LAN should make this connection (seethe customer contract or the statement of work).3. Continue with Connecting the remote maintenance board.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machinesAdministering remote machinesRemote machine administration includes the following tasks:! Adding new remote machines! Modifying existing remote machines! Renaming remote machines! Deleting remote machines! Converting an Interchange remote machine to a Message Networking remote machine! Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping! Administering numeric address mapping! Administering telephone number mapping for Modular Messaging! Administering directory views! Performing remote updates! Monitoring port activity! Performing SMTP security administration! Administering host names! Administering Serenade Digital sender Dial Plan Mapping
33! Testing connections to remote machines! Viewing postmaster@domain! Viewing a list of remote machines! Viewing remote machines Dial Plan Lists! Administering the Message Networking as a remote machine on each remote machineNote: You can also add, modify, and delete remote machines on the Message Networking system using anLDAP client. See LDAP overview for information on Message's Networking's LDAP interface.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding new remote machinesAdding new remote machinesYou can add the following types of remote machines to the Message Networking system:! Adding an INTUITY-related remote machine! Adding an AMIS Analog remote machine! Adding an Aria Analog remote machine! Adding a Serenade Analog remote machine! Adding an Octel 100 remote machine! Adding a Modular Messaging/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine! Adding an Aria Digital remote machine! Adding an Serenade Digital remote machine! Adding a VPIM remote machine! Adding an SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine! Adding an LDAP Client! Adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS remote machine! Adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine! Adding a non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machineNote: You can also add remote machines to Message Networking via an LDAP client. See LDAP overview forinformation on Message Networking's LDAP interface.Top of page
34Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an INTUITY-type remotemachineAdding an INTUITY-type remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an INTUITY-related remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem (DEFINITY ONE Release 2.0, INTUITY AUDIX Release 4.0 or later, IP600 9.2.1, <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770, INTUITYAUDIX LX Release 1.0 and greater, and Interchange Release 5.4.Note: Checklists that provide a list of steps you must complete when adding a new remote machine areavailable for each of the INTUITY-type remote machines:! INTUITY AUDIX Release 4.0 or later! DEFINITY ONE and IP600! INTUITY AUDIX LX and <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770! Interchange Release 5.4To add an INTUITY Release 4.0 remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select INTUITY 4.0 or later from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine? and IP Address fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating. For information onvalid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.6. Click Next Step.The Password field displays.7. Type the password exactly as it is administered on the remote system.8. Click Next Step.The Message Transmission Schedule fields display on the page.9. Complete the Message Transmission Schedule fields. For information on completing the fields, click thefield names or Help on the Web-based administration page.10. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.11. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.12. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.13. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.14. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:
35" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new INTUITY Release 4.0 or later remote machineChecklist for adding a new INTUITY Release 4.0 or later remotemachineThe following table lists the procedures for adding new INTUITY Release 4.0 or later remote machines to theMessage Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the INTUITY AUDIX system. If you are unfamiliar with the INTUITYAUDIX, ask the INTUITY AUDIX system administrator to assist you.Note: TCP/IP administration must be completed on the INTUITY AUDIX system before you add the remotemachine to the Message Networking system.CompletedTaskOn the INTUITY AUDIX system:Gather information about the INTUITY AUDIX remote machine that youare adding. You should obtain the following information:1. Log into the INTUITY AUDIX system.2. From the INTUITY Main Menu, select Audix <strong>Administration</strong>. Fromthe command prompt, type display machine and press Enter. TheMachine Profile screen displays.3. From the Machine Profile screen, obtain the following information:" The machine name from the Local Machine Name field." The IP address from the Dial Str field." The system's network password from the Password field." The extension length from the Extension Length field." Extension rangesNote: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, and so on.Note: The Data Rate and Channel fields on the Local Machine<strong>Administration</strong> screen should contain 0 and 00 respectively.4. Press F7 to go to the next page.5. From the Machine Profile screen, Page 2, make sure that theAllow Automatic Full Updates field is set to y.6. For TCP/IP Networking, set Network Turnaround to n.Obtain a test mailbox number on the INTUITY system from the INTUITY
36AUDIX system administrator. You will use this mailbox to send andreceive test messages through Message Networking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the INTUITY AUDIX subscribers via the PBX. You canobtain the area code and local exchange from the switch administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit INTUITY AUDIXextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theINTUITY AUDIX system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the password in the Password field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.On the INTUITY AUDIX system:Administer the Message Networking system as a remote machine on theINTUITY system.1. From the Main Menu, select Networking <strong>Administration</strong>.2. From the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Local Machine<strong>Administration</strong>. The Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen displays.
373. On the Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen, verify that the LocalMachine Name and Password fields have been administered. (Theother fields on this screen are only relevant if you are performinginternal loop-around testing.)4. Press F6 to return to the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu, andthen select Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong>.5. From the Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select DigitalNetworking Machine <strong>Administration</strong>.6. On the Digital Network Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen:" In the Machine Name field, type the name of the MessageNetworking system. The name must be unique to any othersystem that the INTUITY AUDIX communicates with andmust be an exact case-sensitive match of the MessageNetworking Local Machine Name you recorded on theGeneral Parameters page on the Message Networkingsystem." In the Connection field, type TCP/IP." In the Dial Str field, type the IP address of the MessageNetworking system." In the Message Transmission Schedule Start, End, andInterval fields, you normally use the defaults. It isrecommended that the first row be 00:01, 23:59, and 00:01,respectively. However, if there are many INTUITY AUDIXsystems in the Message Networking network, considerstaggering the start times on each system." In the Data Rate field, type 0. This time is irrelevant sincethe connection uses TCP/IP." In the Password field, type the password you recorded fromthe Password field on the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Channel field, type 00 to configure the INTUITYAUDIX system to use whatever channel is available." In the Machine Type field, press F2 to view the choices, andthen select Intuity 4.0 or later. Message Networking istreated as a networked INTUITY AUDIX 4.0 system by theINTUITY system." In the Send Multimedia Messages field, type y. Generally, itis best to allow INTUITY AUDIX to send all components ofmultimedia messages to Message Networking. Then, if thetarget system cannot accept all components, a recordedmessage informs the receiver about the component thatfailed.7. Press F8 to change keys, then press F2 to add the record.8. Press F8 to change keys again, and then press F6 (Cancel) untilyou return to the Main Menu.9. From the Main Menu, select Audix <strong>Administration</strong>.10. From the command prompt, type change machine and then press Enter. The Machine Profilescreen displays.11. On the Machine Profile screen, Page 1:" In the Extension Length field, enter the number of digits that
38you recorded from the Network Address Length field on theGeneral Parameters page in Message Networking." For the Default Community ID field, this field is generally leftat the default of 1." In the Prefix column for ADDRESS RANGES, enter prefixesif appropriate. Generally, you will leave these fields blank." In the first fields in the Start Ext. and End Ext. columns, typethe start and end points of the extension ranges on theMessage Networking network. Generally, to cover allnetwork address combinations, you can enter a series of 0'sin the Start Ext. column and as series of 9's in the End Ext.column. Enter the number of 0's or 9's equal to the numberof digits in the Message Networking extension length.12. Press F7 to proceed to the next page. On the Machine Profilescreen, Page 2:" In the Send to Non-Administered Recipients, type y to allowthe INTUITY AUDIX system to send messages toaddresses within the Message Networking range but not yetpart of the INTUITY system's remote database." In the UPDATES: In? field, type y to allow INTUITY AUDIXto accept updates from Message Networking." In the UPDATES: Out? field, type y to allow INTUITYAUDIX to send updates to Message Networking." In the Network Turnaround field, type n.13. Press F3 to update the record.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new INTUITY AUDIXremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the INTUITY AUDIX remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Test LAN connectivity by transmitting test packets.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Run a Demand Remote Update to add remote subscribers to theMessage Networking system.On the INTUITY AUDIX system:1. From the command prompt, type list measurements feature dayand press Enter.2. Record the number of local subscribers listed in the report.
39Note: If you excluded some ranges, subtract those from thesubscriber count.On the Message Networking system:View the Remote Machines List. Locate the INTUITY AUDIX system inthe list. Verify that the number of subscribers matches the number ofsubscribers in the Feature Daily Traffic Report from the INTUITY AUDIXsystem.If the update is still in progress, the total number of subscribers willincrease until all of the subscribers are received. If all subscribers are notreceived, you must determine the cause of the failure.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the INTUITY AUDIX subscribers were correctlypopulated on the Message Networking system based on the Dial PlanMapping you administered.On the INTUITY AUDIX system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe INTUITY AUDIX remote machine on the Message Networkingsystem, perform a get remote update on the INTUITY AUDIX system:1. From the command prompt, type get remote_update and press Enter.2. When the remote update is complete, from the command prompt,type list remote extensions andpress Enter.3. Verify that the appropriate remote users from Message Networkingare listed.Note: On a large network this list can be very long. You can skipthis step and just record the total in step 4 instead.4. From the command prompt, type list measurements feature dayand press Enter.5. Record the number of remote subscribes listed in the report.6. View the Administrator's Log screen to verify that no conflicts orproblems occurred with the remote update.Note: If problems occurred, you must determine the cause of thefailure.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machines to which youwant to add the INTUITY AUDIX subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new INTUITY AUDIX machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the INTUITY AUDIX test mailbox you obtainedfrom the INTUITY AUDIX system administrator. Then log into the test
40mailbox on the INTUITY AUDIX system and verify that the test messagewas delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: INTUITY-related machineAdd or modify a remote machine: INTUITY-related machineUse the Add New Machine: INTUITY 4.0 or later page to add a new INTUITY-related remote machine to theMessage Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select INTUITY 4.0 or later.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page. If this remote machine is an Interchange 5.4system, this field must be set to no.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 29 characters (for example 192.43.235.1). MessageNetworking uses the IP address to contact and send messages to remote machines. Make sure that you enterthe correct IP address as the system does not validate the number you enter. This field is optional for theSMTP-Unified Messenger, SMTP-MM, and other non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME machine types.Note: If you plan to use the Domain Name Server (DNS) feature, you do not have to enter a value for this field.Password: Enter the password exactly as it is administered on the remote system. Five to ten alphanumericcharacters are allowed.Message Transmission Schedule: It is recommended that you stagger start times and intervals for eachremote system so the Message Networking system is not trying to call all remote systems at the same time. Youcan enter up to three message transmission schedules:
41! Start: Type the starting time for a message transmission period to the remote system in hh:mm format,such as 00:01 for one minute after midnight.! End: Type the ending time for a message transmission period to the remote system in hh:mm format,such as 23:59 for one minute before midnight.! Interval: Type the interval at which the Message Networking system will call this remote system inhh:mm format, such as 00:05 for every 5 minutes. Message Networking checks the queue at this interval(such as every 5 minutes) and calls the remote system if something is in the queue for this remotesystem.Channel: Type the number of the channel to be used. Enter 0 to specify that the system selects the first idlechannel it finds for the specified data rate.Send Multimedia Messages (e.g., FAX): Specify whether the remote machine accepts multimedia messages,such as fax. Select yes if you want the remote machine to accept multimedia messages. Select no if you do notwant the remote machine to accept multimedia messages.Note: Only INTUITY AUDIX Release 3.0 or higher and INTUITY AUDIX LX accept multimedia messages.<strong>Avaya</strong> Interchange: Specify whether the new remote machine is an Interchange 5.4 system. Select 5.4 if thenew remote machine is an Interchange 5.4 system. Select no if the new remote machine is not an Interchangesystem. The default for this field is no.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:
42! directory-view: Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View.! dynamic: Select dynamic to specify that the remote machine should receive updates for subscribersthat exchange messages with this remote machine.! full: Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking systemto this remote machine. If you select full, verify that the remote machine has enough space forinformation on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is dynamic. To receive no updates, select directory-view, make sure no views aredefined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.Network Turnaround: Turnaround is the ability to return updated information using the same connection. Usethis field to specify whether the Message Networking network connection can turn around after sending networkdata to a remote machine. Select yes to enable network turnaround for this remote machine. Select no isdisable network turnaround for this remote machine. The default for this field is yes.Provide Local Mapped Addresses: Specify whether the local mailbox ID is provided, in terms of the networkaddress, if a full remote update is specified (see the Subscriber Updates Type field). Select yes to provide thelocal mailbox ID. Select no if you do not want to provide the local mailbox ID. The default for this field is no.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of page
43Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new DEFINITY ONE or IP600 remote machineChecklist for adding a new DEFINITY ONE or IP600 remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding new DEFINITY ONE or IP600 remote machines to theMessage Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 remote system. If you are unfamiliarwith the remote machine type you are adding, ask the system administrator to assist you.Note: TCP/IP administration must be completed on the remote system before you proceed.CompletedTaskOn the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theremote system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the password in the Password field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 subscribers via the PBX. Youcan obtain the area code and local exchange from the switchadministrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit remote systemextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-
4434. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.Obtain a test mailbox number on the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 systemfrom the system administrator. You will use this mailbox to send andreceive test messages through Message Networking.On the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 system:Gather information about the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 remote machinethat you are adding. You should obtain the following information:1. Start the Windows administration.2. Click Administer System and then log in to the system.3. Under System <strong>Administration</strong>, select Audix Networking.The Audix Networking page displays.4. Select Administrative Menu.The Administrative menu displays.5. From the Administrative Menu, select Local Machine<strong>Administration</strong>.The Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.6. On the Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page, make sure that thepassword is set for the local machine, and obtain the followinginformation:" The machine name from the Local Machine Name field." The IP address from the IP Address field." The system's network password from the Password field.7. Click Back.The Administrative Menu displays.8. Select Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong>.The Digital Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.9. On the Digital Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page, click Add NewMachine.10. On the Digital Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page, enter:" In the Machine Name field, type the name of the MessageNetworking system. The name must be unique to any othersystem that the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 systemcommunicates with and must be an exact case-sensitivematch of the Message Networking Local Machine Nameyou recorded on the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Connection field, type TCP/IP." In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the MessageNetworking system." In the Message Transmission Schedule Start, End, andInterval fields, you normally use the defaults. It is
45recommended that the first row be 00:01, 23:59, and 00:01,respectively. However, if there are many DEFINITY ONE orIP600 systems in the Message Networking network,consider staggering the start times on each system." In the Password field, type the password you recorded fromthe Password field on the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Machine Type field, type Intuity 4.0 or later.Message Networking is treated as a networked INTUITYAUDIX 4.0 system by the remote system." In the Send Multimedia Messages field, select Yes.Generally, it is best to allow the DEFINITY ONE or IP600system to send all components of multimedia messages toMessage Networking. Then, if the target system cannotaccept all components, a recorded message informs thereceiver about the component that failed.11. Click Add to add the Message Networking system to theDEFINITY ONE or IP600 system.12. When the message displays that the remote machine has beenadded, click Back.The Digital Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.On the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 system:1. Go to Audix <strong>Administration</strong>.2. At the command prompt, type change machine and press Enter.The Machine Profile screen displays.3. On the Machine Profile screen, Page 1:" In the Extension Length field, enter the number of digits thatyou recorded from the Network Address Length field on theGeneral Parameters page in Message Networking." For the Default Community ID field, this field is generally leftat the default of 1." In the Prefix column for ADDRESS RANGES, enter prefixesif appropriate. Generally, you will leave these fields blank." In the first fields in the Start Ext. and End Ext. columns, typethe start and end points of the extension ranges on theMessage Networking network. Generally, to cover allnetwork address combinations, you can enter a series of 0'sin the Start Ext. column and as series of 9's in the End Ext.column. Enter the number of 0's or 9's equal to the numberof digits in the Message Networking extension length.4. Press F7 to proceed to the next page. On the Machine Profilescreen, Page 2:" In the Send to Non-Administered Recipients, type y to allowthe remote system to send messages to addresses withinthe Message Networking range but not yet part of theDEFINITY ONE system's remote database." In the UPDATES: In? field, type y to allow DEFINITY ONEor IP600 to accept updates from Message Networking." In the UPDATES: Out? field, type y to allow DEFINITY ONEor IP600 to send updates to Message Networking.
46" In the Network Turnaround field, type n.5. Press F3 to update the record.On the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 system:1. From the Audix <strong>Administration</strong> command prompt, type displaymachine and press Enter. The Machine Profile screen for the localmachine displays.2. From the Machine Profile screen, obtain the following information:" The extension length from the Extension Length field." Extensions rangesNote: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, an so on.3. Press F7 to go to the next page.4. From the Machine Profile screen, Page 2, make sure that theAllow Automatic Full Updates field is set to y.5. For TCP/IP Networking, set Network Turnaround to n.6. Type y, if necessary, in the other fields on the screen.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new INTUITY AUDIXremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 remote machine has been addedto the Message Networking system by viewing the Remote MachinesList.On the Message Networking system:Test LAN connectivity by transmitting test packets.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Run a Demand Remote Update to add remote subscribers to theMessage Networking system.On the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 system:1. Go to Audix <strong>Administration</strong>.2. From the command prompt, type list measurements feature dayand press Enter.3. Record the number of local subscribes listed in the report.Note: If you excluded some ranges, subtract those from thesubscriber count.On the Message Networking system:View the Remote Machines List. Locate the DEFINITY ONE or IP600
47system in the list. Verify that the number of subscribers matches thenumber of subscribers in the Feature Daily Traffic Report from the remotesystem.If the update is still in progress, the total number of subscribers willincrease until all of the subscribers are received. If all subscribers are notreceived, you must determine the cause of the failure.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the remote system subscribers were correctlypopulated on the Message Networking system based on the Dial PlanMapping you administered.On the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe remote machine on the Message Networking system, perform a getremote update on the remote system:1. From the command prompt, type get remote_update and press Enter.2. When the remote update is complete, from the command prompt,type list remote extensions andpress Enter.3. Verify that the appropriate remote users from Message Networkingare listed.4. From the command prompt, type list measurements feature dayand press Enter.5. Record the number of remote subscribes listed in the report.6. View the <strong>Administration</strong> Log screen to verify that no conflicts orproblems occurred with the remote update.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machines to which youwant to add the DEFINITY ONE or IP600 subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new remote machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the test mailbox you obtained from the remotesystem administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on the remotesystem and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of page
48Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 remote machineChecklist for adding a new INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 remotemachineThe following table lists the procedures for adding new INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 remote machines tothe Message Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 remote system. If you areunfamiliar with the remote machine type, ask the remote system administrator to assist you.Note: TCP/IP administration must be completed on the remote system before you add the remote machine tothe Message Networking system.CompletedTaskOn the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 system:Gather information about the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 remotemachine that you are adding. You should obtain the following information:1. Log into the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 system.2. From the Main Menu, select Global <strong>Administration</strong>.The Global <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.3. From the Global <strong>Administration</strong> page, click Messaging<strong>Administration</strong>.4. Log in to the system.5. From the command prompt, type display machine and press Enter.The Machine Profile screen displays.6. From the Machine Profile screen, Page 1, obtain the followinginformation:" The local machine name from the Machine Name field" The extension length from the Extension Length field" Extension rangesNote: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, and so on.7. Press F7 to go to the next page.8. From the Machine Profile screen, Page 2, obtain the following:" The IP address from the IP Address field." The system's network password from the Password field.9. Make sure that the Allow Automatic Full Updates field is set to y.10. Make sure that Updates In and Updates Out are set to y.Obtain a test mailbox number on the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770system from the system administrator. You will use this mailbox to sendand receive test messages through Message Networking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.
49Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the INTUITY AUDIX subscribers via the PBX. You canobtain the area code and local exchange from the switch administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit INTUITY AUDIXextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theINTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the password in the Password field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.On the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 system:Administer the Message Networking system as a remote machine on theINTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 system.1. Log into the INTUITY AUDIX LX or <strong>Avaya</strong> IA770 system.2. From the Main Menu, select Global <strong>Administration</strong>.The Global <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.3. From the Global <strong>Administration</strong> page, click Messaging<strong>Administration</strong>.4. Log in to the system.5. From the command prompt, type add machine and press Enter.
506. On the Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen:" In the Machine Name field, type the name of the MessageNetworking system. The name must be unique to any othersystem that the INTUITY AUDIX LX or IA770 systemcommunicates with and must be an exact case-sensitivematch of the Message Networking Local Machine Nameyou recorded on the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Extension Length field, enter the number of digits thatyou recorded from the Network Address Length field on theGeneral Parameters page in Message Networking." For the Default Community ID field, this field is generally leftat the default of 1." In the Prefix column for ADDRESS RANGES, enter prefixesif appropriate. Generally, you will leave these fields blank." In the first fields in the Start Ext. and End Ext. columns, typethe start and end points of the extension ranges on theMessage Networking network. Generally, to cover allnetwork address combinations, you can enter a series of 0'sin the Start Ext. column and as series of 9's in the End Ext.column. Enter the number of 0's or 9's equal to the numberof digits in the Message Networking extension length.7. Press F7 to proceed to the next page. On the Machine Profilescreen, Page 2:" In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the MessageNetworking system." In the Password field, type the password you recorded fromthe Password field on the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Send to Non-Administered Recipients, type y to allowthe INTUITY LX or IA770 system to send messages toaddresses for which no subscriber name is known." In the UPDATES: In? field, type y to allow INTUITY LX orIA770 to accept updates from Message Networking." In the UPDATES: Out? field, type y to allow INTUITY LX orIA770 to send updates to Message Networking." In the Network Turnaround field, type n.8. From the command prompt, type change machine and then press Enter. The Machine Profilescreen displays.9. Press F3 to update the record.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new INTUITY AUDIXremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:
51Verify that the INTUITY LX or IA770 remote machine has been added tothe Message Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Test LAN connectivity by transmitting test packets.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Run a Demand Remote Update to add remote subscribers to theMessage Networking system.On the INTUITY LX or IA770 system:1. From the command prompt, type list measurements feature dayand press Enter.2. Record the number of local subscribes listed in the report.Note: If you excluded some ranges, subtract those from thesubscriber count.On the Message Networking system:View the Remote Machines List. Locate the INTUITY LX or IA770 systemin the list. Verify that the number of subscribers matches the number ofsubscribers in the Feature Daily Traffic Report from the INTUITY LX orIA770 system.If the update is still in progress, the total number of subscribers willincrease until all of the subscribers are received. If all subscribers are notreceived, you must determine the cause of the failure.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the INTUITY LX or IA770 subscribers were correctlypopulated on the Message Networking system based on the Dial PlanMapping you administered.On the INTUITY LX or IA770 system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe INTUITY LX or IA770 remote machine on the Message Networkingsystem, perform a get remote update on the INTUITY LX or IA770system:1. From the command prompt, type get remote_update and press Enter.2. When the remote update is complete, from the command prompt,type list remote extensions andpress Enter.3. Verify that the appropriate remote users from Message Networkingare listed.4. From the command prompt, type list measurements feature dayand press Enter.5. Record the number of remote subscribes listed in the report.
526. View the <strong>Administration</strong> Log screen to verify that no conflicts orproblems occurred with the remote update.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machines to which youwant to add the INTUITY LX or IA770 subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new INTUITY LX or IA770 machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the INTUITY LX or IA770 test mailbox youobtained from the INTUITY LX or IA770 system administrator. Then loginto the test mailbox on the INTUITY LX or IA770 system and verify thatthe test message was delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new Interchange Release 5.4 remote machineChecklist for adding a new Interchange Release 5.4 remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding new Interchange Release 5.4 remote machines to theMessage Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Interchange system. If you are unfamiliar with the Interchange,ask the Interchange system administrator to assist you.Note: TCP/IP administration must be completed on the Interchange system before you add the remote machineto the Message Networking system.CompletedTaskOn the Interchange system:Gather information about the Interchange remote machine that you areadding. You should obtain the following information:1. Log into the Interchange system.2. From the Interchange Main Menu, select Networking<strong>Administration</strong>. The Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu displays.3. From the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Local Machine<strong>Administration</strong>. The Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screendisplays.4. From the Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen, obtain thefollowing information:" The machine name from the Local Machine Name field.
53Notes:" The system's password from the Password field." The Dial Str field might be populated but you do not need torecord this field." The Data Rate and Channel fields on the Local Machine<strong>Administration</strong> screen should contain 0 and 00 respectively.5. Press F6 to return to the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu.6. From the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select TCP/IP<strong>Administration</strong>. The TCP/IP <strong>Administration</strong> screen displays.7. Record the IP address from the IP Address field.8. Press F6 until you return to the Interchange Main Menu.9. From the Interchange Main Menu, select System Parameters.The General Parameters menu displays.10. From the System Parameters menu, select General Parameters.The General Parameters screen displays.11. On the General Parameters screen, obtain the followinginformation:" The Network Address Length" Verify that Updates In and Updates Out are set to y.Obtain a test mailbox number on a remote system connected toInterchange. You will use this mailbox to send a message from anendpoint on the Interchange system to an endpoint on the MessageNetworking system.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theInterchange system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the password in the Password field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.All Interchange and Message Networking systems in the networkmust have the same Network Address Length.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.On the Interchange system:Administer the Message Networking system as a remote machine on theInterchange system.1. From the Main Menu, select Networking <strong>Administration</strong>.2. From the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Local Machine<strong>Administration</strong>. The Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen displays.3. On the Local Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen, verify that the LocalMachine Name and Password fields have been administered. (Theother fields on this screen are only relevant if you are performinginternal loop-around testing.)
544. Press F6 to return to the Networking <strong>Administration</strong> menu, andthen select Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong>.5. From the Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select AudixDigital Network Machine <strong>Administration</strong>.6. On the Audix Digital Network Machine <strong>Administration</strong> screen:" In the Machine Name field, type the name of the MessageNetworking system. The name must be unique to any othersystem that the Interchange communicates with and mustbe an exact case-sensitive match of the MessageNetworking Local Machine Name you recorded on theGeneral Parameters page on the Message Networkingsystem." In the Connection field, type TCP/IP." In the Dial Str field, type the IP address of the MessageNetworking system." In the Message Transmission Schedule Start, End, andInterval fields, you normally use the defaults. It isrecommended that the first row be 00:01, 23:59, and 00:01,respectively. However, if there are many Interchangesystems in the Message Networking network, considerstaggering the start times on each system." In the Data Rate field, type 0. This time is irrelevant sincethe connection uses TCP/IP." In the Password field, type the password you recorded fromthe Password field on the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Channel field, type 00 to configure the Interchangesystem to use whatever channel is available." In the Machine Type field, press F2 to view the choices, andthen select Intuity 4.0 or later. Message Networking istreated as a networked INTUITY 4.0 system by theInterchange system." In the Send Multimedia Messages field, type y. Generally, itis best to allow Interchange to send all components ofmultimedia messages to Message Networking. Then, if thetarget system cannot accept all components, a recordedmessage informs the receiver about the component thatfailed.7. Press F8 to change keys, then press F2 to add the record.8. Press F8 to change keys again, and then press F6 until you returnto the Main Menu.9. From the Main Menu, select Interchange <strong>Administration</strong>.10. From the <strong>Avaya</strong> Interchange <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select RemoteMachine <strong>Administration</strong>. The Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong>menu displays.11. From the Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select RemoteMachine Parameters. The Remote Machine Parameters screendisplays.12. On the Remote Machine Parameters screen, Page 1:" In the Remote Machine field, press F2 to view the choicesand then select the Message Networking system you
55added." In the <strong>Avaya</strong> Interchange field, press F2 to view the choicesand then select 5.4." In the Mailbox ID Length field, type the network address ofthe Message Networking system and press Enter." Set the Failed Msg. Notification, Priority, Msg ID, and SendMessage for Warning fields as appropriate." In the Address Range Start field, enter a series of 0's equalto the number of digits in a network address on theMessage Networking system. In the Address Range endfield, enter a series of 9's equal to the number of digits in anetwork address on the Message Networking system.13. Press F5 to view the details screen:" Set the Subscriber Update field to full." Set the Updates In and Updates Out fields to y." Set the Voiced Names for Dynamic to n because this is notrequired for full updates." Leave the Dynamic Sub Expiration Days at the systemdefault because you are using full updates.14. Press F3 to update the record.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new Interchangeremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the Interchange system. Enter anextension range starting with a series of 0's equal to the number of digitsin an Interchange network address and ending with a series of 9's equalto the number of digits in an Interchange network address.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Interchange remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Test LAN connectivity by transmitting test packets.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Interchange system:1. From the Interchange <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select RemoteMachine <strong>Administration</strong>. The Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong>menu displays.2. From the Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select RemoteMachine Lists. The Remote Machine Lists menu displays.3. From the Remote Machine Lists menu, select Remote MachinesList. The list of remote machines displays.4. At the end of the list, record the total number of subscribers.Note: Any other Message Networking or Interchange systems
56must be excluded from the total count. Only remote machinesconnected directly to this Interchange system are sent to otherMessage Networking or Interchange systems.On the Message Networking system:View the Remote Machines List. Locate the Interchange system in thelist. Verify that the number of subscribers matches the number ofsubscribers in the Remote Machines List from the Interchange system.If the update is still in progress, the total number of subscribers willincrease until all of the subscribers are received. This screen is notdynamic so you must Cancel and then return to the screen to see thechanges.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the Interchange subscribers were correctly populatedon the Message Networking system based on the Dial Plan Mapping youadministered.On the Interchange system:Perform a get remote update on the Interchange system:1. From the Interchange <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select RemoteMachine <strong>Administration</strong>. The Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong>menu displays.2. From the Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select DemandRemote Updates. The Demand Remote Updates screen displays.3. From the Demand Remote Updates screen, press F2 to view thechoices and then select the Message Networking machine fromthe list.4. Press F3 to continue. A message displays prompting you to pressContinue again to start the remote update.5. Press F3 to start the update. In the upper-right corner of thewindow, a message "Working" displays, followed by the message"Update queued."6. Once the update is queued, press F6 to cancel out of the screen.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the Interchange subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new Interchange machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the test mailbox number that you obtained on aremote system connected to Interchange. Then log into the test mailboxon the remote system and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of page
57Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an AMIS Analog remotemachineAdding an AMIS Analog remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an AMIS Analog remote machine.Note: The checklist for adding a new AMIS Analog remote machine provides a list of steps you must completewhen adding a new AMIS Analog remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add an AMIS Analog remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field is displayed on the page.3. Select AMIS Analog from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine? and Dial String fields are displayed on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field is not displayed if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. In the Dial String field, type the gateway telephone number of the AMIS Analog remote machine.Message Networking uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. Forinformation on valid dial strings, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.6. Click Next Step.The remaining networking fields display on the page.7. Complete the networking fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.8. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.9. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.10. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of page
58Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new AMIS Analog remote machineChecklist for adding a new AMIS Analog remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new AMIS Analog remote machine to the MessageNetworking system. The procedures are listed in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the AMIS system. If you are unfamiliar with the AMIS, ask the AMISsystem administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskOn the Message Networking system:Check the Customer Options page to verify that the AMIS Nodes field isset to ON.On the AMIS system:Gather information about the AMIS remote machine that you are adding.You should obtain the following information:! The AMIS incoming dial string, which is the telephone number thatMessage Networking will dial to call the system.! The range of mailbox extensions (mailbox IDs).! The prefix or prefixes that the Message Networking system willattach to mailbox IDs so that they fit the Message Networkingnetwork dial plan.! A specific mailbox ID on the AMIS system that will receive andsend a test message through Message Networking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the AMIS subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain the areacode and local exchange from the switch administrator. You also need toobtain the extension range for the AMIS system. You can obtain thisrange from the AMIS system administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit AMIS extension.This example assumes the network address requires 10-digit dialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial plan
59mapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theAMIS system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.On the AMIS Analog Parameters page:! Record the Country Code, Area/Trunk, and Telephone Numberfields.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new AMIS remotemachine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the AMIS timing parameters, if necessary, for the new remotemachine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Administer subscribers. For AMIS remote machines, the followingmethods of adding subscribers from the remote machine to the MessageNetworking system are supported (listed in order of preference):! Initiate Bulk Add by File from the Message Networking system.! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voiced names.! Send a message from the new subscriber.! Register through Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> page on the MessageNetworking system.! Perform a Bulk Add by Range.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the AMIS remote machine has been added to the MessageNetworking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the AMIS system:
60Administer Message Networking as a remote machine on the AMISremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Perform an analog remote machine connectivity test.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the AMIS system test mailbox you obtained fromthe AMIS system administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on theAMIS system and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: AMIS AnalogAdd or modify a remote machine: AMIS AnalogUse the Add New Machine: AMIS Analog page to add a new AMIS Analog remote machine to the MessageNetworking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select AMIS Analog.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).Dial String: Type the main telephone number of the AMIS system, up to 30 characters. The MessageNetworking system uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. The dial stringtypically consists of the dial-access code needed to reach the network, followed by a pause interval, followed bythe telephone number of the remote machine.
61Note: You can make the Message Networking system pause for a specific length of time by entering"P" (including quotes) in the dial string. A single "P" causes the system to pause approximately 1.5 seconds; a"P" followed by a digit from 1 to 9 causes the system to wait the specified number of seconds.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Allow Private Messages?: Indicates whether to allow private messages to be sent to the AMIS subscriber. y orn Default - nCaution: If set to y, subscribers can forward a private message they have received.Include Voice Name of Sender?: Indicates whether to include the sender's voice name with the message. y orn Default - nInclude Message Marking (Private/Priority)?: Indicates whether to include a private or priority marking with amessage. y or n Default - nDefault Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Maximum Simultaneous Connections: Maximum number of ports that will simultaneously handle outgoingtraffic for this machine. Enter an integer of 1 through 9 The default for this field is 1.Timing Type: Select the appropriate AMIS timing type for the remote machine you are defining from the dropdownlist. You can use the AMIS Timing Parameters page to add, modify, and delete AMIS timing parameters.Message Networking Callback Number: Identifies the Message Networking system to this remote machineand is used for protocol exchanges with AMIS Analog remote machines. The defaults for these fields are
62provided by the AMIS Analog Parameters page, but you can modify the fields to use different numbers.! Country Code: Identifies the unique country code that helps identify the Message Networking system tothis remote machine. Enter 1 to 4 digits. This field is optional.! Area/Trunk: Identifies the unique area code or trunk that helps identify the Message Networking systemto this remote machine. Enter 1 to 6 digits. This field is optional.! Telephone Number: Identifies the unique telephone number that helps identify the Message Networkingsystem to this remote machine. Enter 1 to 10 digits.Remote Machine ID: Identifies this remote machine:! Country Code: Identifies the unique country code that helps identify the remote machine. Enter 1 to 4digits. This field is optional.! Area/Trunk: Identifies the unique area code or trunk that helps identify the remote machine. Enter 1 to 6digits. This field is optional.! Telephone Number: Identifies the unique telephone number that helps identify the remote machine.Enter 1 to 10 digits.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer dial plan mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer dial plan mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an Aria Analog remotemachineAdding an Aria Analog remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an Aria Analog remote machine to the Message Networking system.Note: The checklist for adding a new Aria Analog remote machine provides a list of steps you must completewhen adding a new Aria Analog remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add an Aria Analog remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field is displayed on the page.3. Select Aria Analog from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine?, Send FAX Messages, and Dial String fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.
635. For the Send FAX Messages field, select Yes to allow fax messages or No to restrict fax messages.6. In the Dial String field, type the gateway telephone number of the Aria Analog remote machine. MessageNetworking uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. For information onvalid dial strings, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.8. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.9. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.10. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.11. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new Aria Analog remote machineChecklist for adding a new Aria Analog remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new Aria Analog remote machine to the MessageNetworking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Aria Analog system. If you are unfamiliar with the Aria Analog,ask the Aria Analog system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskOn the Aria Analog system:Check the Customer Options page to verify that the Octel Analog Nodesfield is set to ON.On the Aria Analog system:Gather information about the Aria Analog system that you are adding.You should obtain the following information from the Aria Analog systemadministrator:On the Installation Information screen:! From the VPMOD Phone Number field, record the system phonenumber.From the Software Features Installed screen, Page 1:! Record the Network Serial #.! Check the Software Rel. field. If it does not display Aria 2.03 or
64higher, the system must be upgraded to work with MessageNetworking.Note: Aria 3.0 is not supported for use with Message Networking.The system must be upgraded to Release 3.01.! Check that the following fields are marked with a Y:" 44 - Networking" 56 - Fax Processing" 66 - Fax Delivery MailboxFrom the Software Feature Installed screen, Page 2:! Check that the 73 - Connectivity field is marked with a Y.From the Aria Analog system administrator, obtain:! A specific mailbox ID on the Aria Analog system that will receiveand send a test message through Message Networking.From the Port Assignments screen:! Check the N (Network) column for ports that have Y. You musthave at least one port enabled for networking to connect toMessage Networking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the Aria subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain the areacode and local exchange from the switch administrator. You also need toobtain the extension range for the Aria system. You can obtain this rangefrom the Aria system administrator or from the Octel Mailbox Managersoftware, if you have purchased this software.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit Aria extension. Thisexample assumes the network address requires 10-digit dialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:
65Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theAria Analog system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Octel Analog Serial Number.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.On the AMIS Analog Parameters page:! Record the Telephone Number field.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new Aria Analogremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Administer subscribers. For Aria Analog remote machines, the followingmethods of adding subscribers from the remote machine to the MessageNetworking system are supported (listed in order of preference):! Set up the Self Registration Agent ID on the General Parameterspage, and instruct remote subscribers on the new system to senda message.! Use FTP to upload a subscriber list to the Message Networkingsystem.! Initiate Bulk Add by File from the Message Networking system.! Perform a Bulk Add by Range.On the Aria Analog system:Administer the Message Networking system as a Aria network node onthe Aria system:On the Valid Node Numbers and Message Queues Selected screen:! In the Select Node field, enter 0.! In the Select Message Queue field, enter 0.On the Valid Node Numbers and Message Queues List screen:! Check the list of numbers in the Node # column, and note thenumbers available in the sequence.On the Node Profile screen:! In the Node Number field, enter the node number for MessageNetworking.! In the Node Name field, type the name of the Message Networkingsystem.! In the Number of Digits in a Mailbox field, enter the number ofdigits that appears in the Network Address Length field on theGeneral Parameters page in Message Networking.! In the Serial Number field, type the serial number that appears inthe Octel Analog Networking Serial Number field on the General
66Parameters page in Message Networking.! In the NameNet Type field, type 0 for COS-based type. This entryrequires that subscribers on the Aria system have a specific classof service that allows their name to appear in the MessageNetworking subscriber database.! In the NameSend field, type 0 for None because NameNet is notavailable for Octel Analog Networking connections.! In the Phone Number field, type the analog phone number of theMessage Networking system. This number is combined with theentry in the Dialing Sequence field to form the complete dialsequence that Aria performs. The Message Networking phonenumber can be found in the Telephone Number field on the AMISAnalog Parameters page in Message Networking.! (Optional) In the Dialing Sequence field, type the dialing sequence,which is to be included with the Phone Number field.! In the Access Type field, type 0 for Direct Dial.! In the Maximum Simultaneous Analog Transmissions field, type 1,which is normally the number of simultaneous connection youneed. However, if you anticipate heaving remote messaging traffic,you can enter 2 or 3. Note that this number cannot exceed thenumber of ports administered for networking.! In the Threshold field, type the number of outgoing messages(msgs) in queue after which the system uses an additionaltransmission connection for networked messages to MessageNetworking. Also type the cumulative number of minutes (mins) ofmessages after which an additional transmission connection isused. The Threshold applies only if the Maximum SimultaneousAnalog Transmissions is greater than 1.! In the Name Transmission Allowed field, type N to avoid havingrecipients of messages from Aria Analog subscribers hear thesender's name twice.! In the Play Node Name field, type N to avoid having recipients ofmessages from Aria Analog subscribers hear the sender's nametwice.! In the ASCII Name Check field, type 1 to allow Aria to verify ASCIIremote subscriber names when receiving messages fromMessage Networking.! In the Node Response Allowed field, type N. This capability is notallowed for Octel Analog Networking.On the Node Profile (Weekday Schedule) screen:! In the Begin and End fields for Window 1, type the range of timefor Aria to send messages to Message Networking. For example, ifyou enter 12:00a in the Begin field and 11:59p in the End field,delivery can occur 24 hours a day.! In the Interval field for Window 1, type 0 for Immediate. This valuemeans that Aria will pass messages to Message Networking assoon as they are recorded and queued.! In the Priority field for Window 1, type A for AdministrativeMessages. Administrative messages are system-level messageslike subscriber updates.! In the Begin and End fields for Window 2, type the range of time
67for Aria to send messages to Message Networking.! In the Interval field for Window 2, type 0 for Immediate.! In the Priority field for Window 2, type 0 for Non-Urgent/StandardSubscriber Messages. These messages are regular subscribermessages with normal priority.On the Node Profile (Weekend Schedule) screen:! In the Begin and End fields for Window 1, type the range of timefor Aria to send messages to Message Networking.! In the Interval field for Window 1, type 0 for Immediate.! In the Priority field for Window 1, type A for AdministrativeMessages.! In the Begin and End fields for Window 2, type the range of timefor Aria to send messages to Message Networking.! In the Interval field for Window 2, type 0 for Immediate.! In the Priority field for Window 2, type 0 for Non-Urgent/StandardSubscriber Messages.On the Node Profile screen (Blank Prefix Page):! In the Enter prefix to be added field (for the first field of thePREFIX column), type the first prefix for Message Networkingmessages.! In the Number of additional digits field (for the first field of the Dcolumn), type the number of additional digits that must be added tothe prefix to create a complete Message Networking networkaddress. For example, if you enter 9, this indicates that 9 or moredigits must be added to the prefix.! Add additional prefix and additional digits combinations asrequired for the Message Networking address ranges.As an example, suppose the Message Networking system has a 7-digit dial plan and it has three remote machines in its network (inaddition to the Aria Analog system that you are adding). Onesystem has mailbox IDs that begin with 538. Therefore,subscribers are addressed as 538XXXX. In the second system,subscribers are addressed as 607XXXX. And in the third system,subscribers are addressed as 444XXXX. In this example, youwould enter three prefixes in the PREFIX column, each with theNumber of additional digits set to 4.Note: The combination of prefix and number of digits you enter forMessage Networking must be unique to any other systems towhich the Aria system is networked. Otherwise, if two remotesystems have the same local mailbox IDs and you enter the sameprefixes, then when the local subscribers address messages, theremight be two or more possible destinations for their messages.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Aria Analog remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Perform an analog remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:
68View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the Aria Analog subscribers were correctly populatedon the Message Networking system based on the Dial Plan Mapping youadministered.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe Aria Analog remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push to the Ariasystem to add subscribers from other remote machines to the AriaAnalog system.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theAria Analog system must have the capacity to accommodate all of thesubscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the Aria Analog subscribers.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the Aria test mailbox you obtained from the Ariasystem administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on the Aria systemand verify that the test message was delivered.Update existing remote machines in the Message Networking network forsubscribers on the new Aria Analog system. The Adding and updatingsubscribers overview provides information on how subscribers areupdated for the different types of remote machines.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: Aria AnalogAdd or modify a remote machine: Aria AnalogUse the Add New Machine: Aria Analog page to add a new Aria Analog remote machine to the MessageNetworking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.
69! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select Aria Analog.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).Send FAX Messages?: Specify whether fax messages are allowed for the remote machine. Select Yes to allowfax messages or No to restrict fax messages.Dial String: Type the gateway telephone number of the remote machine, up to 30 characters. The MessageNetworking system uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. The dial stringtypically consists of the dial-access code needed to reach the network, followed by a pause interval, followed bythe telephone number of the remote machine.You can enter the following characters in the dial string field: 0 - 9, P, #, *, and ". To make the MessageNetworking system pause for a specific length of time, type "P" (including the quotes) in the dial string. Includea single "P" to cause the system to pause approximately 1.5 seconds. Include a "P" followed by a digit from 1 to9 to cause the system to wait the specified number of seconds.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.
70Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Default Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:! directory-view: Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View.! dynamic: Select dynamic to specify that the remote machine should receive updates for subscribersthat exchange messages with this remote machine.! full: Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking systemto this remote machine. If you select full, verify that the remote machine has enough space forinformation on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is dynamic. To receive no updates, select directory-view, make sure no views aredefined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.Voiced Names for Dynamic: This field specifies whether to include the subscriber's voiced name in updateswhen the Subscriber Updates Type is set to Dynamic. This field is always set to yes for Aria Analog remotemachines and cannot be modified.ASCII Name Confirmation?: Specify whether the ASCII name is verified when a subscriber sends a messageusing NameNet. If the name does not match, the Message Networking system requests an update. Select yesto verify the ASCII name. Select no if you do not want to verify the ASCII name. The default for this field is yes.Admin Mode?: Specify that when Message Networking delivers a message to a remote machine using theOctel Analog Networking gateway, Message Networking automatically requests a subscriber update for thereceiving subscriber. Select yes to automatically request a subscriber update. Select no if you do not want toautomatically request a subscriber update. The default for this field is no.Octel Analog Serial Number: Type the serial number of the analog remote machine, either 4 or 5 digits.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Record Delay (Sec): The Record Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel Analog Networking protocolthat specifies the number of seconds before recording begins. The default for this field is 3. If clipping occurs atthe beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, increase this value toeliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networkingremote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate the silence.Maximum Simultaneous Connections: Maximum number of ports that will simultaneously handle outgoingtraffic for this machine. Enter an integer of 1 through 9 The default for this field is 1.Voiced Name Delay (Sec): The Voiced Name Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel AnalogNetworking protocol that specifies the number of seconds before a remote subscriber's name is voiced. Thedefault for this field is 3. If clipping occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel AnalogNetworking remote subscriber, increase this value to eliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of a
71message received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate thesilence.System Mailbox ID: This field specifies the system mailbox number used by the protocol for the remotemachine, up to 10 digits. The default for this field is 0. This mailbox address must match the system mailbox setup on the remote machine.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding a Serenade Analog remotemachineAdding a Serenade Analog remote machineThis topic provides information on adding a Serenade Analog remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem.Note: The checklist for adding a new Serenade Analog remote machine provides a list of steps you mustcomplete when adding a new Serenade Analog remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add a Serenade Analog remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select Serenade Analog from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine?, Send FAX Message, and Dial String fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. For the Send FAX Message field, select Yes to allow fax messages or No to restrict fax messages.6. In the Dial String field, type the gateway telephone number of the Serenade Analog remote machine.Message Networking uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. Forinformation on valid dial strings, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page toview more information.7. Click Next Step.The remaining networking fields display on the page.8. Complete the networking fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.9. Click Next Step.
72The administration fields display on the page.10. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.11. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new Serenade Analog remote machineChecklist for adding a new Serenade Analog remote machineThe following table lists the procedures required for adding a new Serenade Analog remote machine to theMessage Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Serenade Analog system. If you are unfamiliar with the SerenadeAnalog, ask the Serenade Analog system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskOn the Message Networking system:Check the Customer Options page to verify that the Octel Analog Nodesfield is set to ON.On the Serenade Analog system:Gather information about the Serenade Analog system that you areadding. You should obtain the following information from the SerenadeAnalog system administrator:On the system feature screen:! Obtain the system name, software release, and serial number.From the Serenade Analog system administrator, obtain:! The system mailbox number (parameter index 248).! A specific mailbox ID on the Serenade Analog system that willreceive and send a test message through Message Networking.On the Serenade Analog system:Check the Serenade Dial Plan:! In the First Digit Table, note the numbers in the First Digit columnthat are followed by an entry in the Mailbox Length column. Theseare the potential mailbox ranges.! List mailbox users according to a common class of serviceattribute, such as 17 (send network messages immediately) or 18,
73(send network messages only at night). When the system displaysthe list of subscribers, note the ranges the subscribers are listed inand match these ranges against the ranges from the First DigitTable. You will use these ranges when you administer the DialPlan Mapping for the Serenade Analog machine.Note: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, an so on.On the Serenade Analog system:From the Serenade system administration, obtain a specific mailbox IDon the Serenade Analog system that will receive and send a testmessage through Message Networking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the Serenade subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain thearea code and local exchange from the switch administrator. You alsoneed to obtain the extension range for the Serenade system. You canobtain this range from the Serenade system administrator or from theOctel Mailbox Manager software, if you have purchased this software.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit Serenadeextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theSerenade Analog system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Octel Analog Serial Number.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.
74On the AMIS Analog Parameters page:! Record the Telephone Number field.On the Serenade Analog system:Administer the Message Networking system as a Serenade network nodeon the Serenade system:Look for or add the route or routes the Serenade system uses forMessage Networking:! To determine if a suitable route already exists, check the RouteTable for any entries that Serenade can use to route calls toMessage Networking. Use of routes depends on whether thephone number uses an internal phone network or a public networkand on whether calls to Message Networking are local, longdistance, or international calls.! If no routes are appropriate, add a new route. To add a new route,type a new route name, n for no dropped line capability, and thedialed digits of the route.Add the Message Networking system as a new location on the Serenadesystem:! Type a name of 6 digits or less for the Message Networkingsystem on the Serenade.! Enter 5 (Octel Analog Networking) for the protocol to use with thesystem.! For the serial number, use the serial number that appears in theOctel Analog Networking Serial Number field on the GeneralParameters page in Message Networking.! When asked whether the sender's name should be embedded inmessages sent to Message Networking, select N to avoid havingrecipients of messages from Serenade Analog subscribers hearthe sender's name twice.! For the route names, type the name of route that you identified orentered previously.! For the network schedule to be used for the Message Networkingsystem, type none to have Serenade send messages to remoteMessage Networking subscribers immediately after they thesender sends them.! For a Public Network Number, type the phone number of theMessage Networking system.If you entered a trunk access code or long distance code in theroute, do not enter it again in this field. Also, if the Serenadesystem is to call Message Networking over a tie trunk or privatenetwork, leave this field blank.When Message Networking dials the Serenade system, the phonenumber you enter must work in sync with the route you specified.The number must also take into account whether the calls are tooccur over a private or public network. This accounting, in turn,determines whether an outside access number (normally 9), anetwork access number (normally 8), or a private networkextension (normally 4 or 5 digits) are to be used, and whether along-distance number has to be included.! For the TIE Network Number, leave the field blank if you entered a
75public phone number. Otherwise, type the private network numberfor Message Networking.! When asked whether Message Networking is accessible over thedigital network, type n.Add a numbering plan for the Message Networking system:! In the Network Location Name column, enter the name of theMessage Networking system as entered in the Location Table.! In the Initial Digits Expected column, enter the prefix for MessageNetworking messages. This prefix, along with the Mailbox Length,is a code to tell the Serenade system to send the message toMessage Networking. Therefore, the combination of prefix andMailbox Length must be unique within the numbering plan. Theprefix may or may not contain digits from actual MessageNetworking addresses.! In the Network Mailbox Length column, enter the number of digitsin the Message Networking dial plan, normally 7 or 10 digits, plusthe number of other digits identifying Message Networking.! In the Number of Digits to Strip column, enter the number of initialdigits Serenade removes from the Message Networking addressdialed by the sender. Normally, with Message Networking, youstrip off the number of digits identified in the Initial Digits Expectedfield.! In the Number of Digits to Strip from Self column, always set to 0when using Protocol 5.Note: It is possible to establish a numbering plan that does not strip offdigits. In this way, the addresses that Serenade subscribers enter whensending message to Message Networking subscribers can be theMessage Networking addresses with no additional digits. For this plan tobe possible, there can be no point-to-point systems networked toSerenade that use the same combination of initial digits and networkmailbox length.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new Serenade Analogremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Serenade Analog remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Administer subscribers. For Serenade Analog remote machines, thefollowing methods of adding subscribers from the remote machine to theMessage Networking system are supported (listed in order ofpreference):! Set up the Self Registration Agent ID on the General Parameters
76page and instruct remote subscribers on the new system to send amessage.! Use FTP to upload a subscriber list to the Message Networkingsystem.! Initiate Bulk Add by File from the Message Networking system.! Perform a Bulk Add by Range.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the Serenade Analog subscribers were correctlypopulated on the Message Networking system based on the Dial PlanMapping you administered.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe Serenade Analog remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push tothe Serenade system to add subscribers from other remote machines tothe Serenade Analog system.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theSerenade Analog system must have the capacity to accommodate all ofthe subscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the Serenade Analog subscribers.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the Serenade test mailbox you obtained from theSerenade system administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on theSerenade system and verify that the test message was delivered.Update existing remote machines in the Message Networking network forsubscribers on the new Serenade Analog system. The Adding andupdating subscribers overview provides information on how subscribersare updated for the different types of remote machines.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Top of page
77Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: Serenade AnalogAdd or modify a remote machine: Serenade AnalogUse the Add New Machine: Serenade Analog page to add a new Serenade Analog remote machine to theMessage Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select Serenade Analog.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).Send FAX Messages?: Specify whether fax messages are allowed for the remote machine. Select Yes to allowfax messages or No to restrict fax messages.Dial String: Type the gateway telephone number of the remote machine, up to 30 characters. The MessageNetworking system uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. The dial stringtypically consists of the dial-access code needed to reach the network, followed by a pause interval, followed bythe telephone number of the remote machine.You can enter the following characters in the dial string field: 0 - 9, P, #, *, and ". To make the MessageNetworking system pause for a specific length of time, type "P" (including the quotes) in the dial string. Includea single "P" to cause the system to pause approximately 1.5 seconds. Include a "P" followed by a digit from 1 to9 to cause the system to wait the specified number of seconds.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.
78Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Default Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:! directory-view: Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View.! dynamic: Select dynamic to specify that the remote machine should receive updates for subscribersthat exchange messages with this remote machine.! full: Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking systemto this remote machine. If you select full, verify that the remote machine has enough space forinformation on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is dynamic. To receive no updates, select directory-view, make sure no views aredefined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.ASCII Name Confirmation?: Specify whether the ASCII name is verified when a subscriber sends a messageusing NameNet. If the name does not match, the Message Networking system requests an update. Select yesto verify the ASCII name. Select no if you do not want to verify the ASCII name. The default for this field is yes.Admin Mode?: Specify that when Message Networking delivers a message to a remote machine using theOctel Analog Networking gateway, Message Networking automatically requests a subscriber update for the
79receiving subscriber. Select yes to automatically request a subscriber update. Select no if you do not want toautomatically request a subscriber update. The default for this field is no.Octel Analog Serial Number: Type the serial number of the analog remote machine, either 4 or 5 digits.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Record Delay (Sec): The Record Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel Analog Networking protocolthat specifies the number of seconds before recording begins. The default for this field is 3. If clipping occurs atthe beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, increase this value toeliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networkingremote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate the silence.Maximum Simultaneous Connections: Maximum number of ports that will simultaneously handle outgoingtraffic for this machine. Enter an integer of 1 through 9 The default for this field is 1.Voiced Name Delay (Sec): The Voiced Name Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel AnalogNetworking protocol that specifies the number of seconds before a remote subscriber's name is voiced. Thedefault for this field is 3. If clipping occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel AnalogNetworking remote subscriber, increase this value to eliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of amessage received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate thesilence.System Mailbox ID: The System Mailbox ID is the system mailbox number used by the protocol for the remotemachine, up to 10 digits. The default for this field is 0. This mailbox address must match the system mailbox setup on the remote machine. For information on the system mailbox, see your remote machine administrationdocumentation.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an Octel 100 remotemachineAdding an Octel 100 remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an Octel 100 remote machine to the Message Networking system.Message Networking uses the Octel Analog Networking protocol to communicate with Octel 100 remotemachines.Note: The checklist for adding a new Octel 100 remote machine provides a list of steps you must completewhen adding a new Octel 100 remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add an Octel 100 remote machine on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. For
80information on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select Octel 100 from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine?, Send FAX Messages, and Dial String fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. For the Send FAX Messages field, select Yes to allow fax messages or No to restrict fax messages.6. In the Dial String field, type the gateway telephone number of the Octel 100 remote machine. MessageNetworking uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. For information onvalid dial strings, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.The remaining networking fields display on the page.8. Complete the networking fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.9. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.10. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.11. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new Octel 100 remote machineChecklist for adding a new Octel 100 remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new Octel 100 remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Octel 100 system. If you are unfamiliar with the Octel 100, askthe Octel 100 system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskOn the Message Networking system:Check the Customer Options page to verify that the Octel Analog Nodesfield is set to ON.On the Octel 100 system:
81Gather information about the Octel 100 system that you are adding. Youshould obtain the following information from the Octel 100 systemadministrator:! From the upper border of the OS/2 desktop, obtain the system'sname displayed in the upper border of the desktop window.! From the Networking Parameters screen, obtain the Serial # andSystem Telephone Access #.! From the Mailbox Status Report, obtain the range of extensions(Mailbox IDs).Note: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, an so on.! The number of digits in the Octel 100 system dial plan information.! A specific mailbox ID on the Octel 100 system that will receive andsend a test message through Message Networking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the Octel 100 subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain thearea code and local exchange from the switch administrator. You alsoneed to obtain the extension range for the Octel 100 system. You canobtain this range from the Octel 100 system administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit Octel 100extension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theOctel 100 system:
82On the General Parameters page:! Record the Octel Analog Serial Number.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.On the Octel 100 system:Run the ViewSent command:! Check the Revision field and verify that it is 3.2.9D.! Check that the Fax Retrieval, Fax Mail, and ONet fields are set toy.On the Octel 100 system:On the Port Parameters screen:! Check the Outbound Usage Permitted section and theAMIS/OctelNet field for the number of ports. If there are no portsenabled for networking, work with the Octel 100 systemadministrator to determine which ports should be enabled for usewith Message Networking.On the NameNet Parameters screen:! Verify that the setting in the Maximum Number of NameNetRecords field is sufficient for the number of remote subscribersthat the Octel 100 system will store.! Record the number in the Maximum Number of Idle Days forNameNet Records field. When you administer the Octel 100system on Message Networking, make sure that the Dynamic SubExpiration Days that you enter matches this number.On the Fax Parameters screen:! Verify whether a Fax Board Type is set. If the field is set to None,this system is not enabled for fax.On the Octel 100 system:Administer the Message Networking system as an Octel AnalogNetworking node on the Octel 100 remote machine:! In the System Name field, type the name of the MessageNetworking system.! In the Prefix Code field, type the prefix necessary for the networkaccess the Octel 100 system will use, usually 8 or 9.! In the Access Phone Number field, type the analog telephonenumber of the Message Networking system. This number mustalso be combined with the entry in the Prefix field for the completedial sequence that Octel 100 performs. You can locate this numberin the Telephone Number field on the AMIS Analog Parameterspage on the Message Networking system.! In the Insignificant Digits field, type the number of Node Numberdigits that Octel 100 should strip off the addresses of messagessent to Message Networking.! In the Mailbox Length field, type the number of digits in theMessage Networking Network Address Length field.! In the Answer Time field, leave the default of 0.! In the System Prompt field, leave the field blank.
83! In the Serial Number field, enter the serial number that appears inthe Octel Analog Networking Serial Number field on the GeneralParameters page on the Message Networking system.! In the Number Attempts field, leave the default of 5.! In the Network Node Type field, select OctelNet.! Check the Response Allowed checkbox to allow MessageNetworking to retrieve queried messages from the Octel 100system during the same session in which Message Networkingdelivers messages to the Octel 100 system. This field performs thesame function as the Network Turnaround field in MessageNetworking.! Leave the Transmit Name field unchecked to avoid havingrecipients of messages from Octel 100 subscribers hear thesender's name twice.! In the Maximum Messages field, type the number of outgoingmessages in queue after which the system uses an additionaltransmission connection for networked messages to MessageNetworking.! In the Maximum Delay field, type the cumulative number ofminutes any single message can wait in queue, after which anadditional transmission connection is used.! In the Economy Dispatch Weekday On and Weekday Off fields,you normally leave the default times from the NetworkingParameters window. However, you might want to change the timesspecifically for Message Networking if, for example, there is asignificant time zone difference.! In the System Administrator Information fields, type any contactinformation you might find useful.Note: Every Octel 100 subscriber who sends a message to a remotesubscriber through Message Networking will need to add the MessageNetworking node number to the remote subscriber's address. Forexample, if the Message Networking node number assigned on the Octel100 is 156, and a remote subscriber in the Message Networking networkhas a 10-digit address like 3035551212, the Octel 100 subscriberaddresses a message to that remote subscriber with 1563035551212.On the Octel 100 system:Run the Class of Service Report to verify that the Octel 100 subscribersare enabled for Octel Analog Networking. If subscribers are not enabled,edit the subscriber mailboxes to enable Octel Analog Networking.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new remote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Octel 100 remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:
84Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Administer subscribers. For Octel 100 remote machines, the followingmethods of adding subscribers from the remote machine to the MessageNetworking system are supported (listed in order of preference):! Set up the Self Registration Agent ID on the General Parameterspage and instruct remote subscribers on the new system to send amessage.! Use FTP to upload a subscriber list to the Message Networkingsystem.! Initiate Bulk Add by File from the Message Networking system.! Perform a Bulk Add by Range.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the Octel 100 subscribers were correctly populated onthe Message Networking system based on the Dial Plan Mapping youadministered.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe Octel 100 remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push to the Octel100 system to add subscribers from other remote machines to the Octel100 system.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theOctel 100 system must have the capacity to accommodate all of thesubscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the Octel 100 subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new SMTP/MIME machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the Octel 100 test mailbox you obtained from theOctel 100 system administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on theOctel 100 system and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of pageHome | Search
85Message Networking HelpPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: Octel 100Add or modify a remote machine: Octel 100Use the Add New Machine: Octel 100 page to add a new Octel 100 remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type the name of the Octel 100 system that you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select Octel 100.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).Send FAX Messages?: Specify whether fax messages are allowed for the remote machine. Select Yes to allowfax messages or No to restrict fax messages.Dial String: Type the main telephone number of the Octel 100 remote machine, up to 30 characters. TheMessage Networking system uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. The dialstring typically consists of the dial-access code needed to reach the network, followed by a pause interval,followed by the telephone number of the remote machine.You can enter the following characters in the dial string field: 0 - 9, P, #, *, and ". To make the MessageNetworking system pause for a specific length of time, type "P" (including the quotes) in the dial string. Includea single "P" to cause the system to pause approximately 1.5 seconds. Include a "P" followed by a digit from 1 to9 to cause the system to wait the specified number of seconds.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.
86Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Default Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:! directory-view: Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View.! dynamic: Select dynamic to specify that the remote machine should receive updates for subscribersthat exchange messages with this remote machine.! full: Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking systemto this remote machine. If you select full, verify that the remote machine has enough space forinformation on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is dynamic. To receive no updates, select directory-view, make sure no views aredefined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.ASCII Name Confirmation?: Specify whether the ASCII name is verified when a subscriber sends a messageusing NameNet. If the name does not match, the Message Networking system requests an update. Select yesto verify the ASCII name. Select no if you do not want to verify the ASCII name. The default for this field is yes.Admin Mode?: Specify that when Message Networking delivers a message to a remote machine using theOctel Analog Networking gateway, Message Networking automatically requests a subscriber update for thereceiving subscriber. Select yes to automatically request a subscriber update. Select no if you do not want to
87automatically request a subscriber update. The default for this field is no.Octel Analog Serial Number: Type the serial number of the analog remote machine, either 4 or 5 digits.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the MaximumNumber of Days for NameNet Records field on the Octel 100 system. The default for this field is 90. Theminimum for this field is 1. The maximum for this field is 999.Record Delay (Sec): The Record Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel Analog Networking protocolthat specifies the number of seconds before recording begins. The default for this field is 3. If clipping occurs atthe beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, increase this value toeliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networkingremote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate the silence.Maximum Simultaneous Connections: Maximum number of ports that will simultaneously handle outgoingtraffic for this machine. Enter an integer of 1 through 9 The default for this field is 1.Voiced Name Delay (Sec): The Voiced Name Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel AnalogNetworking protocol that specifies the number of seconds before a remote subscriber's name is voiced. Thedefault for this field is 3. If clipping occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel AnalogNetworking remote subscriber, increase this value to eliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of amessage received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate thesilence.Note: The default Voiced Name Delay for the Octel 100 is 2 seconds.System Mailbox ID: This field specifies the system mailbox number used by the protocol for the remotemachine, up to 10 digits. The default for this field is 0. This mailbox address must match the system mailbox setup on the remote machine.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding a ModularMessaging/Exchange or UM Analog remote machineAdding a Modular Messaging/Exchange or UM Analog remote machineThis topic provides information on adding a UM Analog or Modular Messaging/Exchange remote machine to theMessage Networking system. Message Networking uses the Octel Analog Networking protocol to communicatewith Modular Messaging/Exchange and UM Analog remote machines.Note: The checklist for adding a new Modular Messaging/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine provides alist of steps you must complete when adding a new MM/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine to theMessage Networking system.To add a Modular Messaging/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.
882. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select UM Analog from the Machine Type menu to indicate that you are adding a UM Analog or anMM/Exchange using OAN remote machine.The Bridged Machine?, Send FAX Messages, and Dial String fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. For the Send FAX Messages field, select Yes to allow fax messages or No to restrict fax messages.Note: Modular Messaging/Exchange systems using Octel Analog Networking require a separate faxserver to support fax components.6. In the Dial String field, type the gateway telephone number of the UM Analog or MM/Exchange remotemachine. Message Networking uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine.For information on valid dial strings, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.Additional remote machine parameter fields display on the page.8. Complete the fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help on the Webbasedadministration page.9. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.10. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.11. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new UM Analog remote machineChecklist for adding a new Modular Messaging/Exchange or UMAnalog remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new Modular Messaging/Exchange using OAN or UMAnalog remote machine to the Message Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in whichthey are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Modular Messaging/Exchange or UM Analog system. If you areunfamiliar with Modular Messaging or Unified Messenger, ask the system administrator to assist you.CompletedTask
89On the Message Networking system:Check the Customer Options page to verify that the Octel Analog Nodesfield is set to ON.On the MM/Exchange using OAN or UM Analog system:Gather information about the MM/Exchange or UM Analog system thatyou are adding. You should obtain the following information from theMM/Exchange or UM Analog system administrator:! Obtain the system's name.! Obtain the Serial # and System Telephone Access #.! Obtain the range of extensions (Mailbox IDs).Note: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, an so on.! The number of digits in the MM/Exchange or UM Analog systemdial plan information.! A specific mailbox ID on the MM/Exchange or UM Analog systemthat will receive and send a test message through MessageNetworking.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the MM/Exchange or UM Analog subscribers via the PBX.You can obtain the area code and local exchange from the switchadministrator. You also need to obtain the extension range for theMM/Exchange or UM Analog system. You can obtain this range from theMM/Exchange or UM Analog system administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit remote systemextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.
90On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theMM/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Octel Analog Serial Number.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.Also need the Message Networking access telephone number, which youcan obtain from the Message Networking system administrator.On the MM/Exchange or UM Analog system:Administer the Message Networking system as an Octel AnalogNetworking node on the MM/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new remote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the MM/Exchange or UM Analog remote machine has beenadded to the Message Networking system by viewing the RemoteMachines List.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Administer subscribers. For MM/Exchange or UM Analog remotemachines, the following methods of adding subscribers from the remotemachine to the Message Networking system are supported (listed inorder of preference):! Perform a demand remote update.Note: UM and MM/Exchange systems cannot request a remoteupdate from the Message Networking system. In addition, theMessage Networking system cannot push a remote update to UMAnalog or MM/Exchange using OAN systems.! Set up the Self Registration Agent ID on the General Parameterspage and instruct remote subscribers on the new system to send amessage.! Use FTP to upload a subscriber list to the Message Networkingsystem.! Initiate Bulk Add by File from the Message Networking system.! Perform a Bulk Add by Range.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networking
91system. Verify that the UM Analog subscribers were correctly populatedon the Message Networking system based on the Dial Plan Mapping youadministered.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the MM/Exchange or UM Analog test mailbox youobtained from the MM/Exchange or UM Analog system administrator.Then log into the test mailbox on the MM/Exchange or UM Analogsystem and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: ModularMessaging/Exchange or UM AnalogAdd or modify a remote machine: Modular Messaging/Exchange or UMAnalogUse the Add New Machine: UM Analog page to add a new Modular Messaging/Exchange using OAN or UManalog remote machine to the Message Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select UM Analog to add a Modular Messaging/Exchange using OAN or UM Analog remotemachine.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Options
92page is set to 500 (the maximum).Send FAX Messages?: Specify whether fax messages are allowed for the remote machine. Select Yes to allowfax messages or No to restrict fax messages.Note: Modular Messaging/Exchange systems using Octel Analog Networking require a separate fax server tosupport fax components.Dial String: Type the gateway telephone number of the remote machine, up to 30 characters. The MessageNetworking system uses the dial string to contact and send messages to the remote machine. The dial stringtypically consists of the dial-access code needed to reach the network, followed by a pause interval, followed bythe telephone number of the remote machine.You can enter the following characters in the dial string field: 0 - 9, P, #, *, and ". To make the MessageNetworking system pause for a specific length of time, type "P" (including the quotes) in the dial string. Includea single "P" to cause the system to pause approximately 1.5 seconds. Include a "P" followed by a digit from 1 to9 to cause the system to wait the specified number of seconds.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Default Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Subscriber Updates Type: Leave this field at the default, dynamic. This field does not apply to UM Analog andModular MM/Exchange using OAN systems because they cannot request remote updates from MessageNetworking and Message Networking cannot push remote updates to these remote machines.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information from
93this remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Leave this field at the default, no. This field does not apply to UM Analog and ModularMM/Exchange using OAN systems because Message Networking cannot push remote updates to these remotemachines.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: Leave this field at the default, yes. This field does not apply to UM Analog andModular MM/Exchange using OAN systems because Message Networking cannot push remote updates tothese remote machines.ASCII Name Confirmation?: Specify whether the ASCII name is verified when a subscriber sends a messageusing NameNet. If the name does not match, the Message Networking system requests an update. Select yesto verify the ASCII name. Select no if you do not want to verify the ASCII name. The default for this field is yes.Admin Mode?: Specify that when Message Networking delivers a message to a remote machine using theOctel Analog Networking gateway, Message Networking automatically requests a subscriber update for thereceiving subscriber. Select yes to automatically request a subscriber update. Select no if you do not want toautomatically request a subscriber update. The default for this field is no.Octel Analog Serial Number: Type the serial number of the analog remote machine, either 4 or 5 digits.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Record Delay (Sec): The Record Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel Analog Networking protocolthat specifies the number of seconds before recording begins. The default for this field is 3. If clipping occurs atthe beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, increase this value toeliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel Analog Networkingremote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate the silence.Maximum Simultaneous Connections: Maximum number of ports that will simultaneously handle outgoingtraffic for this machine. Enter an integer of 1 through 9 The default for this field is 1.Voiced Name Delay (Sec): The Voiced Name Delay is a timing parameter used by the Octel AnalogNetworking protocol that specifies the number of seconds before a remote subscriber's name is voiced. Thedefault for this field is 3. If clipping occurs at the beginning of a message received by an Octel AnalogNetworking remote subscriber, increase this value to eliminate clipping. If silence occurs at the beginning of amessage received by an Octel Analog Networking remote subscriber, decrease this value to eliminate thesilence.System Mailbox ID: This field specifies the system mailbox number used by the protocol for the remotemachine, up to 10 digits. The default for this field is 0. This mailbox address must match the system mailbox setup on the remote machine.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of page
94Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an Aria Digital remotemachineAdding an Aria Digital remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an Aria Digital remote machine.Note: The checklist for adding an Aria Digital remote machine provides a list of steps you must complete whenadding a new Aria Digital remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add an Aria Digital remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select Aria Digital from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine?, Send FAX Message, and IP Address fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. For the Send FAX Message field, select Yes to allow fax messages or No to restrict fax messages.6. In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating. For information onvalid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.The remaining networking fields display on the page.8. Complete the networking fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.9. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.10. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the web-based administration page.11. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of page
95Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferencehHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new Aria Digital remote machineChecklist for adding a new Aria Digital remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new Aria Digital remote machine to the MessageNetworking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Aria Digital system. If you are unfamiliar with the Aria Digital, askthe Aria Digital system administrator to assist you.Note: The menu options provided in the checklist assume that Aria is being accessed from a local terminal ormodem port and it not being accessed via a flex port.CompletedTaskOn the Aria Digital system:Gather information about the Aria Digital system that you are adding:1. From the Main Menu, select System Maintenance (menu option13), followed by Display Software Levels (menu option 4). On theDisplay Software Levels screen:" Record the Network Serial #." Check the Software Rel. field. If it does not display Aria02.05 or greater, the system must be upgraded to work withMessage Networking. Message Networking supports AriaDigital Release A2.05 and greater and A3.X.2. From the Main Menu, select System Maintenance (menu option13), followed by Display Software Features Installed (menu option7). On the Display Software Features Installed screen, check thatthe following fields are marked with a Y:" 44 - Networking" 56 - Fax Processing" 66 - Fax Delivery Mailbox3. Go to Page 2 of the Display Software Feature Installed screen andcheck that the following fields are marked with a Y:" 74 - Digital Networking" 73 - Connectivity4. From the Aria Digital system administrator, obtain:" A specific mailbox ID on the Aria Digital system that willreceive and send a test message through MessageNetworking.On the Aria Digital system:Verify that the Aria Digital system is enabled for digital networking:1. From the Main Menu, select LAN Interface Management (menuoption 22), followed by IP Address and Net Mask Configuration(menu option 1). On the IP Address and Net Mask Configurationscreen:" Check that the This Server's IP Address field is complete,
96and record the IP address." Check that the IP Net Mask field is complete, and recordthe Net Mask.Note: If either field is not complete, have the Aria systemadministrator enter the appropriate information on the Aria system.2. From the Main Menu, select LAN Interface Management (menuoption 22), followed by TCP/IP Parameter Configuration (menuoption 2). On the TCP/IP Parameter Configuration screen:" Check that the Gateway IP Address field is complete. If thefield is not complete, get the appropriate gateway IPaddress from the LAN administrator and have the AriaDigital system administrator enter it in this field.Note: if the Aria system and the Message Networking system areto communicate over the Internet, this address must be aregistered IP address.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the Aria subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain the areacode and local exchange from the switch administrator. You also need toobtain the extension range for the Aria system. You can obtain this rangefrom the Aria system administrator or from the Octel Mailbox Managersoftware, if you have purchased this software.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit Aria extension. Thisexample assumes the network address requires 10-digit dialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theAria Digital system:On the General Parameters page:
97! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.! Record the Octel Analog Serial Number.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.On the Aria Digital system:Administer the Message Networking system on the Aria Digital system:1. From the Main Menu, select Network Management (menu option15), followed by OctelNet <strong>Administration</strong> (menu option 1), and ListValid Node Numbers on the Network (menu option 5). On the ValidNode Numbers and Message Queues Selected screen:" In the Select Node field, enter 0." In the Select Message Queue field, enter 9.2. On the Valid Node Numbers and Message Queues List screencheck the list of numbers in the Node # column, and record thenumbers available in the sequence.3. From the Octel <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Define/Change NodeProfile (menu option 3). On the Node Profile screen, complete thefollowing fields:a. Enter the first available node number from the list yourecorded in the previous step. this will be the node numberfor the Message Networking system.b. In the Node Name field, enter the Message NetworkingLocal Machine Name, which you recorded.c. In the Node Type field, type 2 for Digital Networking.d. In the Number of Digits in a Mailbox field, enter the numberof digits that appears in the Network Address Length fieldon the General Parameters page in Message Networking.e. In the Serial Number field, type the serial number thatappears in the Octel Analog Serial Number field on theGeneral Parameters page in Message Networking.f. In the NameNet Type field, it is recommended that you type0 for COS-based type.g. In the NameSend field, type 3 for Send and Receive. Thisentry allows voice names to be sent to and from MessageNetworking.h. The Aria system requires you to enter a number in thePhone Number field. However, this number is not used byMessage Networking for digital nodes, so enter any numberin this fieldi. In the IP Address field, type the IP address that appears inthe Local Machine IP Address field on the GeneralParameters page in Message Networking.j. In the Name Transmission Allowed field, type N to avoidhaving recipients of messages from Aria Digital subscribershear the sender's name twice.k. In the Play Node Name field, type N.
98l. In the ASCII Name Check field, type 1 for Check AllMessages. This value tells the Aria system to check that theASCII names attached to messages sent to the Aria systemare correct.4. On the Node Profile (weekday schedule) screen, complete thefollowing fields:a. In the Begin and End fields for Window 1, type the range oftime for Aria to send messages to Message Networking. Forexample, if you enter 12:00a in the Begin field and 11:59pin the End field, delivery can occur 24 hours a day.b. In the Interval field for Window 1, type 0 for Immediate. Thisvalue means that Aria will pass messages to MessageNetworking as soon as they are recorded and queued.c. In the Priority field for Window 1, type A for AdministrativeMessages. Administrative messages are system-levelmessages like subscriber updates.d. In the Begin and End fields for Window 2, type the range oftime for Aria to send messages to Message Networking.e. In the Interval field for Window 2, type 0 for Immediate.f. In the Priority field for Window 2, type 0 for Non-Urgent/Standard Subscriber Messages. These messagesare regular subscriber messages with normal priority.5. On the Node Profile (weekend/holiday schedule) screen, completethe following fields:a. In the Begin and End fields for Window 1, type the range oftime for Aria to send messages to Message Networking forweekend/holiday times.b. In the Interval field for Window 1, type 0 for Immediate.c. In the Priority field for Window 1, type A for AdministrativeMessages.d. In the Begin and End fields for Window 2, type the range oftime for Aria to send messages to Message Networking.e. In the Interval field for Window 2, type 0 for Immediate.f. In the Priority field for Window 2, type 0 for Non-Urgent/Standard Subscriber Messages.6. On the Node Profile screen (prefix page), in the Enter option field,type A to add a prefix.Enter the prefix plus additional digits needed to address messagesthrough the Message Networking system. Contact the Aria systemadministrator for help completing this screen. Keep in mind thatany network addresses that need to be addressed from the AriaDigital system to the Message Networking system must be addedto this screen.If there are no conflicts due to using point-to-point networkingpreviously administered, you can set up the prefix plus additionaldigits combinations to cover all possible combinations, as shown inthe example that follows. However, if there are conflicts, the Ariaadministrator might need to help you determine the correct prefixplus additional digits to enter to ensure that the correct digits aresent to the Message Networking system.The following table provides a sample prefix plus additional digitsconfiguration for sending to a 10-digit Message Networkingsystem. In this example, there are no conflicts due to previously
99administered point-to-point networking, so the prefix and remainingdigit combinations in the Node Profile screen allow for all possible10-digit combinations of network addresses.ExamplePrefixAdditional digits0 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 9On the Aria Digital system:Ensure that the NameSend Capability is on for subscribers in the Class ofService profile on the Aria system:From the Main Menu, select Change Class of Service Profile (menuoption 7). On the Class of Service Profile Selection screen, go to Page 2:! On the Change Class of Service Profile screen, enter a valid Classof Service (1 to 64).! For each Class of Service used for subscribers who will havevoice/fax messaging capability to the Message Networkingnetwork, verify that the NameSend Capability field has a Y.Note: If you want the Aria Digital subscribers to have faxcapability, make sure fax is enabled in their classes of service.On the Aria Digital system:From the Main Menu, select Service Operations (menu option 20),followed by LAN Utilities (menu option 14), and Ping (menu option 1).Ping the Message Networking system.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new Aria Digitalremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Aria Digital remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Aria Digital system:From the Main Menu, select System Maintenance (menu option 13),followed by Name Send Utility (16).On the NameSend Utility screen:
1001. Enter the starting Aria mailboxes that are to be sent to theMessage Networking system and press Enter.2. Enter the ending Aria mailboxes that are to be sent to theMessage Networking system and press Enter.3. Enter the node number you assigned to the Message Networkingsystem when you administered it on the Aria system and pressEnter twice.4. When a message asks if you want to queue NameSendmessages, type y and press Enter.5. When you see the message that the NameSend is complete,press any key to continue.On the Message Networking system:View the Remote Machines List. Locate the Aria Digital system in the listand verify that the number of subscribers in the Subs column matchesthe numbers of subscribers that should have been added to the MessageNetworking system.If the update is still in progress, the total number of subscribers willincrease until all of the subscribers are received. If all subscribers are notreceived, you must determine the cause of the failure.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the Aria Digital subscribers were correctly populatedon the Message Networking system based on the Dial Plan Mapping youadministered.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe Aria Digital remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push to the Ariasystem to add subscribers from other remote machines to the Aria Digitalsystem.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theAria Digital system must have the capacity to accommodate all of thesubscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the Aria Digital subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new Aria Digital machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system through theMessage Networking, using the network address of the Aria test mailboxthat you obtained from the Aria system administrator. Then log into thetest mailbox on the Aria system and verify that the test message wasdelivered.
101Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: Aria DigitalAdd or modify a remote machine: Aria DigitalUse the Add New Machine: Aria Digital page to add a new Aria Digital remote machine to the MessageNetworking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select Aria Digital.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).Send FAX Messages?: Specify whether fax messages are allowed for the remote machine. Select Yes to allowfax messages or No to restrict fax messages.IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 29 characters (for example 192.43.235.1). MessageNetworking uses the IP address to contact and send messages to remote machines. Make sure that you enterthe correct IP address as the system does not validate the number you enter. This field is optional for theSMTP-Unified Messenger, SMTP-MM, and other non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME machine types.Note: If you plan to use the Domain Name Server (DNS) feature, you do not have to enter a value for this field.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.
102However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Default Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:! Directory View: A directory view containing static updates.! Dynamic: A directory view containing dynamic updates.! Full: A directory view containing updates for all remote machines is provided. If this field is set to Full,verify that the remote machine has enough space for information on all subscribers from all remotemachines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is Dynamic. To select no updates, select Directory View in this field, make sure that noviews are defined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.ASCII Name Confirmation: Specify whether the ASCII name is verified when a subscriber sends a messageusing NameNet. If the name does not match, Message Networking requests an update. Select yes to verify theASCII name. Select no if you do not want to verify the ASCII name. The default for this field is yes. For AriaDigital remote machines, you can select no because Message Networking will rely on Aria's NameSendcapability to keep names up to date.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist without
103performing any activity; that is, without sending or receiving messages. This number must match the number ofaging days administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1.The maximum for this field is 999. Note that this number should match the entry in the Aging Out Period (days)field on the Aria system.Serial Number: Type the serial number of the system, usually 4 or 5 digits.System Mailbox ID: The System Mailbox ID is the system mailbox number used by the protocol for the remoteOctel Analog Networking machine, up to 10 digits. The default for this field is 0. This mailbox address mustmatch the system mailbox set up on the remote Octel Analog Networking machine. For information on thesystem mailbox, see your Octel machine administration documentation.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding a Serenade Digital remotemachineAdding a Serenade Digital remote machineThis topic provides information on adding a Serenade Digital remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem.Note: The checklist for adding a Serenade Digital remote machine provides a list of steps you must completewhen adding a new Serenade Digital remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add a Serenade Digital remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field then click Next Step. For informationon valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page to viewmore information.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select Serenade Digital from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine?, Send FAX Message, and IP Address fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. For the Send FAX Message field, select Yes to allow fax messages or No to restrict fax messages.6. In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating. For information onvalid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.The remaining networking fields display on the page.8. Complete the networking fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help on
104the Web-based administration page.9. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.10. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.11. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Note: In some dial plans when a message is going to a Serenade user, Message Networking must add a prefixto the network address to build a complete sender address. You can administer a Serenade Digital Sender DialPlan to specify the prefix to add to a network address.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new Serenade Digital remote machineChecklist for adding a new Serenade Digital remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new Serenade Digital remote machine to the MessageNetworking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Serenade Digital system. If you are unfamiliar with the SerenadeDigital, ask the Serenade Digital system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskOn the Serenade Digital system:Record the system's serial number and verify the installed featurepackages:1. At the initial Serenade system login, write down the S/N numberlisted above the login prompt. This is the Serenade system's serialnumber.2. From the @ prompt, type l f and press Enter to list the installedfeature packages. Verify that the following feature packages areinstalled:" SWx0004" SWx0049where x is the release number of the Serenade system.On the Serenade Digital system:Verify that the Serenade system has an installed board for digitalnetworking:At the dot prompt (in update mode), type l slot and press Enter. Checkfor a LAN card from the list that displays.
105On the Serenade Digital system:From the Serenade system administration, obtain a specific mailbox IDon the Serenade Digital system that will receive and send a test messagethrough Message Networking.On the Serenade Digital system:Verify with the Serenade system administration that the Serenade Digitalsystem has the most current software patches installed.On the Serenade Digital system:Gather information about the Serenade Digital system that you areadding. You should obtain the following information from the SerenadeDigital system administrator:From the dot prompt, type l sys and press Enter to view the systemparameter table. From the system parameter table:1. Record the Installation Name (parameter index 1) and System ID(parameter index 2).2. Check the number of Fax Ports Used (parameter index 4). If thisnumber is 0, the Serenade Digital system is not enabled for fax.3. Verify that DNET: Digital Networking Enabled (parameter index225) is set to YES.4. Record the Serenade system's IP address, specified in the LAN:Name Server IP Address field (parameter index 233).5. Record the gateway IP address for the Serenade system,specified in the LAN: Gateway IP Address field (parameter index234).6. Verify that the DNET: Switch to Analog Standby field (parameterindex 253) is set to NO.7. Verify that the DNET: Enable ASCII Name Verification field(parameter index 257) is set to YES.8. Verify that the NameSend: Delivery Mode (parameter index 276) isset to IMMED, which enables immediate NameSend updates.9. Verify that the NameSend: Maximum Names to Send in a Session(parameter index 277) is set to 0, which means that it is unlimited.10. Verify that the NameSend: Enable by Default for New Users(parameter index 278), which allows Serenade to enable asubscriber automatically for NameSend when the subscriber isadded, is set to YES.11. Verify that the NameSend Automatic Name Propagation(parameter index 280) is set to YES, which allows new users to beautomatically distributed by NameSend.12. Verify that the GWL: Gateway Link Installed (parameter index 281)is set to YES because a gateway link is required for the TCP/IPnetwork connection. This parameter requires that parameters 284and 285 are enabled first.13. Verify that the GWL: Generic Error Mailbox (parameter index 284)has been populated with a mailbox number. This mailbox mustexist before the Serenade system will allows a gateway link inparameter 281.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters page
106on the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the Serenade subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain thearea code and local exchange from the switch administrator. You alsoneed to obtain the extension range for the Serenade system. You canobtain this range from the Serenade system administrator or from theOctel Mailbox Manager software, if you have purchased this software.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit Serenadeextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Serenade Digital system:Gather the range of valid Serenade system mailboxes:From the dot prompt, type l users and press Enter to view the Serenadesystem subscribers by mailbox number. Depending on the number ofsubscribers, the list might be very long. You can also obtain the validmailbox ranges from the Serenade system administrator.Note: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that will neverreceive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletin boards, an soon.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theSerenade Digital system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.! Record the Octel Analog Serial Number.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.
107On the Serenade Digital system:Add the Message Networking system as a new location on the Serenadesystem:From the dot prompt, type a loc and press Enter to add a new location tothe location table:1. Type a name of 6 characters or less and then press Enter tospecify a name for the Message Networking system on theSerenade.2. For the protocol to use with the system, enter 5 and then pressEnter.3. For the serial number, type the serial number that appears in theOctel Analog Networking Serial Number field on the GeneralParameters page in Message Networking and then press Enter.4. When asked whether the sender's name should be embedded inmessages sent to Message Networking, select N and then pressEnter to avoid having recipients of messages from SerenadeDigital subscribers hear the sender's name twice.5. For route names, leave the field blank because a route is notnecessary for digital networking subscribers.6. For the network schedule to be used for the Message Networkingsystem, type none and then press Enter to have Serenade sendmessages to remote Message Networking subscribersimmediately after they the sender sends them.7. For a Public Network Number, leave the field blank becauseSerenade Digital uses TCP/IP to connect to Message Networking.8. For the TIE Network Number, leave the field blank.9. When asked whether Message Networking is accessible over thedigital network, type y and then press Enter.10. For the digital location name, type the full name of the MessageNetworking system and then press Enter.11. For the IP address, type the IP address from the Local Machine IPAddress field on the Message Networking General Parameterspage and then press Enter.12. When asked whether NameSend should be enabled, type y andthen press Enter to send names to Message Networking.13. When asked whether there is a high-speed digital link to MessageNetworking, type n and then press Enter.14. Press Enter to return to the dot prompt.On the Serenade Digital system:Add a numbering plan for the Message Networking system:From the dot prompt, type a num and then press Enter.At the ADD: prompt, type the following in order, separated by commas,for each entry you want to add to the numbering plan:! The name of the Message Networking system as entered in theLocation Table! The initial digits expected for Message Networking messages! The Message Networking system network address length! The number of digits to strip
108! The number of digits to strip from self, and then press Enter.For example: mnsystem, 1, 11, 1, 3where:! mnsystem is the name of the Message Networking system! 1 is the initial digits to expect for messages being sent to MessageNetworking! 11 is the Message Networking system network address length! 1 is the number of digits to strip from the beginning of the address! 3 is the number of digits to strip from self (depends on the numberof digits set for self)The combination of the Initial Digits to Expect and the Mailbox Lengthindicates that the messages should be sent from the Serenade system toMessage Networking. Therefore, the combination of the Initial Digits toExpect and the Mailbox Length must be unique within the numberingplan. Multiple entries might need to be added to the numbering table toinclude all possible combinations of network addresses in the MessageNetworking system. If there are no conflicts due to using point-to-pointnetworking previously administered, the Initial Digits to Expect cancontain digits from actual Message Networking addresses. If there areconflicts, the Serenade administrator might need to determine how to setup the numbering plan for the Message Networking system so that thecorrect number of digits are sent.The Network Mailbox Length can be the number of digits in the NetworkAddress Length field on the General Parameters page in MessageNetworking if there are no conflicts due to point-to-point systempreviously administered. If there are conflicts, the Serenade administratormight need to determine how to set up the numbering plan for theMessage Networking system so that the correct number of digits aresent.The Number of Digits to Strip might be needed if the number of digits inthe network address length is greater than the number of digits expectedby Message Networking. In this case, the Serenade system removes theappropriate number of digits from the Message Networking addressdialed by the sender. Normally, with Message Networking, you strip offthe number of digits identified in the Initial Digits Expected field, ifnecessary.Note: It is possible to establish a numbering plan that does not strip offdigits. In this way, the addresses that Serenade subscribers enter whensending message to Message Networking subscribers can be theMessage Networking addresses with no additional digits. For this plan tobe possible, there can be no point-to-point systems networked toSerenade that use the same combination of initial digits and networkmailbox length.On the Serenade Digital system:Ping the Message Networking system from the Serenade Digital system:From the @ prompt, type test dnet followed by the location name of theMessage Networking system and then press Enter.The Serenade system pings the Message Networking system. If the pingis successful, the CONNECTION SETUP field displays OK.Note: Disregard the CONFIG field output message as this only applies to
109point-to-point networking between Serenade systems.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new Serenade Digitalremote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Serenade Digital sender dial plan for the remote machine,if appropriate.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Serenade Digital remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Serenade Digital system:Run NameSend from the Serenade system to the Message Networkingsystem to add remote subscribers:1. From the @ prompt, type namesend queue add and press Enter.2. Type the location name of the Message Networking system andpress Enter.3. Type the starting number in the mailbox range of Serenademailboxes, followed by a dash, followed by the ending mailboxnumber in the range of Serenade mailboxes, and then pressEnter.4. When asked whether you want to view the subscribers beingadded to the queue, type v for verbose or q for quiet and pressEnter.5. When asked whether you want to add all mailboxes to the locationlist, type y and press Enter.On the Message Networking system:View the Remote Machines List. Locate the Serenade Digital system inthe list and verify that the number of subscribers in the Subs columnmatches the numbers of subscribers that should have been added to theMessage Networking system.If the update is still in progress, the total number of subscribers willincrease until all of the subscribers are received. If all subscribers are notreceived, you must determine the cause of the failure.On the Message Networking system:View the Subscriber List by Machine Name on the Message Networkingsystem. Verify that the Serenade Digital subscribers were correctlypopulated on the Message Networking system based on the Dial PlanMapping you administered.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates and
110you do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe Serenade Digital remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push to theSerenade system to add subscribers from other remote machines to theSerenade Digital system.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theSerenade Digital system must have the capacity to accommodate all ofthe subscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new Serenade Digital machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network through the Messaging Networking system to thenetwork address of the Serenade test mailbox you obtained from theSerenade system administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on theSerenade system and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: Serenade DigitalAdd or modify a remote machine: Serenade DigitalUse the Add New Machine: Serenade Digital page to add a new Serenade Digital remote machine to theMessage Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select Serenade Digital.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being used
111as a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).Send FAX Messages?: Specify whether fax messages are allowed for the remote machine. Select Yes to allowfax messages or No to restrict fax messages.IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 29 characters (for example 192.43.235.1). MessageNetworking uses the IP address to contact and send messages to remote machines. Make sure that you enterthe correct IP address as the system does not validate the number you enter.Note: If you plan to use the Domain Name Server (DNS) feature, you do not have to enter a value for this field.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Default Community ID: Community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine. An integer of 1through 15.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:! directory-view: Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View.! dynamic: Select dynamic to specify that the remote machine should receive updates for subscribersthat exchange messages with this remote machine.! full: Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking system
112to this remote machine. If you select full, verify that the remote machine has enough space forinformation on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is dynamic. To receive no updates, select directory-view, make sure no views aredefined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.ASCII Name Confirmation?: Specify whether the ASCII name is verified when a subscriber sends a messageusing NameNet. If the name does not match, the Message Networking system requests an update. Select yesto verify the ASCII name. Select no if you do not want to verify the ASCII name. The default for this field is yes.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.System Mailbox ID: The System Mailbox ID is the system mailbox number used by the protocol for the remotemachine, up to 10 digits. The default for this field is 0. This mailbox address must match the system mailbox setup on the remote machine. For information on the system mailbox, see your remote machine administrationdocumentation.Note: This field must be completed for Serenade Analog remote machines and must match the Serenadesystem mailbox ID.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Note: In some dial plans when a message is going to a Serenade user, the Message Networking system mustadd a prefix to the network address to build a complete sender address. You can administer a Serenade DigitalSender Dial Plan to specify the prefix to add to a network address.Top of page
113Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding a VPIM remote machineAdding a VPIM remote machineThis topic provides information on adding a VPIM remote machine to the Message Networking system.Note: The checklist for adding a VPIM remote machine provides a list of steps you must complete when addinga new VPIM remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add a VPIM remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select VPIM from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine? and IP Address fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. In the IP Address field, you can optionally type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating.For information on valid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.6. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.7. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.8. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.9. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.10. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of page
114Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new VPIM remote machineChecklist for adding a new VPIM remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new VPIM remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the VPIM system. If you are unfamiliar with the VPIM system, askthe VPIM system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskOn the VPIM system:Gather information about the VPIM system that you are adding. Youshould obtain the following information from the VPIM systemadministrator:! The VPIM system name.! The VPIM system fully qualified domain name that includes theserver name.! One of the following:" Determine the IP address of the VPIM system. The addressof the system must be a fully qualified domain name server.If Message Networking will use this address to exchangemessages with the system, you do not need to obtain theDNS addresses." Determine the IP address of DNS 1 and, if available, DNS 2and DNS 3. These addresses are the IP addresses throughwhich Message Networking will determine the address ofthe VPIM remote machine.! The starting and ending extensions of the voice mailboxes on theVPIM system.Note: Exclude address ranges associated with mailboxes that willnever receive messages, such as automated attendants, bulletinboards, an so on.! The prefix or prefixes that the Message Networking system willattach to mailbox IDs so that they fit the Message Networkingnetwork address length.! A specific mailbox ID on the VPIM system that will receive andsend a test message through Message Networking.! If your VPIM supports network updates, make sure that the remotemachine is set up to allow incoming and outgoing updates. MostVPIM systems do not support network updates.Gather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sent
115through the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the VPIM subscribers via the PBX. You can obtain the areacode and local exchange from the switch administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit VPIM extension.This example assumes the network address requires 10-digit dialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new VPIM remotemachine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Add the VPIM system subscribers to the Message Networking system byusing one of the following methods to administer subscribers (in order ofpreference):! Use FTP to add subscribers.! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voiced names (if using thismethod, have the VPIM system administrator provide the MessageNetworking Self Registration Agent ID, which can be obtained fromthe Message Networking General Parameters page.! Send a message from the new subscriber to an existing subscriberon the Message Networking system.! Add manually through the Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Initiate Bulk Add by Range from the Message Networking system.Message Networking also supports administering subscribers via anLDAP Client using Message Networking's LDAP interface.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the INTUITY AUDIX remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the VPIM system:
116Administer the Message Networking system as a VPIM network node onthe VPIM system. You might need the following information, dependingon your VPIM system type:! The fully qualified domain name and IP address of the MessageNetworking system. The VPIM system uses this information tosend messages to the Message Networking system.! The Message Networking network address length.! The Message Networking network address ranges for othermessaging systems in the network. Depending on the specificVPIM system, the address ranges that are required are generallythe dial plan mapping entries for each remote machine on theMessage Networking system. In other cases, you might need alldigits of the address ranges. In addition to the dial plan map, youmight need to add a prefix to address messages to the MessageNetworking system.! If you need to specify a server type, obtain this information fromthe VPIM system administrator.! If you need to specify a protocol type, select VPIM.Note: The VPIM system must pass to Message Networking only thoseaddressing digits used in the Message Networking network. When usingtelephones, subscribers on the VPIM system might have to dial additionaldigits to address messages to remote subscribers on the MessageNetworking network. This is sometimes referred to as a prefix. Thesedigits might be required for the following reasons:! The VPIM system can identify the addressee as a remotesubscriber.! The VPIM system can identify the remote system where theremote subscriber resides (in this case, the Message Networkingsystem).Do not administer the VPIM system to pass any other digits to theMessage Networking system. Instead, administer the VPIM system sothat it strips off these additional addressing digits when it passes themessage to the Message Networking system. Only addresses within theranges specified for Message Networking remote machines (specified inthe Dial Plan Mapping) are to be sent to the Message Networkingsystem.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the VPIM subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new VPIM machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from remote VPIM system test mailbox that youobtained from the VPIM system administrator to another messagingsystem in the Message Networking network. Verify that the test messagewas delivered to the remote system mailbox.
117Send a test message from another messaging system in the MessageNetworking network to the remote VPIM system test mailbox that youobtained from the VPIM system administrator. Then log into the testmailbox on the VPIM system and verify that the test message wasdelivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: VPIMAdd or modify a remote machine: VPIMUse the Add New Machine: VPIM page to add a new VPIM remote machine to the Message Networking system.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select VPIM.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 15 characters (for example 192.43.235.1).Note: If you plan to use the DNS (Domain Name Server) feature, you do not have to enter a value for this field.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that you
118subsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Subscriber Updates Type: This field is always set to Dynamic for VPIM remote machines.Default Community ID: Specifies the community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine.Type an integer from 1 through 15.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Use DNS?: Indicates whether DNS option is being used. Select yes to use DNS. Select no to not use DNS.The default for this field is no. If you select yes, the primary DNS IP address specified on the GeneralParameters page is used to resolve the IP address for the VPIM machine. If you retain the default of no, youmust specify an IP address on this page.Port: Type the number of the port being used by the machine you are adding. The default for this field is 25, thestandard SMTP port number, which will be used by most systems. If you want to use another port number,specify a number from 1000 to 65000. Some of the numbers within the range might be unusable.Domain Name: Type the fully qualified name of the VPIM remote machine. Every email address with a domainmatching the one you define in this field is considered a subscriber of this machine.If you want this remote machine to be the default Internet remote machine used to handle SMTP messagesfrom remote machines not administered on the Message Networking system, leave this field blank. There canbe only one default Internet remote machine on each Message Networking system. If you leave this field blank,any email address with a domain that does not match any other domain name of any other SMTP machine isconsidered a subscriber of this default Internet machine.It is strongly recommended that you enter all domain names in lower-case letters to ensure that all domainnames across the network are in the same case.
119If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OKTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an SMTP/MIME–UnifiedMessenger remote machineAdding an SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine to the MessageNetworking system.Note: The checklist for adding an SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine provides a list of steps youmust complete when adding a new SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine to the MessageNetworking system.To add an SMTP/MIME for Unified Messenger remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select SMTP–Unified Messenger from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine? and IP Address field appears on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. In the IP Address field, you can optionally type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating.For information on valid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.6. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.7. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.8. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.9. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.10. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.
120" If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machineChecklist for adding a new SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remotemachineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine tothe Message Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.CompletedTaskGather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the SMTP/MIME subscribers via the PBX. You can obtainthe area code and local exchange from the switch administrator. You alsoneed to obtain the extension range for the SMTP/MIME system. You canobtain this range from the remote system administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit remote machineextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the SMTP/MIME-Unified Messenger system:Gather information about the SMTP/MIME system that you are adding:
1211. The IP address of the SMTP/MIME system (optional).2. The number of digits in mailbox IDs on the SMTP/MIME system.3. The domain name of the email address that corresponds to thisSMTP/MIME machine.4. The IP address or domain name of the mail transfer agent, thesoftware component that exchanges mail with other systems(optional).5. Obtain a specific mailbox ID on the SMTP/MIME system that willreceive and send a test message through Message Networking.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the SMTP/MIME remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Use one of the following methods to administer subscribers on theMessage Networking system (in order of preference):! Use FTP to add subscribers.! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voiced names.! Register through the <strong>Administration</strong> page.On the SMTP/MIME-Unified Messenger system:On Unified Messenger for Lotus Notes 5.0 or later systems, you mustadminister remote subscribers as users on the Lotus Notes/Dominosystem.On the SMTP/MIME-Unified Messenger system:On Unified Messenger for Microsoft Exchange 5.0 or later systems, youmust administer remote subscribers as users on the Microsoft Exchangesystem.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type forthe remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push to the SMTP/MIMEsystem to add subscribers from other remote machines to theSMTP/MIME system.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theSMTP/MIME system must have the capacity to accommodate all of thesubscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:
122Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the SMTP/MIME subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new SMTP/MIME machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system through theMessage Networking, using the network address of the SMTP/MIME testmailbox that you obtained from the SMTP/MIME system administrator.Then log into the test mailbox on the SMTP/MIME system and verify thatthe test message was delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: SMTP–Unified MessengerAdd or modify a remote machine: SMTP–Unified MessengerUse the Add New Machine: SMTP–Unified Messenger page to add a new SMTP–Unified Messenger remotemachine to the Message Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select SMTP–Unified Messenger.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 15 characters (for example, 192.43.235.1). This field is
123optional because the system uses the domain name to recognize the sending machine.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Subscriber Updates Type: This field is always set to Dynamic for SMTP/MIME–UM remote machines.Default Community ID: Specifies the community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine.Type an integer from 1 through 15.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Use DNS?: Indicates whether DNS option is being used. Select yes to use DNS. Select no to not use DNS. It isstrongly recommended that you use DNS. The default for this field is no.If you select yes:! You must administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The primary DNS IP address specified on the General Parameters page is used to resolve the IP addressfor the remote machine.
124If you retain the default of no:! Do not administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The outgoing MTA for this remote machine must be an IP address, unless you edit the /etc/hosts file toadminister host names. If you do not specify an outgoing MTA, then the incoming domain name must bean IP address.Port: Type the number of the port being used by the machine you are adding. The default for this field is 25, thestandard SMTP port number, which will be used by most systems. If you want to use another port number,specify a number from 1000 to 65000. Some of the numbers within the range might be unusable.Domain Name: Type the domain name of the email address that corresponds to this machine. This field can bea fully qualified domain name (such as system.location.company.com), or just a domain (such ascompany.com). Every email address with a domain that matches the one you define in this field is considered asubscriber of this machine.It is strongly recommended that you enter all domain names in lower-case letters to ensure that all domainnames across the network are in the same case.Outgoing MTA: Type the IP address or domain name of the mail transfer agent, the software component thatexchanges mail with other systems. If you specify an outgoing MTA, every message whose destination is asubscriber of this SMTP/MIME machine is routed through this MTA. This field is optional.Preferred Encoding Type: Select the encoding type in which voice messages are transcoded when comingfrom a non-SMTP end node. Select GSM 6.10, GSM 7.11 u-law, or GSM 7.11 A-law.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an LDAP clientAdding an LDAP clientThis topic provides information on adding an LDAP client to the Message Networking system. An LDAP clientrepresents a trusted server that can be used to perform directory queries and Message Networking systemadministration. For more information on Message Networking's LDAP interface, see LDAP overview.To add an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the LDAP client in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select LDAP Client from the Machine Type menu.The IP Address fields appear on the page.4. In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the LDAP client. For information on valid IP addresses,
125click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. Click Next Step.The Organization, Organization Unit, and Comments fields display on the page.6. You can optionally enter information in these fields about the LDAP client. For information on completingthe fields, click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.The Subscriber Update Type, LDAP Server, and LDAP Password fields display on the page.8. Complete the fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help on the Webbasedadministration page.9. Click Add this Machine to add the LDAP client to the Message Networking system.10. Once the message displays that the parameters have been saved, click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: LDAP ClientAdd or modify a remote machine: LDAP ClientUse the Add New Machine: LDAP Client page to add a new LDAP client to the Message Networking system orto modify an existing LDAP client. An LDAP client represents a trusted server that that can be used to performdirectory queries and Message Networking system administration. For more information on MessageNetworking's LDAP interface, see LDAP overview.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the LDAP client that you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select LDAP Client.IP address: Type the IP address of the LDAP client machine, up to 15 characters (for example, 192.43.235.1).This field is optional because the system uses the domain name to recognize the sending machine.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.
126Subscriber Updates Type: Use this field to specify whether subscriber updates should be sent, as they occuron the Message Networking system, to the the remote LDAP server:! Select no if you do not want updates to be sent to the LDAP remote machine automatically.! Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking system tothe LDAP client remote machine.! Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the LDAP remote machine only for thenetwork address ranges defined in the LDAP Client's Directory View.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this LDAP client. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information from thisLDAP client. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user information from thisLDAP client. The default for this field is no.Updates Out?: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this LDAPclient. Select yes if Message Networking should send updated user information updates to this LDAP client.Select no if you do not want Message Networking to send user information updates to this LDAP client. Thedefault for this field is no.LDAP server: Type the name of the LDAP server to be used for directory updates.LDAP Password: Type the LDAP Password of the LDAP client that you are administering. If you do not havethis password, contact the administrator of the LDAP client. An LDAP Password is required for the localMessage Networking system and the LDAP client to secure the connection when performing queries andtransfers.Note: The LDAP Password for the local Message Networking system is entered on the General Parameterspage.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Add this Machine. If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have beensaved. Click OK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> ModularMessaging/MSS remote machineAdding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS remote machine to the MessageNetworking system.Note: The checklist for adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS Release 1 or Release 2 and later remotemachine provides a list of steps you must complete when adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS remotemachine to the Message Networking system.To add an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.
1273. Select <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine? and IP Address fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. In the IP Address field, you can optionally type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating.For information on valid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.6. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.7. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.8. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.9. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.10. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS Release 1 remote machineChecklist for adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS Release 1remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS Release 1 remotemachine to the Message Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they areperformed.Some of these tasks require you to access the Modular Messaging/MSS system. If you are unfamiliar with theModular Messaging, ask the Modular Messaging system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskGather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the Modular Messaging subscribers via the PBX. You can
128obtain the area code and local exchange from the switch administrator.You also need to obtain the extension range for the Modular Messagingsystem. You can obtain this range from the Modular Messaging systemadministratorFor example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit Modular Messagingextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theModular Messaging system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the password in the LDAP Password field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.On the Modular Messaging system:Administer the Messaging Networking system as a remote machine onthe Modular Messaging system:1. After logging into the Modular Messaging MSS, from the<strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Global <strong>Administration</strong> > Messaging<strong>Administration</strong>.2. Log in at the SSH login.The Messaging <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.3. Record the local machine name that displays in the upper-leftcorner of the page.4. From the command prompt, type display machine and press Enter.The information for the local machine displays.5. Verify that the Machine Name matches the machine name yourecorded in Step 3.6. Record the following parameter settings:
129" Mailbox # Length" Address Ranges7. Press F7 to advance to the next page.Page 2 displays.8. Record the following parameter settings:" IP Address of the Modular Messaging MSS." Password9. Verify that the Updates In and Updates Out fields are set to y.10. From the command prompt, type add remote and press Enter.The Add Machine page displays.11. Complete the following fields on the Add Machine page:" In the Machine Name field, type the Local Machine Namethat you recorded from the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Machine Type field, select LDAP." In the Mailbox # Length field, type the the number of digitsin the Network Address Length field that you recorded fromthe General Parameters page on the Message Networkingsystem." In the Community ID field, assign the appropriate ID ifdifferent than the default of 1." In the Prefix field, enter a prefix if one is required." For the Address Ranges, in the Start Num. field, type allzeros and in the End Num. field, type all 9s toaccommodate all combinations, unless you are using pointto-pointnetworking that might conflict with this range. If youare using point-to-point networking, enter the appropriateaddress ranges for the Messaging Networking system." Press F7 to advance to the next page.Page 2 displays." In the IP Address field, type the IP Address that yourecorded from the General Parameters page on theMessage Networking system." In the Password field, type the LDAP Password, type theLDAP password that you recorded from the GeneralParameters page on the Message Networking system." Set the Updates In and Updates Out fields to y.12. Press Enter to save the Messaging Networking as a remotemachine on the Modular Messaging system.13. Click Return to Main.14. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Global <strong>Administration</strong> >Subscriber Management. The Subscriber Management pagedisplays.15. Verify that the Message Networking system appears underRemote Subscribers. The subscriber count will be 0 because youhave not yet added the Message Networking subscribers to theModular Messaging system.On the Message Networking system:
130Administer the remote machine parameters for the new <strong>Avaya</strong> ModularMessaging remote machine.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Add the Modular Messaging system subscribers to the MessageNetworking system by performing a Demand Remote Update.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the Modular Messaging remote machine has been added tothe Message Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test for SMTP and LDAP. Verifythat the connection was successful.On the Message Networking system:If the Message Networking system has more than 250,000 subscribers,administer a Directory View for the Modular Messaging system to includeno more than 250,000 subscribers. Modular Messaging will not acceptmore than 250,000 subscribers (with or without voice name) during anupdate.On the Modular Messaging system:Add the Messaging Networking subscribers to the Modular Messagingsystem:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Global <strong>Administration</strong> >Messaging <strong>Administration</strong>.2. From the command prompt, type get remote and press Enter.The Messaging Networking subscribers are added to the ModularMessaging system.3. To verify that the Messaging Networking subscribers are beingtransferred, view the Subscriber Management page and verify thatthe Total Subscribers for the Message Networking remotemachine reflects that subscriber transfer is in progress or iscomplete. If all subscribers are not received, you must determinethe cause of the failure.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new Modular Messaging machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system through theMessage Networking, using the network address of the ModularMessaging test mailbox that you obtained from the Modular Messagingsystem administrator. Then log into the test mailbox on the ModularMessaging system and verify that the test message was delivered.Top of page
131Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular MessagingAdd or modify a remote machine: <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSSUse the Add New Machine: <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging page to add a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSSremote machine to the Message Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging to add an <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging/MSS system.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 15 characters (for example, 192.43.235.1). This field isoptional because the system uses the domain name to recognize the sending machine.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.
132Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Subscriber Updates Type: Select Full for most Modular Messaging systems. When you select Full as theupdate type, a directory view containing updates for all remote machines is provided. Verify that the remotemachine has enough space for information on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to theMessage Networking system.Modular Messaging systems do not accept more than 250,000 subscribers (with or without voice names) duringan update. Therefore, if the Message Networking system has more than 250,000 subscribers, set theSubscriber Update Type to directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View. You must then administer aDirectory View for the Modular Messaging system to include no more than 250,000 subscribers.Note: If the Block MM to MM Updates field on the General Parameters page is set to yes, the system blockssubscriber updates between Modular Messaging remote machines through the Message Networking system,even though the Subscriber Updates Type field is set to Full.Default Community ID: Specifies the community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine.Type an integer from 1 through 15.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Use DNS?: Indicates whether DNS option is being used. Select yes to use DNS. Select no to not use DNS. It isstrongly recommended that you use DNS. The default for this field is no.If you select yes:! You must administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The primary DNS IP address specified on the General Parameters page is used to resolve the IP addressfor the remote machine.If you retain the default of no:! Do not administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The outgoing MTA for this remote machine must be an IP address, unless you edit the /etc/hosts file toadminister host names. If you do not specify an outgoing MTA, then the incoming domain name must bean IP address.Port: Type the number of the port being used by the machine you are adding. The default for this field is 25, the
133standard SMTP port number, which will be used by most systems. If you want to use another port number,specify a number from 1000 to 65000. Some of the numbers within the range might be unusable.Domain Name: Type the domain name of the email address that corresponds to this machine. This field can bea fully qualified domain name (such as system.location.company.com) or just a domain (such as company.com).Every email address with a domain that matches the one you define in this field is considered a subscriber ofthis machine. The domain name you enter in this field must match the entry in the LDAP Server field on thispage.Outgoing MTA: Type the IP address or domain name of the mail transfer agent, the software component thatexchanges mail with other systems. If you specify an outgoing MTA, every message whose destination is asubscriber of this SMTP/MIME machine is routed through this MTA. This field is optional.Preferred Encoding Type: Select the encoding type in which voice messages are transcoded when comingfrom a non-SMTP end node. Select GSM 6.10, GSM 7.11 u-law, or GSM 7.11 A-law.Updates In: Specify whether incoming LDAP updates are allowed for this remote machine. Select Yes to allowincoming updates or No to prevent incoming LDAP updates.Updates Out: Specify whether outgoing LDAP updates are allowed for this remote machine. Select Yes toallow outgoing updates or No to prevent outgoing LDAP updates.LDAP server: Type the name of the LDAP server to be used for directory updates. If you are using the ModularMessaging server as the LDAP server, which is the most common configuration, the name you enter in this fieldmust match the entry in the Domain Name field on this page. It is possible for systems to configure a separateLDAP server. In this case, you must specify the name of the server being used for LDAP.LDAP Password: Type the LDAP Password of the remote Modular Messaging machine that you areadministering. If you do not have this password, contact the administrator of the remote Modular Messagingsystem. An LDAP Password is required for the local Message Networking system and the Modular Messagingremote machine to secure the connection when performing LDAP queries.Note: The LDAP Password for the local Message Networking system is entered on the General Parameterspage.LDAP Port: Type the number of the port on the remote machine to which Message Networking connects forLDAP updates.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OKTop of page
134Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> MessageNetworking remote machineAdding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine to the MessageNetworking system.Note: The checklist for adding an <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine provides a list of steps you mustcomplete when adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine to the Message Networking system.To add an <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration pageto view more information.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking from the Machine Type menu.The IP Address field appears on the page.4. In the IP Address field, you can optionally type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating.For information on valid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.5. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.6. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.7. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.8. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.9. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of page
135Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machineChecklist for adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remotemachineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine to theMessage Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.CompletedTaskOn the remote Message Networking system:Gather the information about the Message Networking system that youwill need when administering the Message Networking system on theModular Messaging system:On the General Parameters page:! Record the Local Machine Name.! Record the IP address from the Local Machine IP Address field.! Record the password in the LDAP Password field.! Record the number of digits in the Network Address Length field.If this is a new Message Networking system and the fields on the GeneralParameters page are not yet completed, you must administer the GeneralParameters page before continuing.On the local Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the <strong>Avaya</strong> MessageNetworking remote machine that you are adding. Be sure to enter theexact name, domain name, and IP address of the Message Networkingsystem.Add each Message Networking system in the network as a remotemachine on every other Message Networking system in the network.On the local Message Networking system:Verify that the Message Networking remote machine has been added tothe Message Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.Note: Any other Message Networking or Interchange systems must beexcluded from the total count. Only remote machines connected directlyto this Message Networking system are sent to other MessageNetworking or Interchange systems.On the local Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test for SMTP and LDAP.On the local Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new Message Networking system's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.
136Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: <strong>Avaya</strong> Message NetworkingAdd or modify a remote machine: <strong>Avaya</strong> Message NetworkingUse the Add New Machine: SMTP–Message Networking page to add a new <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remotemachine to the Message Networking system or to modify an existing machine.This page contains the following fields.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote MachinesList on all Message Networking systems in your network.Machine Type: Select <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking.IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 15 characters (for example, 192.43.235.1). This field isoptional because the system uses the domain name to recognize the sending machine.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.
137Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Subscriber Updates Type: Select the type of remote subscriber updates to be sent to this remote machine:! directory-view: Select directory-view to specify that updates should be sent to the remote machine onlyfor the network address ranges defined in the remote machine's Directory View.! dynamic: Select dynamic to specify that the remote machine should receive updates for subscribersthat exchange messages with this remote machine.! full: Select full if you want full updates sent for all remote machines on the Message Networking systemto this remote machine. If you select full, verify that the remote machine has enough space forinformation on all subscribers from all remote machines connected to the Message Networking system.The default for this field is dynamic. To receive no updates, select directory-view, make sure no views aredefined for this remote machine, and then set the Updates: Out? field to n.Default Community ID: Specifies the community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine.Type an integer from 1 through 15.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Use DNS?: Indicates whether DNS option is being used. Select yes to use DNS. Select no to not use DNS. It isstrongly recommended that you use DNS. The default for this field is no.If you select yes:! You must administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The primary DNS IP address specified on the General Parameters page is used to resolve the IP addressfor the remote machine.If you retain the default of no:! Do not administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The outgoing MTA for this remote machine must be an IP address, unless you edit the /etc/hosts file toadminister host names. If you do not specify an outgoing MTA, then the incoming domain name must bean IP address.Port: Type the number of the port being used by the machine you are adding. The default for this field is 25, thestandard SMTP port number, which will be used by most systems. If you want to use another port number,specify a number from 1000 to 65000. Some of the numbers within the range might be unusable.Domain Name: Type the domain name of the email address that corresponds to this machine. This field can bea fully qualified domain name (such as system.location.company.com) or just a domain (such as company.com).Every email address with a domain that matches the one you define in this field is considered a subscriber ofthis machine. The domain name you enter in this field must match the entry in the LDAP Server field on this
138page.It is strongly recommended that you enter all domain names in lower-case letters to ensure that all domainnames across the network are in the same case.Outgoing MTA: Type the IP address or the machine name and domain name of the remote MessageNetworking machine. Every message whose destination is a subscriber of this SMTP/MIME machine is routedthrough this MTA. This field is required for Message Networking remote machines.Preferred Encoding Type: Select the encoding type in which voice messages are transcoded when comingfrom a non-SMTP end node. Select GSM 6.10, GSM 7.11 u-law, or GSM 7.11 A-law.Updates In: Specify whether the Message Networking system can receive updated user database informationfrom this remote machine. Select yes if this Message Networking system accepts updated user information fromthis remote machine. Select no if this Message Networking system does not accept updated user informationfrom this remote machine. The default for this field is no.Updates Out: Specify whether Message Networking is able to send user information updates to this remotemachine. Select yes if this Message Networking system sends user information updates to remote machines.Select no if this Message Networking system does not send user information updates to remote machines. Thedefault for this field is no.LDAP server: Type the name of the LDAP server to be used for directory updates. The name you enter in thisfield must match the entry in the Domain Name field on this page.LDAP Password: Type the LDAP Password of the remote Message Networking machine. An LDAP Passwordis required for both the local Message Networking system and the remote machine to secure the connectionwhen performing LDAP queries. If you do not have the LDAP password of the remote Message Networkingsystem, contact the administrator of the remote system.Note: The LDAP Password for the local Message Networking system is entered on the General Parameterspage.LDAP Port: Type the number of the port on the remote machine to which Message Networking connects forLDAP updates.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OKTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Adding remote machines > Adding an SMTP/MIME-Otherremote machineAdding an SMTP/MIME-Other remote machineThis topic provides information on adding an SMTP/MIME-Other remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem. Use this remote machine type to add non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machine to the MessageNetworking system.Notes:! The checklist for adding a non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machine provides a list of steps you mustcomplete when adding a new non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machine to the Message Networkingsystem.
139! It is recommended that you administer a default SMTP/MIME remote machine to handle SMTPmessages from remote machines not administered on Message Networking.To add an SMTP/MIME remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Add Remote Machine.The system displays the Add a New Machine page.2. Type a name for the new machine in the New Machine Name field, and then click Next Step. Forinformation on valid machine names, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.A Machine Type field appears on the page.3. Select Other SMTP/MIME from the Machine Type menu.The Bridged Machine? and IP Address fields appear on the page.Note: The Bridged Machine? field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the CustomerOptions page is set to 500 (the maximum).4. In the Bridged Machine? field, specify whether this remote machine is a bridged machine. For informationon bridged machines, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. In the IP Address field, you can optionally type the IP address of the remote machine you are creating.For information on valid IP addresses, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.6. Click Next Step.The remote machine parameter fields display on the page.7. Complete the remote machine parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.8. Click Next Step.The administration fields display on the page.9. Complete the administration fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.10. Click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add thisMachine if you do not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:" If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays." If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. ClickOK.Top of page
140Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Checklists for administering new remote machines >Checklist for adding a new non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machineChecklist for adding a new non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machineThe following table lists the procedures for adding a new non-<strong>Avaya</strong> SMTP/MIME remote machine to theMessage Networking system. The procedures appear in the sequence in which they are performed.Some of these tasks require you to access the SMTP/MIME system. If you are unfamiliar with the remotesystem, ask the remote SMTP/MIME system administrator to assist you.CompletedTaskGather the information that you will need when you later administer thedial plan mapping on the Message Networking system.Obtain the Network Address Length from the General Parameters pageon the Message Networking system. This number represents the specificnumber of digits, usually 7 or 10, required for messages to be sentthrough the Message Networking system. Generally, the network addressconsists of the dial plan mapping plus the extension. Usually, for your dialplan mapping, you will use the same area code and local exchange (DID)used to reach the SMTP/MIME subscribers via the PBX. You can obtainthe area code and local exchange from the switch administrator. You alsoneed to obtain the extension range for the SMTP/MIME system. You canobtain this range from the remote system administrator.For example, for a system requiring 10-digit dialing, mailboxes in therange 20000 to 29999 might normally be preceded by 555-12. If anoutside caller wants to leave a message for mailbox 20001, the callerneeds to dial 555-122-0001. This same number can be used to create thenetwork address. In this case, 55512 is the dial plan mapping on theMessage Networking system and 20001 is the 5-digit remote machineextension. This example assumes the network address requires 10-digitdialing.However, it is possible in a 7-digit or 10-digit dialing area that differentranges on the new system could be preceded by different dial planmapping. Therefore, although some mailboxes are preceded by 555-12,a different extension range 50000 to 59999 might be preceded by 555-34. In this case, an outside caller would dial 555-345-0002 to call mailbox50002. These numbers can also be used to create the networkaddresses. In this example, to create the network address on theMessage Networking system, you can add a Dial Plan mapping for thisremote machine where, for mailbox ranges 50000 to 59999, youadminister a Map To of 55534. This configuration adds 55534 to themailbox IDs in the specified range to create the 10-digit networkaddresses.On the SMTP/MIME system:Gather information about the SMTP/MIME system that you are adding:1. The IP address of the SMTP/MIME system (optional).2. The number of digits in mailbox IDs on the SMTP/MIME system.3. The domain name of the email address that corresponds to thisSMTP/MIME machine.
1414. The IP address or domain name of the mail transfer agent, thesoftware component that exchanges mail with other systems(optional).5. Obtain a specific mailbox ID on the SMTP/MIME system that willreceive and send a test message through Message Networking.On the Message Networking system:Administer the remote machine parameters for the new non-<strong>Avaya</strong>SMTP/MIME remote machine.On the Message Networking system:If you are setting up this remote machine as the default SMTP/MIMEremote machine to handle SMTP messages from remote machines notadministered on Message Networking:! Enter a value in the SMTP/MIME Auto-Assign Mailbox ID field onthe General Parameters page.! Use the SMTP Security page to control incoming and outgoingSMTP/MIME messages, either by domain name or by networkaddress.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machine, using the DialPlan Mapping requirements you obtained.On the Message Networking system:Verify that the SMTP/MIME remote machine has been added to theMessage Networking system by viewing the Remote Machines List.On the Message Networking system:Use one of the following methods to administer subscribers on theMessage Networking system (in order of preference):! Use FTP to add subscribers.! Initiate Bulk Add from the Message Networking system.! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voiced names.! Send a message from the new subscriber.! Register through the <strong>Administration</strong> page.On the Message Networking system:Perform a remote machine connectivity test.On the SMTP/MIME system:Administer the Message Networking system as a network node on theSMTP/MIME system. Be sure to enter the exact name, domain name,and IP address of the Message Networking system.On the Message Networking system:Note: Most remote machines are administered for Dynamic updates andyou do not need to take any action.If you selected Full or Directory View as the Subscriber Updates Type for
142the remote machine, run a Demand Remote Push to the SMTP/MIMEsystem to add subscribers from other remote machines to theSMTP/MIME system.Note: Remember, if you select Full as the Subscriber Updates Type, theSMTP/MIME system must have the capacity to accommodate all of thesubscribers in the Message Networking network.On the Message Networking system:Administer the Directory View for any remote machine to which you wantto add the SMTP/MIME subscribers.On the Message Networking system:Update the other remote machines in the Message Networking networkfor the new SMTP/MIME machine's subscribers.Note: Most remote machines will be configured for Dynamic updates.Send a test message from another messaging system through theMessage Networking, using the network address of the SMTP/MIME testmailbox that you obtained from the SMTP/MIMEsystem administrator.Then log into the test mailbox on the SMTP/MIME system and verify thatthe test message was delivered.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Add or modify a remote machine: Other SMTP/MIMEAdd or modify a remote machine: Other SMTP/MIMEUse the Add New Machine: SMTP/MIME page to add a new SMTP/MIME-Other remote machine to theMessage Networking system or to modify an existing machine. Use this machine type for non-<strong>Avaya</strong>SMTP/MIME remote machines.Note: It is recommended that you administer a default SMTP/MIME remote machine to handle SMTP messagesfrom remote machines not administered on Message Networking. When you create the default SMTP/MIMEremote machine, leave the Domain Name and Outgoing MTA fields blank for that remote machine. There canbe only one default Internet remote machine on each Message Networking system.New Machine Name: Type a unique name for the remote machine you are adding. The machine name can beup to 23 alphanumeric characters:! Enter uppercase letters as uppercase.! Enter lowercase letters as lowercase.! Use a hyphen (-) or an underscore (_).! These names cannot start with a number.! There can be no blank spaces.Note: The name must be unique on both the local Message Networking network as well as any other MessageNetworking systems in the network. To ensure that you are using a unique name, check the Remote Machines
143List on all Message Networking systems in your network.This page contains the following fields.Machine Type: Select Other SMTP/MIME.Bridged Machine: Specify whether this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. Bridged machinesare used by Message Networking to pass messages between nonbridged remote machines. Select yes toindicate that this remote machine is to be used as a bridged machine. If this remote machine is not being usedas a bridged machine, select no. The number of remote machines that can be used as a bridge is specified bythe Number of Bridged Nodes field on the Customer Options page.Note: The Bridged Machine field does not appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Optionspage is set to 500 (the maximum).IP address: Type the IP address of the machine, up to 15 characters (for example, 192.43.235.1). This field isoptional because the system uses the domain name to recognize the sending machine.Mailbox ID Length: Type the number of digits in mailbox IDs on the remote machine, up to 10 digits.Note: To change the Mailbox ID Length after initial system administration, see Changing a remote machine'smailbox number length for the steps you must complete to successfully change this field.Default Language: Use this field to specify the default language on the remote machine. If more than onelanguage is installed on the system, select the language from the drop-down menu. The default for this field isen-US (US English).If you change the Default Language after initial remote machine administration, subscribers that yousubsequently add to the remote machine are assigned the new Default Language as their default Language ID.However, the Language IDs of existing subscribers on the remote machine do not change.Failed Msg. Notification Priority?: Indicates whether to mark failed message notifications with priority status.Select yes to mark failed message notifications with priority status. Select no if you do not want to mark failedmessage notifications with priority status. The default for this field is no.Msg ID?: Specify whether to include the original message ID in failed message notifications. Select yes toinclude the original message ID. Select no if you do not want to include the original message ID in failedmessage notifications. The default for this field is no.Send Message for EAW?: Specify whether the original message is sent back to a subscriber after thatsubscriber has sent a message from this machine to an Aria machine that has the Extended Absence Greeting(EAG) warning activated. This message return is in addition to the message indicating the actual EAG warningcondition. Select yes to return the original message. Select no if you do not want to return the original message.The default for this field is no.Default NameNet Type: Specify the default NameNet type, set up on the remote machine, that is used foraging purposes by the remote machine. Type p if directory entries are permanent. Type u if entries are usagebased,which indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic of a particularremote machine. The default for this field is u.Organization: Use this field to provide a description of the organization using Message Networking, up to 64characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Organization Unit: Use this field to provide a description of the organization unit using Message Networking, upto 64 characters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Node ID: Unique node ID for this remote machine. This field is display-only and cannot be modified.Comments: You can optionally type any comments about this remote machine, up to 68 alphanumericcharacters. This field is optional and for informational purposes only.Subscriber Updates Type: This field is always set to Dynamic for SMTP/MIME–Other remote machines.Default Community ID: Specifies the community identifier for all subscribers added to this remote machine.Type an integer from 1 through 15.Voiced Names for Dynamic?: If the Subscriber Updates Type is set to dynamic, specify whether to include thesubscriber's voiced name in the update. You cannot modify this field until a new remote machine issaved .Select yes to include the voiced name. Select no if you do not want to include the voiced name. Thedefault for this field is yes.
144Dynamic Sub Expiration Days: Type the number of days a dynamically-added subscriber can exist withoutperforming any activity (without sending or receiving messages). This number must match the number of agingdays administered on the remote machine. The default for this field is 90. The minimum for this field is 1. Themaximum for this field is 999.Use DNS?: Indicates whether DNS option is being used. Select yes to use DNS. Select no to not use DNS. It isstrongly recommended that you use DNS. The default for this field is no.If you select yes:! You must administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The primary DNS IP address specified on the General Parameters page is used to resolve the IP addressfor the remote machine.If you retain the default of no:! Do not administer the DNS servers on the General Parameters page.! The outgoing MTA for this remote machine must be an IP address, unless you edit the /etc/hosts file toadminister host names. If you do not specify an outgoing MTA, then the incoming domain name must bean IP address.Port: Type the number of the port being used by the machine you are adding. The default for this field is 25, thestandard SMTP port number, which will be used by most systems. If you want to use another port number,specify a number from 1000 to 65000. Some of the numbers within the range might be unusable.Domain Name: Type the domain name of the email address that corresponds to this machine. This field can bea fully qualified domain name (such as system.location.company.com) or just a domain (such as company.com).Every email address with a domain that matches the one you define in this field is considered a subscriber ofthis machine.If you want this remote machine to be the default Internet remote machine used to handle SMTP messagesfrom remote machines not administered on Message Networking, leave this field blank. If you leave this fieldblank, any email address whose domain does not match any other domain name of any other SMTP machine isconsidered a subscriber of this default Internet machine.It is strongly recommended that you enter all domain names in lower-case letters to ensure that all domainnames across the network are in the same case.Outgoing MTA: Type the IP address or domain name of the mail transfer agent, the software component thatexchanges mail with other systems. If you specify an outgoing MTA, every message whose destination is asubscriber of this SMTP/MIME machine is routed through this MTA. This field is optional.Preferred Encoding Type: Select the encoding type in which voice messages are transcoded when comingfrom a non-SMTP end node. Select GSM 6.10, GSM 7.11 u-law, or GSM 7.11 A-law.If you are modifying an existing machine, click Save to save your changes. If you are adding a new machine,click Next Step to save the remote machine and administer Dial Plan Mapping, or click Add this Machine if youdo not want to administer Dial Plan Mapping at this time:! If you click Next Step, the Administer Dial Plan Mapping page displays.! If you click Add this Machine, a message displays that the parameters have been saved. Click OK.Top of page
145Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Modifying existing remote machinesModifying existing remote machinesThis topic provides information on modifying the settings of an existing remote machine.To modify the settings of an existing remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine Parameters.The system displays the Remote Machine Parameters page.2. Select the name of the remote machine that you want to modify from the Remote Machine Name menu.The remote machine parameters for the selected remote machine display.3. Modify the fields that you want to change for this remote machine. The fields on the page depend on thetype of remote machine that you are modifying:" AUDIX 4.0 or later remote machine" AMIS Analog remote machine" Aria Analog remote machine" Serenade Analog remote machine" Octel 100 remote machine" UM Analog remote machine" Aria Digital remote machine" Serenade Digital remote machine" VPIM remote machine" SMTP/MIME–Unified Messenger remote machine" <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging remote machine" <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machine" Other SMTP/MIME remote machineFor information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.4. Click Save.5. If you want to modify another remote machine, click Back until you return to the Remote MachineParameters page or, if you are done modifying remote machines, click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
146Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Renaming a remote machineRenaming a remote machineThis topic provides information on renaming a remote machine.Warning! It is strongly recommended that you do not rename a remote machine after subscribers from thatremote machine have been pulled into the Message Networking system. The only way to properly rename aremote machine after subscribers have been pulled into the system is to:! Delete the remote machine (which also deletes subscribers and all Dial Plan Mapping for that machine)! Add the remote machine back into the system with the new name! Perform updatesTo rename a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine Parameters.The system displays the Remote Machine Parameters page.2. Select the name of the remote machine that you want to modify from the Remote Machine Name menu.The remote machine parameters for the selected remote machine display.3. Click Rename this Node.The Rename a Machine page displays.4. In the New Node Name field, enter the new name for the remote machine.For information on completing this field, click the field name or Help on the Web-based administrationpage.5. Click Save.The Remote Machine Parameter page displays.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Deleting a remote machineDeleting a remote machineThis topic provides information on deleting a remote machine.Deleting a remote machine has the following effects on Message Networking:! All associated information about the remote machine is also deleted, such as:" Dial Plan Mapping" Directory views" Subscribers
147" Messages in queue! Message statuses that have been sent from the deleted remote machine with a return receipt or positivedelivery notification are not received.! Subscribers on INTUITY AUDIX Enhanced Lists (ELAs) or Personal Lists that exist on the deleted remotemachine are deleted from the Message Networking system.To ensure that the other Message Networking systems and remote machines in the Message Networkingnetwork know about the deleted subscribers, Demand Remote Updates and Demand Remote Pushes areexecuted to update the database.To delete a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine Parameters.The system displays the Remote Machine Parameters page.2. Select the name of the remote machine that you want to modify from the Remote Machine Name menu.The remote machine parameters for the selected remote machine display.3. Click Delete this Node.A message asks you to confirm the deletion.4. Click OK to delete the node.A message displays that the machine has been deleted.5. Click OK.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan MappingAdministering remote machine Dial Plan MappingDial Plan Mapping allows you to map existing mailbox addresses to unique network addresses. MessageNetworking uses a uniform, single-length dial plan for its network, from 3 to 10 digits. However, it is usuallyrecommended that Message Networking use a 7-digit or 10-digit dial plan. The remote machines that you add tothe Message Networking system will likely have a different dial plan that usually uses 4 or 5 digits. In mostcases, therefore, you will have to map the dial plan of the remote machine to the Message Networking networkaddress length. The required length of network addresses on the Message Networking system is specified bythe Network Address Length field on the System Parameters page.If subscribers on a remote system use their full 7-digit or 10-digit telephone numbers as their mailbox IDs, andthe digit length matches the Message Networking network address length, you do not need to map the dial planfor that remote machine. For example, if the Message Networking dial plan calls for 10-digit addresses, and themailbox IDs on the remote machine always use 10 digits, you do not need to map new dial plans. As anotherexample, if the Message Networking dial plan uses the 5-digit uniform dial plan of a private network, and thenew systems' mailbox IDs also use the same 5-digit uniform dial plan within the same private network, then youdo not need to map the dial plans.Note: Because every Message Networking address must be unique, there might be circumstances in which thenew system's mailbox ID length matches the Message Networking dial plan, but because the new system is notpart of the same switch private network, the mailbox IDs might not be unique within the Message Networkingnetwork. This situation is common, which is why it is normally recommended to use a 10-digit MessageNetworking dial plan and dial plan mapping.
148Dial Plan Mapping involves the following tasks:! Adding new Dial Plan Mapping! Changing existing Dial Plan Mapping! Deleting a Dial Plan Mapping! Adding a new Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan! Adding all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entries! Changing a Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan! Deleting Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan! Deleting all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entriesDial Plan Mapping samples are provided to aid you in administering Dial Plan Mapping for remote machines.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Addingnew Dial Plan MappingAdding new Dial Plan MappingThis topic provides information on adding new Dial Plan Mapping for a remote machine. Dial Plan Mappingallows you to map existing mailbox addresses to unique network addresses.To add new Dial Plan Mapping for a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Dial Plan Mapping.The system displays the Dial Plan Mapping page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want to administer Dial Plan Mapping from the Remote MachineName menu.The current Dial Plan Mapping settings for the selected remote machine display.3. Specify the Dial Plan Mapping for the selected remote machine:" In the Mailbox ID Number Range fields, enter the the range of mailbox IDs that you want toreplace with the digits specified in the Network Address Dial Plan Mapping. You can enter up toten mailbox ID ranges." In the Network Address Dial Plan Mapping fields, specify the digits that replace the matching digitsin the mailbox IDs. You can specify a maximum of 50 Dial Plan Mappings on the page at a time.After you click Save, 50 additional blank fields display, allowing you to enter another 50 mappings.You can specify a total of 2,000 Dial Plan Mappings.4. Click Save to save the Dial Plan Mapping.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageHome | Search
149Message Networking HelpPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > ChangingDial Plan MappingChanging Dial Plan MappingThis topic provides information on changing the Dial Plan Mapping for a remote machine.Warning! You cannot change existing Dial Plan Mapping after initial system administration. When subscribersare added to Message Networking, they are associated with the Dial Plan Mapping for their remote machine.When you change a Dial Plan Mapping, subscribers continue to be associated with the mapping as it existedwhen they were initially added to Message Networking, regardless of any changes you make. The only way toproperly change an existing Dial Plan Mapping after subscribers have been pulled into the system is to:! Delete the remote machine (which also deletes subscribers and all Dial Plan Mapping for that machine).! Add the remote machine back into the system.! Set up a new dial plan map.! Perform updates.The only scenario in which you can safely change a dial plan map is while you are initially administering a newMessage Networking system, before subscribers from that remote machine have been pulled into the MessageNetworking system.To change an extension range of a dial plan map:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Dial Plan Mapping.The system displays the Dial Plan Mapping page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want to change the Dial Plan Mapping from the RemoteMachine Name menu.The current Dial Plan Mapping settings for the selected remote machine display.3. Modify the Dial Plan Mapping for the selected remote machine.4. Click Save to save the Dial Plan Mapping changes.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > DeletingDial Plan MappingDeleting Dial Plan MappingThis topic provides information on deleting Dial Plan Mapping from a remote machine.Warning! You cannot delete Dial Plan Mapping after initial system administration. When subscribers are addedto Message Networking, they are associated with the Dial Plan Mapping set up for their remote machine. Whenyou delete a Dial Plan Mapping, subscribers continue to be associated with the mapping as it existed when theywere initially added to Message Networking, regardless of the deletion. The only way to properly delete an
150existing Dial Plan Mapping after subscribers have been pulled into the system is to:! Delete the remote machine (which also deletes subscribers and all Dial Plan Mapping for that machine).! Add the remote machine back into the system.! Set up a new dial plan map.! Perform updates.The only scenario in which you can safely delete a dial plan map is while you are initially administering a newMessage Networking system, before subscribers from that remote machine have been pulled into the MessageNetworking system.To delete Dial Plan Mapping entries for a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Dial Plan Mapping.The system displays the Dial Plan Mapping page.2. From the Remote Machine Name menu, select the remote machine for which you want to delete a DialPlan Mapping entry.The current Dial Plan Mapping for the selected remote machine display.3. Modify the Dial Plan Mapping to delete the Mailbox ID ranges or Network Address Dial Plan Mappingentries that you want to remove for the selected remote machine.4. Click Save to save the Dial Plan Mapping changes.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Deletinga dial plan extension rangeDeleting a dial plan extension rangeThis topic provides information on deleting a dial plan extension range from a remote machine.Warning! You cannot delete dial plan extension ranges after initial system administration. When subscribers areadded to Message Networking, they are associated with the Dial Plan Mapping set up for their remote machine.When you delete a dial plan extension range, subscribers continue to be associated with the mapping as itexisted when they were initially added to Message Networking, regardless of the deletion. The only way toproperly delete an existing dial plan extension range after subscribers have been pulled into the system is to:! Delete the remote machine (which also deletes subscribers and all Dial Plan Mapping for that machine).! Add the remote machine back into the system.! Set up a new dial plan map.! Perform updates.The only scenario in which you can safely delete a dial plan extension range is while you are initiallyadministering a new Message Networking system, before subscribers from that remote machine have beenpulled into the Message Networking system.To delete a dial plan extension range from a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Dial Plan Mapping.The system displays the Dial Plan Mapping page.
1512. Select the remote machine for which you want to delete a dial plan extension range from the RemoteMachine Name drop-down menu.The current Dial Plan Mapping settings for the selected remote machine display.3. Select the extension that you want to delete in the Mailbox ID table.4. Click Delete Extension Range.A message asks you to confirm that you want to delete the extension range.5. Click OK.The selected extension is deleted.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Adding anew Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanAdding a new Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanIn some cases, the network address length of a Serenade remote machine is longer than the MessageNetworking network address length. In these cases, when Message Networking is sending a message to aSerenade user, Message Networking must add a prefix to the Serenade user's Message Networking networkaddress to build a complete address that matches the user's network address on the Serenade remote system.You can create a Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan to specify any prefixes that need to be added to buildcomplete Serenade user network addresses. This topic provides information about adding a Serenade DigitalSender Dial Plan.To add a new Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.The system displays the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.2. Select the Serenade remote machine for which you want to add a Dial Plan from the Remote MachineName drop-down menu.Any existing Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plans for the selected remote machine display.3. Click Add A New Sender Dial Plan.The system displays the Add New Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.4. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.Note: The maximum number of entries allowed in the table for each node is 20.5. Click Add.The status line displays a message that the Dial Plan has been successfully added.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
152Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Add New/Change Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanAdd New/Change Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanIn some rare cases, the Message Networking numbering plan created on the Serenade system includes extradigits, which are used by the Serenade system to identify the Message Networking system. However, theSerenade system strips the numbers off when it sends messages. In these cases, you need to create aSerenade Digital Sender Dial Plan to identify those extra digits used by the Serenade system. MessageNetworking adds the digits in the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan to the addresses of subscribers who sendmessages to the Serenade. This allows the Serenade system to identify that the message came throughMessage Networking and permit proper message confirmations and returns.Use this page to add a new Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan or change an existing Serenade Digital SenderDial Plan.This page contains the following fields.Machine Name: Displays the name of the remote machine for which you are adding a new Serenade DigitalSender Dial Plan from the drop-down menu.Sender's Network Address Digits: Type the network address of the sender, up to 15 digits. You can enter apartial address or the full address:! If the digit or digits that Message Networking must insert to create a sender address recognized by theSerenade system are identical for all addresses and nodes in the Message Networking network, leavethis field blank.! If the digits that Message Networking must insert to create a sender address recognized by the Serenadesystem are not identical for all addresses and nodes in the Message Networking network, type the initialdigits of the addresses on a remote system in the network. Type enough digits so that the address isunique to the remote system but will include many or all subscribers on that system.Insert: Type the digits that identify Message Networking to the Serenade system. These are the digits thatMessage Networking inserts in front of sender addresses for messages to the Serenade system, when thosesender addresses begin with the entry in the Sender's Network Address Digits field. Enter an integer of up to 8digits.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Add: Click this button to add the new Serenade Digital Dial Plan.! Cancel: Click this button to return to the previous page without adding the new Serenade Digital DialPlan.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
153Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Adding allSerenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entriesAdding all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entriesThis topic provides information about adding all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entries. When you add allSerenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entries, Message Networking adds the prefix you specify to all sendernetwork addresses for messages going to Serenade users.To add all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.The system displays the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.2. Select the Serenade remote machine for which you want to add all dial plan entries from the RemoteMachine Name drop-down menu.Any existing Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plans for the selected remote machine display.3. Click Add All Sender Dial Plan Entries.A message asks you to confirm that you want to add all dial plan entries.4. Click OK.The system displays the Add All Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan Entries page.5. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.6. Click Add.The status line displays a message that all dial plan entries have been successfully added.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Changinga Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanChanging a Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanThis topic provides information about changing a Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.To change a Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.The system displays the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.2. Select the Serenade remote machine for which you want to change a dial plan from the Remote MachineName drop-down menu.Any existing Serenade Digital sender dial plan entries for the selected remote machine display.3. Select the dial plan that you want to change, and then click Change A Sender Dial Plan.
154The system prompts you to confirm that you want to change the selected dial plan.4. Click OK.The system displays the Change Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.5. Modify the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.6. Click Change.The status line indicates that the dial plan has been successfully changed.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Deletinga Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanDeleting a Serenade Digital Sender Dial PlanThis topic provides information about deleting a Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.To deleting a Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.The system displays the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.2. Select the Serenade remote machine for which you want to delete a dial plan from the Remote MachineName drop-down menu.The existing Serenade Digital sender dial plans for the selected remote machine display.3. Select the dial plan that you want to delete, and then click Delete A Sender Dial Plan.The system prompts you to confirm that you want to delete the selected dial plan.4. Click OK.The status line indicates that the dial plan has been successfully deleted.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
155Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Deletingall Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entriesDeleting all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entriesThis topic provides information about deleting all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entries.To delete all Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan entries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan.The system displays the Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plan page.2. Select the Serenade remote machine for which you want to delete all dial plans from the RemoteMachine Name drop-down menu.Any existing Serenade Digital Sender Dial Plans for the selected remote machine display.3. Click Delete All Dial Plans Entries.The system prompts you to confirm that you want to delete all dial plan entries.4. Click OK.All dial plan entries are deleted.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Dial planmapping samplesDial plan mapping samplesThis topic provides sample Dial Plan Mapping to assist you in configuring dial plans for Message Networkingremote machines.Before administering Dial Plan Mapping for the remote machines on the Message Networking system, you mustobtain the extension ranges, area code, and prefixes for the remote machines. You should also identify anyextensions for which mailboxes do not exist (such as automated attendants) and any extensions within theranges that are used by another remote machine using the same prefix on the Message Networking network.Sample 1: Single unbroken range of mailbox IDsIn this sample, there is a single unbroken mailbox ID range, 2000 to 5999 that is added as an Mailbox ID rangefor this remote machine. To create the 10-digit mailbox IDs required, you must:! Leave the Map From field for this range blank since you want to add the same numbers to the beginningof every mailbox ID to create the network addresses.! In the Map To digits, enter the area code and local exchange 3-digit prefix for the remote machine. In thissample, an area code used is 303, and the 3-digit prefix used is 555. Therefore, 303555 is entered in the
156Map To field.The result of this sample mapping is that the Map To digits, 303555, are added to the beginning of the 4-digitmailbox ID to create 10-digit mailbox IDs ranging from 3035552000 to 3035555999.This same sample could be used to create a network address of any length. For example, if the MessageNetworking system requires 7-digit network addresses, the Map To entry would be three digits instead of the sixdigits shown in the sample.Sample 2: Broken ranges of mailbox IDs with a Map From of 0In this sample, the following broken mailbox ID ranges are each added as extension ranges for the Dial PlanMapping:! 2000 to 2999! 3000 to 3999! 5000 to 5499! 5800 to 5999The ranges 4000 to 4999 and 5500 to 5799 are omitted. Ranges should be omitted when:! The range contains auto-attendant mailboxes or other extensions for which mailboxes have not beenassigned.! Another messaging system, which uses the same prefix as this system, uses the mailbox ranges 4000 to4999 or 5500 to 5799.The following table lists the mailbox ID ranges and the corresponding Map From and Map To digits.Mailbox IDNetwork Address Dial Plan MappingStart End Map From Map To2000 2999 2 30355523000 3999 3 30355535000 5499 5 30355555800 5999In this sample, you can use a Map From entries of one digit, which should be the first digit in the mailboxranges. You do not need to create a separate mapping for each of the ranges that begin with 5, since a singledial plan mapping with a Map From of 5 will match both ID ranges.The result of this sample mapping is that the first number of each mailbox ID in the range is replaced by the MapTo digits that correspond to the matching Map From entry. For example, for the first extension range (2000 to2999), the first digit (2) matches the dial plan mapping with a Map From entry of 2. In this case, the digit in theMap From entry (2) is removed from the mailbox ID, and the Map To digits (3035552) are added to thebeginning of the mailbox IDs to create a range of 10-digit network addresses from 3035552000 to 3035552999.The Message Networking does not change the mailbox IDs not included in the extension ranges.Note that in the sample if the extensions 5500 to 5799 are not omitted from the Mailbox ID ranges and a rangeof 5000 to 5999 is entered, the Map From entry must be two digits to allow the exclusion of the extensions in the5500 to 5799 range. Because the number of digits in the Map From field must be the same for all entries for aremote machine, this scenario would require many more dial plan mappings to create the same results as thesample shown. An example of this scenario is shown in Sample 4.Sample 3: Ranges that require different prefixesIn this sample, the following broken mailbox ID ranges are each added as extension ranges for the Dial PlanMapping:! 2000 to 2999! 3000 to 3999
157! 5000 to 5999One of the mailbox ID ranges (5000 to 5999) requires a different Map To prefix.The following table lists the mailbox ID ranges and the corresponding Map From and Map To digits.Mailbox IDNetwork Address Dial Plan MappingStart End Map From Map To2000 2999 2 55523000 3999 3 55535000 5999 5 5515The result of this sample mapping is that the first number of each mailbox ID range is replaced by the Map Todigits for that range. For example, for the first extension range (2000 to 2999), the first digit (2) is removed andthe Map To digits (5552) are added to the beginning of the mailbox IDs to create a range of 7-digit networkaddresses from 5552000 to 5552999. For the third extension range (5000 to 5999), the first digit (5) is removedand the Map To digits (5515) are added to the beginning of the mailbox IDs to create a range of networkaddresses from 5515000 to 5515999.Sample 4: Ranges with different prefixes and shared Start digitsIn this sample, the system has two mailbox ID ranges with the same initial digit (5), but their DID prefixes aredifferent and must be differentiated in the dial plan. Also, because entries in the Map From field must be unique,you must use two Map From digits.The mailbox ID ranges for this sample are as follows:! 2000 to 2999! 3000 to 3999! 5000 to 5499! 5500 to 5999You must enter a separate mailbox ID range for each set of extensions that have the same two Start numbers.For example, you must break down the 2000 to 2999 mailbox ID range into separate ranges based on the firsttwo numbers in the ID (2000 to 2099, 2100 to 2199, and so on).The following table lists the mailbox ID ranges and the corresponding Map From and Map To digits.Mailbox IDNetwork address Dial Plan MappingStart End Map From Map To2000 2999 20 3035552021 3035552122 3035552223 3035552324 3035552425 3035552526 3035552627 3035552728 3035552829 303555293000 3999 30 3035553031 30355531
15832 3035553233 3035553334 3035553435 3035553536 3035553637 3035553738 3035553839 303555395000 5499 50 3035555051 3035555152 3035555253 3035555354 303555545500 5999 55 7205515556 7205515657 7205515758 7205515859 72055159The result of this sample mapping is that the first two numbers of each mailbox ID range is replaced by the MapTo digits for that range. For example, for the first extension range (2000 to 2099), the first two digits (20) areremoved, and the Map To digits (30355520) are added to the beginning of the mailbox IDs to create a range of10-digit network addresses from 3035552000 to 3035552999. For the fourth extension range (5500 to 5599),the first two digits (55) are removed, and the Map To digits (72055155) are added to the beginning of the rangesmailbox IDs to create a range of 10-digit network addresses from 7205515000 to 7205515999.Sample 5: Prefixes replaces initial mailbox digitsIn this sample, there are broken Mailbox ID ranges, and the two ranges have different Map To prefixes.Additionally, the mailbox IDs are part of a 5-digit Uniform Dial Plan across two switches so that the initial digitsof the mailbox IDs overlap the final digits of the telephone number prefixes. In this case, the dial plan map willreplace the initial digits of the mailbox ID ranges with a different digit.The mailbox ID ranges for this sample are as follows:! 20000 to 29999! 50000 to 59999The following table lists the mailbox ID ranges and the corresponding Map From and Map To digits.Mailbox IDNetwork address Dial Plan MappingStart End Map From Map To20000 29999 2 30355550000 59999 5 720551In this sample, the first digit in the mailbox ID is replaced by the local area code and prefix to create the 10-digitmailbox ID required on the Message Networking system. For example, a mailbox in the first range might be21333, but its external phone number would be 303-555-1333. So the Dial Plan Mapping is configured toreplace the first digit in the mailbox ID (2) with the local area code and prefix (303555).
159Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Administering numeric addressesAdministering numeric address mappingA numeric address is an alternate method that Modular Messaging system subscribers can use to addressmessages. The numeric addressing feature of Message Networking allows you to define numeric addresses forsubscribers on non-Modular Messaging remote machines. These numeric address can then be used by theModular Messaging subscribers in your network.Message Networking provides two ways for you to configure variable length addressing:! On a remote machine basis, by administering numeric address mapping. The mapping is then used togenerate numeric addresses for those subscribers based on either their mailbox number or their networkaddress. The numeric address mapping functions similarly to the Message Networking dial plan mappingfeature.! On an individual subscriber basis, by modifying the Numeric Address field on the Subscriber Parameters<strong>Administration</strong> page.Note: Numeric addresses for subscribers on Modular Messaging and other Message Networking remotemachines are provided to the local Message Networking system through LDAP updates. You can use theSubscriber Parameters page to modify the numeric address for Modular Messaging and Message Networkingremote machine subscribers on an individual basis.The following topics are related to numeric address mapping:! Overview of numeric address mapping! Adding a new numeric address mapping for a remote machine! Modifying a numeric address mapping for a remote machine! Deleting a numeric address mapping for a remote machine! Modifying the numeric address for a subscriber on the Subscriber Parameters pageNumeric address mapping samples are provided to aid you in administering numeric address mapping forremote machines.Top of page
160Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Administering numeric addresses > Numeric addressingoverviewNumeric addressing overviewVariable-length addressing allows Modular Messaging systems to address messages to subscribers on otherremote machines in the network using a number other than the network address. These alternate numbers arecalled numeric addresses.The typical method of addressing messages to remote subscribers is to use the network address, whichprovides a unique address to all subscribers. The network address is required to be a fixed length for allsubscribers in the Message Networking network, and it typically has a length of 10 digits. Numeric addresses donot have to be a fixed length for all subscribers and can range from 3 to 32 digits in length.Although <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging senders enter the numeric address, the email address of the recipients arestill the fixed length network address in the <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking domain. Message Networking does notaccept variable-length network address values from non-<strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging systems. It only supports afixed length of 3 to 10 digits as a recipient value from non-<strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging systems.The Numeric addressing feature of Message Networking functions similarly to the Message Networking dial planmapping feature and provides two ways for you to configure variable length addressing:! On an individual subscriber basis, by modifying the Numeric Address field on the Subscriber Parameters<strong>Administration</strong> page.! On a remote machine basis, by administering numeric address mapping. The mapping is then used togenerate numeric addresses for those subscribers based on either their mailbox number or their networkaddress. The numeric address mapping functions similarly to the Message Networking dial plan mappingfeature. However, unlike the dial plan mapping feature, no specific length is enforced for numericaddresses and you can specify multiple numeric address maps using different lengths.Note: Numeric addresses for subscribers on Modular Messaging and other Message Networking remotemachines are provided to the local Message Networking system through LDAP updates.When you administer numeric address mapping for a remote machine, the numeric address can be left blank orit can be calculated from either the mailbox ID or the network address. The address used to calculate thenumeric address is called the base address. You specify the modifications to be made to the base addressmuch the same as when you administer the system's dial plan mapping. You specify a From field, which is usedto match a portion of the base addresses. A base address matches when the From value is the same as thebeginning portion of the base address. When a match is made, the portion of the base address that wasmatched is stripped, and the To value you specify is added to the beginning of the stripped base address tocreate the numeric address.In Message Networking, there are a number of areas in which subscriber records are created or modified. Thefollowing table lists these areas and describes if and how numeric address mapping applies to each area:Message Networking featureBulk add from FTP fileBulk change from FTP fileBulk add by rangeAuto-add of senderDynamic update of sender duringmessagingSelf-registration/add subscriberApplication of numeric addressingApply the mapping (numeric addressescannot be specified in the FTP file).Leave the numeric address unchanged.Apply the mapping.Apply the mapping.Leave the numeric address unchanged.Apply the mapping.
161Self-registration/change subscriberFull update/add subscriberFull update/change subscriberDelta add/add subscriberDelta update/change subscriberSubscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>page/add subscriberSubscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>page/change subscriberNumeric Addressing <strong>Administration</strong>pageLeave the numeric address unchanged.Apply the mapping.Note: Do not take this action for subscriberadditions made via LDAP.Leave the numeric address unchanged.Note: This does not exclude an LDAPupdate changing the value.Apply the mapping.Note: Do not take this action for subscriberadditions made via LDAP.Leave the numeric address unchanged.Note: This does not exclude an LDAPupdate changing the value.If the numeric address is changed on thescreen, update the subscriber's address.If the numeric address is changed on thescreen, update the subscriber's address.Apply the mapping.Note the following considerations related to numeric addressing:! The numeric address cannot be sent to an Interchange system because the field does not exist inInterchange.! The numeric address should not be generated for any subscribers associated with another MessageNetworking server, including servers running Message Networking 1.0. However, numeric addressespresent for other subscribers from other remote machine should be sent to other Message Networkingservers, including those running Message Networking 1.0, as part of the standard subscriber updates.! The numeric address should not be generated for any subscribers associated with an ModularMessaging. However, numeric addresses present for subscribers from other remote machines should besent to Modular Messaging as part of the standard subscriber updates.! Failure messages generated by the <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking refer to the network address of therecipient instead of the numeric address. However, the voiced name of the recipient is identified in themessage, if available.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Addingnew numeric address mappingAdding new numeric address mappingThis topic provides information on adding new numeric address mapping for a remote machine. Numericaddress mapping allows you to map existing base addresses to unique numeric addresses. Sample numericaddress mappings are provided to help you configure numeric address mapping for remote machines.To add new numeric address mapping for a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine
162<strong>Administration</strong> > Numeric Address Mapping.The system displays the Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want to administer numeric address mapping from the RemoteMachine Name drop-down menu.The current numeric address mapping settings for the selected remote machine display.3. Click Add New Mapping.The Add New Numeric Address Mapping page displays.4. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.5. Click Add to save the new mapping.A dialog box displays a message that the new mapping was successfully added.6. Click OK.The Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the updated mapping for the remote machine.7. Click Apply Mapping to apply the new mapping and update the subscribers on this remote machine.Depending on the number of subscribers on the remote machine, the update can take several minutes.8. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Administering numeric addresses > Add/Change NumericAddress MappingAdd/Change Numeric Address MappingUse this page to add or change the numeric address mapping for a remote machine. A numeric address is analternate method of addressing messages from Modular Messaging systems to subscribers on remotemachines. You cannot add numeric address mapping for Modular Messaging or Message Networking remotemachines.Note: You can also administer numeric addresses for individual subscribers by modifying the Numeric Addressfield on the Subscriber Parameters <strong>Administration</strong> page.This page contains the following fields.Remote Machine Name: Select the name of the remote machine for which you want to add or change numericaddressing.Numeric Address Initialization Type: This display-only field indicates the base number used in the numericaddress mapping. The base address can be:! Null: Select this field to leave the numeric address empty. This is the default setting.! Mailbox ID: Select this option to use the subscribers' mailbox ID as the base address.! Network Address: Select this option to use the subscribers' network address as the base address.Map From: Use this field to specify the digit string, from 0 to 30 digits, that is compared against the subscribers'base addresses, which is specified in the Numeric Address Initialization Type field. A match occurs when thevalue in the Map From value is the same as the beginning portion of the base address. When a match occurs,the portion of the base address that matches the Map From digits is stripped, and the Map To field value isprepended to the base address to create the numeric address. Leave this field blank to add the Map To fromfield digits to every base address.The Map From field can be blank. When you leave the Map From field blank, it matches all base addresses and
163is used when there is no other entry in the Map From field that matches the base address. The Map Fromentries can be different lengths.Map To: Use this field to specify the digits string, from 0 to 30 digits, that is prepended to the base address afterthe digits that match the Map From field are stripped.The Map To field can be left blank or contain the keywords none or no action. You can leave the Map To fieldblank to indicate that nothing should be prepended to the base address after any digit stripping takes place. Anone in the Map To field indicates that the numeric address should set to a blank value. A no action in the MapTo field indicates that the current value of the numeric address should not be modified. The Map To entries canbe different lengths.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Add: Click this button to add the new mapping to the remote machine.! Cancel: Click this button to return to the Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page without saving thechanges.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > ChangingNumeric Address MappingChanging Numeric Address MappingThis topic provides information on changing the numeric address mapping for a remote machine.To change an existing numeric address map:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Numeric Address Mapping.The system displays the Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want to change the numeric address mapping from the RemoteMachine Name drop-down menu.The current numeric address mapping settings for the selected remote machine display.3. Select the numeric address map that you want to change in the table, and then click Change Mapping.4. A message asks you to confirm that you want to change the Numeric Address Mapping.5. Click OK.The Change Numeric Address Mapping page displays.6. Modify the fields on the page to change the mapping.7. Click Change.A dialog box displays a message that the new mapping was successfully added.8. Click OK.The Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the updated mapping for the remote machine.9. Click Apply Mapping to apply the modified mapping and update the subscribers on this remote machine.
164Depending on the number of subscribers whose numeric address changes, the update can take severalminutes.10. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine Dial Plan Mapping > Deletingnumeric address mappingDeleting numeric address mappingThis topic provides information on deleting numeric address mapping from a remote machine.To delete numeric address mapping from a remote machine:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Numeric Address Mapping.The system displays the Numeric Address <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want to delete a numeric address map from the RemoteMachine Name drop-down menu.The current numeric address mapping for the selected remote machine display.3. Select the mapping that you want to delete in the table, and then click Delete Mapping.A message asks you to confirm that you want to delete the selected numeric address map.4. Click OK.The selected numeric address map is deleted.5. Click Apply Mapping to to update the subscribers on this remote machine.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>Use the Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong> page to manually add a subscriber or modify subscriberparameters for an existing subscriber.This page contains the following fields.Mailbox ID: Type the mailbox extension for this subscriber, up to 10 digits.Remote Machine: Select the name of the remote machine on which this subscriber resides.Type: A display-only field that indicates the type of remote machine.
165Network Address: A display-only field that indicates the network address of the subscriber.Name: Type a unique name for this network address and mailbox ID, up to 29 alphabetic characters. The nameshould be unique on the Message Networking system.Community ID: Select the subscriber's Community ID to be used for sending restrictions. AUDIX systems usethis ID for permissions checking. Octel Analog Networking, AMIS Analog, Aria Digital, Serenade Digital, andVPIM v2 subscribers have a default community ID of 1 that can be changed at the subscriber level. The settingfor this field can be from 1 to 15. The default for this field is 1.NameNet Type: Select the NameNet type used by the Octel Analog Networking and Aria Digital protocols foraging purposes:! P: Indicates that directory entries are permanent.! U (usage-based): Indicates that directory entries are temporarily available based on the network traffic ofa particular remote machine. The default for AUDIX, AMIS Analog, Octel Analog Networking, Aria Digital,Serenade Digital, and VPIM v2 machines is U.Voiced Name: A display-only field that indicates whether this subscriber has a recorded voiced name. Whenthe system is full, subscriber names are added to the database, but voiced names are not.Last Updated: A display-only field that indicates the date and time at which this subscriber was added.Last Usage Date: A display-only field that indicates the date and time at which this subscriber last used thismailbox.User ID: On the Message Networking system, this is the equivalent of an email user ID and can be customizedfor non-SMTP subscribers. This provides an email ID for voice messaging subscribers and can be used toreceive electronic mail (if the Message Networking system is properly configured) from the Internet and otherSMTP/MIME electronic mail sources. This field defaults to the network address for all subscriber types, exceptfor SMTP/MIME. For SMTP/MIME, this field defaults to the portion of an email address before the @ (forexample, for a user with an email address of jsmith@company.com, jsmith is the default user ID). It is importantthat you change the user IDs of SMTP subscribers to the subscribers' actual user IDs on the remote machine sothat messages can be sent to and received by the subscribers.Domain Name: This field contains the domain name, which, in an email address, is the part of the address thatfollows the @ sign, as in userid@domain. For non-SMTP/MIME subscribers, this value is the same as themachine name of the Message Networking system. The domain name, combined with the subscriber's user ID,creates an email address for voice messaging subscribers. For example, if an INTUITY subscriber has a user IDof voicemessageuser1 on a Message Networking system called my.company.com, the email address for thatsubscriber would be voicemessageuser1@my.company.com. This field can be a fully qualified domain name(such as system.location.company.com), or just a domain (such as company.com).Voicemail Domain ID: A display-only field that indicates the subscriber's voice mail domain ID for <strong>Avaya</strong> MMremote machine subscribers.UTF8 Name: A display-only field that indicates the subscriber's multibyte character name for <strong>Avaya</strong> MM remotemachine subscribers.Numeric Address: You can optionally use this field to specify a numeric address for the subscriber. A numericaddress is an alternate method for Modular Messaging systems to address messages to subscribers on otherremote systems. This field is blank by default. You can also administer numeric addresses on a remote machinebasis. For more information, see Administering numeric address mapping.Distinguished Name: A display-only field that indicates the unique LDAP entry name for <strong>Avaya</strong> MM remotemachine subscribers. For example:umObjectGUID=a1705ef8f72611d69ef8000347a1d791,ou=People,dc=<strong>Avaya</strong>Subscriber GUID: A display-only field that indicates the unique 128-bit value that identifies the subscriber in thevoice mail domain to which the subscriber is assigned. For example:a1705ef8f72611d69ef8000347a1d791Language ID: Select the preferred language for the subscriber from the drop-down list. The preferred languageis the language in which Message Networking voices prompts for this subscriber. The default for this field isdetermined by the Language ID field of the remote machine associated with the subscriber.
166Host VMS Name: A display-only field that indicates the subscriber's home messaging server for <strong>Avaya</strong> MMremote machine subscribers.Telephone Number: Use this field to specify a Telephone Number, up to 30 digits in length, for the subscriber.Telephone Numbers are used by Modular Messaging systems to identify callers as subscribers within themessaging network. By default, this field displays the result of the Telephone Number <strong>Administration</strong>administered for the remote machine on which this subscriber resides. If you do not administer TelephoneNumber Mapping for the remote machine, this field is blank. If you modify the Telephone Number Mapping ofthe remote machine on which this subscriber resides and apply the mapping, any modifications you made to thisfield are overwritten.Note: This field was named Primary Extension Number in previous releases of Message Networking.Subscriber Permission: Select the Enterprise List permission ID you want to assign to this subscriber. Thepermission IDs listed are those that you administered on the Enterprise Lists System Parameters page. You canalso assign a permission ID to an individual subscriber or a range of subscribers on the Enterprise SubscriberPermissions page.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Add: Click this button to add the subscriber.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Administering numeric addresses > Numeric addressmapping samplesNumeric address mapping samplesThis topic provides sample numeric address mapping to assist you in configuring numeric addressing forMessage Networking remote machines.Sample 1The following sample illustrates a simple numeric address mapping and the resulting numeric address mapping.The following table lists the Map from and Map to numbers entered in the Add/Change Numeric AddressMapping page.Map from7 92847555 12Map toThe following table lists the numeric addresses that result from the mapping in the previous table.Base Address74555 928474555Numeric Address
16755592184 1292184The resulting numeric addresses are calculated as follows:! The first base address (74555) is a match for the first Map From number (7). Therefore, the 7 is strippedfrom the front of the base address and the digits in the Map To column (92847) are added to thebeginning of the base address to form the numeric address 928474555.! The second base address (55592184) is a match for the second Map From number (555). Therefore, the555 is stripped from the front of the base address and the digits in the Map To column (12) are are addedto the beginning of the base address to form the numeric address 1292184.Sample 2The following sample illustrates a numeric address mapping where a base address matches more than one MapFrom entry. This situation occurs when one record contains a Map From value that matches the beginning of theMap From value in another record. Records that can match the same base address are called overlappingrecords. When there are overlapping records, the record that matches the greatest number of digits in the baseaddress is the matching record. Overlapping records can be used to simplify the numeric address mapping.The following two tables illustrate two different numeric address mappings that you could define for the same setof base addresses, ranging from 73410 to 73449. The first table provides a sample numeric address mappingthat does not include overlapping entries. The second table does use overlapping entries. As you can see fromthe tables, the second numeric address mapping that uses overlapping entries is simpler.The following table lists the Map From and Map To entries entered when no overlapping entries are used.Map From7341 8737342 873427343 873437344 87344Map ToThe following table lists Map From and Map To entries that do overlap. The intent of this mapping is to add an 8to the beginning of all addresses except those starting with 7341. For addresses starting with 7342, the intent isto add an 8 and strip the 41.Map From7341 87373 873Map ToUsing these mapping entries, any mailbox ID matching 7341 will use the first entry, because 7341 is longer than73. All other records will use the 73 record.Sample 3The following sample defines a numeric address mapping that sets all numeric addresses to a blank valueexcept those base addresses starting with 74 or 741.Map From(blank)none74 97461741 97411Map ToIn this sample, any base address other than those starting with 74 or 741 match the first entry and will thereforebe set to a blank value, meaning that no numeric address will exist for those base addresses.
168Sample 4The following sample defines a numeric address mapping that strips the 9 from base addresses beginning witha 9. For all other base addresses, the address is copied to the numeric address.Map From(blank)(blank)9 (blank)Map ToThe following table lists the numeric addresses that result from the mapping in the previous table.Base Address9254363 25436355592184 55592184831765432 831765432Numeric AddressIn this sample, the first base address starts with a 9, which matches the second mapping entry. Therefore, the 9is stripped and the resulting numeric address is 254363. The other base addresses match the first mappingentry, which is blank. Therefore, the base address is copied to the numeric address.Sample 5The following sample defines a numeric address mapping that includes a no change value in the Map To field.When no change is entered as the Map To value, it indicates that the current mapping should not be changedby any subsequent mapping. This setting is useful if you modify any numeric addresses manually using theNumeric Address field on the Subscriber Parameters <strong>Administration</strong> page. and do not want any future mappingchanges to affect the numeric address you manually modified.Map From3534123 no change831765432 no changeMap ToIn this sample, any base addresses matching 3534123 or 831765432 will not be changed if other matchingmappings are subsequently applied, unless the subsequent mappings more closely match the base addresses.Top of page
169Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine directory viewsAdministering remote machine directory viewsThe Directory View page allows you to define, for a particular machine, the other remote machines that canprovide updates to that machine. You can specify a range of mailbox IDs from which to accept updateinformation.Administer directory views:! For any remote machines using directory-view as the subscriber updates type.! For remote machines using dynamic as the subscriber update type, if you want to receive updates fromspecific remote machines.Administering directory views includes the following tasks:! Adding a directory view entry! Adding all directory view entries! Changing a directory view entry! Deleting a directory view entry! Deleting all directory view entriesTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines> Administering remote machine directory views > Adding adirectory view entryAdding a directory view entryThis procedure provides information on adding a directory view entry to a remote machine administered on theMessage Networking system. You can also add all directory view entries to a remote machine.Important! There are considerations for configuring directory views for <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging systems thatyou should be aware of before administering the Modular Messaging systems on your network.To add a directory view entry:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Directory Views.The system displays the Directory Views page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want add a directory view from the Machine Name drop-downmenu.The table below the menu displays the current directory views for the selected remote machine.3. Click Add New Directory View.The Add New Directory View page displays.
1704. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.5. Click Save.The new directory view is added to the remote machine.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering remote machine directory views > Add orChange a Directory ViewAdd or Change a Directory ViewUse this page to add a directory view or change an existing directory view for a remote machine. Directory viewsidentify the remote machines for which the selected remote machine can get network updates. You must set upa directory view for a remote machine if you selected directory-view as the Subscriber Updates Type on theRemote Machine Parameters page. You can also add a directory view for a remote machine if you selecteddynamic as the Subscriber Updates Type on the Remote Machine Parameters pageNote: Typically, you do not need to administer directory views for remote machines using full as the subscriberupdates type, except for Modular Messaging systems with more than 250,000 subscribers.This page contains the following fields.Machine Name: This display-only field identifies the remote machine for which you are adding a directory view.Remote Machine Name: Use the drop-down menu to select the remote machines from which you want toreceive updated subscriber information. The selected remote machines are added to the directory view of theremote machine specified in the Machine Name field.Start Network Address: Type the first network address in the range that you want to include in remotesubscriber updates. You can enter from 3 to 23 digits. The addresses you enter must match the addresses asdefined in the system's Dial Plan Mapping. You can specify multiple address ranges for a single directory view.End Network Address: Type the last network address in the range that you want to include in remotesubscriber updates. You can enter from 3 to 23 digits. The addresses you enter must match the addresses asdefined in the system's Dial Plan Mapping. You can specify multiple address ranges for a single directory view.Voiced Name?: Specify whether you want to include the subscribers' voiced names in the update. Select y orn.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Directory Views page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Save: Click this button to accept the page settings and add the new directory view.! Cancel: Click this button to return to the Directory View page.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
171Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines> Administering remote machine directory views > Adding alldirectory view entriesAdding all directory view entriesThis procedure provides information on adding all remote machines administered on Message Networking tothe directory view of a remote machine. You can also add an individual directory view entry to a remotemachine.If there are many systems in the Message Networking network and you want to add most of the remotemachines to the directory view, you can add all entries and then individually delete the remote machines thatyou do not want in the view.To add all directory view entries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Directory Views.The system displays the Directory Views page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want add the directory views from the Machine Name dropdownmenu.The table below the menu displays the current directory views for the selected remote machine.3. Click Add All Directory View Entries.A message asks you to confirm that you want to add all directory view entries.4. Click OK.All of the remote machines are added as new directory views. For each new directory view, a StartNetwork Address of 0000000000 is used and an End Network Address of 9999999999 is used.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines> Administering remote machine directory views > Changing adirectory view entryChanging a directory view entryThis topic provides information on changing a directory view entry currently defined for a remote machine.To change a directory view entry:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Directory Views.The system displays the Directory Views page.2. Select the remote machine that contains the directory view you want to change from the Machine Namedrop-down menu.The table below the menu displays the current directory views for the selected remote machine.
1723. Highlight the directory view you want to change by clicking the name in the table.4. Click Change Selected Directory View.A message asks you to confirm that you want to change the directory view.5. Click OK.The Change Directory View page displays.6. Modify the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.7. Click Save.The changes to the directory view are saved.8. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines> Administering remote machine directory views > Deleting adirectory view entryDeleting a directory view entryThis procedure provides information on deleting a directory view entry currently defined for a remote machine.You can also delete all directory view entries for a remote machine.To delete a directory view entry:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Directory Views.The system displays the Directory Views page.2. Select the remote machine from which you want delete a directory view from the Machine Name dropdownmenu.The table below the menu displays the current directory views for the selected remote machine.3. Highlight the directory view you want to delete by clicking the name in the table.4. Click Delete Selected Directory View.A message asks you to confirm that you want to delete the directory view.5. Click OK.The directory view is deleted for the remote machine.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
173Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines> Administering remote machine directory views > Deleting alldirectory view entriesDeleting all directory view entriesThis procedure provides information on deleting all of the directory view entries for a selected remote machine.You can also delete an individual directory view entry for a remote machine.To delete all directory view entries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Directory Views.The system displays the Directory Views page.2. Select the remote machine for which you want delete the directory views from the Machine Name dropdownmenu.The table below the menu displays the current directory views for the selected remote machine.3. Click Delete All Directory View Entries.A message asks you to confirm that you want to delete all directory view entries.4. Click OK.All of the remote machines are deleted from the remote machine.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Monitoring port activityMonitoring port activityMessage Networking's port monitors allow you to monitor port activity for the following port types:! AUDIX Digital Port Monitor! Analog Monitor! Octel Analog Update Monitor! Aria Digital Port Monitor! Serenade Digital Port Monitor! SMTP Port MonitorTop of page
174Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Port monitors > AUDIX Digital MonitorAUDIX Digital MonitorUse this page to monitor activity on AUDIX Digital ports.To view the AUDIX Digital monitor:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > AUDIX Digital Monitor.The system displays the AUDIX Digital Monitor page, which indicates the AUDIX Digital status. Thefollowing table lists the columns that are displayed in the monitor.Column DescriptionChannelStatusMachineActivityNumber of the channel.Indicates whether the channel is idle (no activity), not equipped, or in use. Astatus of not equipped indicates that the channel was not purchased and is,therefore, not available.Name of the machine associated with the activity in which the port isengaged.Activity in which the port is engaged.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Port Monitors page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Port monitors > Analog MonitorAnalog MonitorUse this page to monitor activity on analog ports.To view the analog monitor:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Analog Monitor.The system displays the Voice Channel Monitor page, which indicates the analog status. The followingtable lists the columns that are displayed in the monitor.ColumnDescription
175ChannelStatusMachineActivityNumber of the channel.Indicates whether the channel is idle (no activity), not equipped, or in use. Astatus of not equipped indicates that the channel was not purchased and is,therefore, not available.Name of the machine associated with the activity in which the port isengaged.Activity in which the port is engaged.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Port Monitors page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Port monitors > Octel Analog Update MonitorOctel Analog Update MonitorUse this page to monitor activity on Octel Analog ports. Octel Analog is used by Serenade Analog, Aria, Analog,Octel 100, and Unified Messenger Analog remote machines.To view the Octel Analog Update Monitor:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Octel Analog Update Monitor.The system displays the Octel Analog Update Monitor page. The following table lists the columns that aredisplayed in the monitor.FieldDescriptionChannelStartNodeNameRangeActivityASCIIChannel being used for the update.Time at which the update started.Name of the remote machine for which the update is being completed.Beginning and ending subscriber addresses for which the update wasgenerated. Also displays the current subscriber address being updated.Indicates whether the activity being performed is one of the following:! Pull: updating subscriber information on a Message Networkingsystem! Push: updating information on a remote Octel Analog NetworkingmachineNumber of subscriber ASCII names that have been updated.
176VoiceErrorNonExTotalNumber of subscriber voiced names that have been updated.Number of subscriber names that could not be updated.Number of subscriber mailboxes that did not exist.Total number of subscriber records that have been updated, including thetotal number of successes, failures, and any nonexistent mailboxes.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Port Monitors page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Port monitors > Aria Digital MonitorAria Digital MonitorUse this page to monitor activity on Aria Digital ports.To view the Aria Digital Monitor:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Aria Digital Monitor.The system displays the Aria Digital Monitor page. The following table lists the columns that aredisplayed in the monitor.Column DescriptionChannelStatusMachineActivityNumber of the channel.Indicates whether the channel is idle (no activity), not equipped, or in use. Astatus of not equipped indicates that the channel was not purchased and is,therefore, not available.Name of the machine associated with the activity in which the port isengaged.Activity in which the port is engaged.The following buttons appear at the bottom of the page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Port Monitors page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
177Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Port monitors > Serenade Digital MonitorSerenade Digital MonitorUse this page to monitor activity on Serenade Digital ports.To view the Serenade Digital Monitor:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Serenade Digital Monitor.The system displays the Serenade Digital Monitor page. The following table lists the columns that aredisplayed in the monitor.ColumnChannelStatusMachineActivityDescriptionNumber of the channel.Indicates whether the channel is idle (no activity), not equipped, or in use. Astatus of not equipped indicates that the channel was not purchased and is,therefore, not available.Name of the machine associated with the activity in which the port isengaged.Activity in which the port is engaged.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Port Monitors page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > Port monitors > SMTP Digital MonitorSMTP Digital MonitorUse this page to monitor activity on SMTP digital ports.To view the SMTP Digital Monitor:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > SMTP Digital Monitor.The system displays the SMTP Monitor page. The following table lists the columns that are displayed inthe monitor.
178ColumnChannelStatusMachineActivityLastUsedDescriptionNumber of the channel.Indicates whether the channel is idle (no activity), not equipped, or in use. Astatus of not equipped indicates that the channel was not purchased and is,therefore, not available.Name of the machine associated with the activity in which the port isengaged.Activity in which the port is engaged.Time that the last activity took place.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Port Monitors page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > SMTP security administrationSMTP security administrationThis topic provides information on administering SMTP/MIME security on the Message Networking system byblocking or accepting incoming and outgoing SMTP/MIME messages, either by domain name or by networkaddress. Administering SMTP/MIME security involves the following tasks:! Adding entries to SMTP security lists! Viewing and modifying SMTP security list entries! Deleting entries from SMTP security listsThe blocking of SMTP/MIME messages takes place at the SMTP/MIME gateway:! Outbound messages are accepted by Message Networking for delivery and are passed to theSMTP/MIME gateway, which then return messages to blocked destinations as undeliverable with asending restrictions error condition.! Incoming messages from blocked domains are rejected by the receiving ESMTP daemon, whichminimizes impact to the system. Rejection is based on the Mail From identification provided by theremote system during mail exchange.Top of page
179Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > SMTP security administration > Adding entries to SMTPsecurity listsAdding entries to SMTP security listsThis topic provides information on adding entries to SMTP security lists. You can add entries by domain nameor network address.Note: You can use the Blocked and Allowed lists together to provide the specific functionality you need. Forexample, you can use the Blocked list to block all incoming SMTP/MIME messages from *.com and then use theAllowed list to still allow incoming SMTP/MIME messages from mycompany.com. You can also use the Domainand Range methods together. For example, if a subscriber record exists on the system for info@company.com(with a network address of 5478265555), you can use the Domain method to block all outgoing SMTP/MIMEmessages to *.company*.com and use the Range method to still allow outgoing messages to 5478265555(info@company.com).To add an entry to an SMTP security list:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong>> Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. In the Display Allowed/Blocked Lists per menu, select the method by which you want to block or allowincoming or outgoing SMTP/MIME messages. Select Domain to block or allow SMTP/MIME messagesby domain name, or select Range to block or allow SMTP/MIME message by networking addresses.The system displays a table containing any existing entries for the selected method, including the range(if the Range method is selected, domain name (if Domain method is selected), direction (either Incomingor Outgoing), and the disposition (either Blocked or Allowed).3. Click Add an Entry.4. Complete the fields that display on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the fieldnames or Help on the Web-based administration page.5. Click Save.The list is updated to reflect the new entry.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong>SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong>Use the SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong> page to control incoming and outgoing SMTP/MIME messages, either bydomain name or by network address. You can use this page to add new entries, view and modify existingentries, and delete entries.
180Note: You can use the Blocked and Allowed lists together to provide the specific functionality you need. Forexample, you can use the Blocked list to block all incoming SMTP/MIME messages from *.com and then use theAllowed list to still allow incoming SMTP/MIME messages from mycompany.com. You can also use the Domainand Range methods together. For example, if a subscriber record exists on the system for info@company.com(with a network address of 5478265555), you can use the Domain method to block all outgoing SMTP/MIMEmessages to *company*.com and use the Range method to still allow outgoing messages to 5478265555(info@company.com).This page contains the following fields.Display/Allowed Blocked Lists per: Select the method for which you want to view, add, modify, or deleteSMTP security entries. When you select the method, a table displays any existing entries for the selectedmethod, including the range (if the Range method is selected, domain name (if Domain method is selected),direction (either Incoming or Outgoing), and the disposition (either Blocked or Allowed).To add a new entry, click Add an Entry. The following fields display.Domain Name: If you select the Domain method, type the domain of the destination for which you want to blockor allow SMTP messages, such as company.com. You can use the asterisk character (*) to replace any stringand use a question mark (?) to replace any character.Start: If you selected the Range method, type the first network address for which you want to block or allowSMTP messages.End: If you selected the Range method, type the last network address for which you want block or allow SMTPmessages. To specify an individual address, type the same network address that you entered in the Start field.Disposition: Select whether SMTP messages are blocked or allowed for the specified destination.Direction: Select whether the entry you are creating is for incoming or outgoing messages.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Remote Machine <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.! Add an Entry: Click this button to create a new entry to the list.! Delete: Click this button to delete the selected entry from the list.! Modify: Click this button to edit the settings of the selected entry.! Save: When you are creating or modifying an entry, click this button to save the page settings.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > SMTP security administration > Viewing and modifying SMTPsecurity list entriesViewing and modifying SMTP security list entriesThis topic provides information on viewing and modifying SMTP security list entries.To view or modify SMTP security list entries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong>> Remote Machine
181<strong>Administration</strong> > SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. In the Display Allowed/Blocked Lists per menu, select the list you want to modify. Select Domain to viewor modify the existing list of entries for domain names, or select Range to view or modify the existing listof entries for networking addresses.The system displays a table containing any existing entries for the selected method, including the range(if the Range method is selected, domain name (if Domain method is selected), direction (either Incomingor Outgoing), and the disposition (either Blocked or Allowed).3. To modify an entry, highlight the entry you want to modify, and click Modify.4. Modify the fields that display on the page. For information on the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.5. Click Save.The list is updated to reflect the changes.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote machine administration > SMTP security administration > Deleting entries from SMTPsecurity listsDeleting entries from SMTP security listsThis topic provides information on deleting entries from SMTP security lists.To delete SMTP security list entries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong>> Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SMTP Security <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. In the Display Allowed/Blocked Lists per menu, select the list from which you want to delete an entry.Select Domain or Range.The system displays a table containing any existing entries for the selected method, including the range(if the Range method is selected, domain name (if Domain method is selected), direction (either Incomingor Outgoing), and the disposition (either Blocked or Allowed).3. Highlight the entry you want to delete and click Delete.A message asks you to confirm whether you want to delete the entry.4. Click OK.The list is updated to reflect the changes.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
182Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Administering host namesAdministering host namesThis topic provides information on how to view or edit the /etc/hosts file, which is used to resolve domain namesto IP addresses when DNS is not used or is unavailable. This feature allows you to specify a machine nameinstead of an IP address in the Outgoing MTA field even if you do not have a domain name server.To administer the /etc/hosts file:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Administer Hosts.The system displays the Administer Hosts page.2. To modify the file contents, type in the text box:" The IP address in the first column." The domain name that corresponds to the IP address in the second column." The corresponding node name in the third column (optional).3. Click Save to save the changes to the /etc/hosts file.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering remote machines > Display "postmaster@domain"Display "postmaster@domain"The Message Networking is capable of receiving messages addressed to postmaster. This special address,which commonly exists on email servers, allows messages to be sent to the administrator of a particular server.The postmaster@domain file contains data addressed to postmaster of the Message Networking system. Thefile cannot exceed 0.5 MB in size. When it reaches this size, the oldest messages are deleted.To display the postmaster@domain file:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Display "postmaster@domain".The system displays the most recently logged data in this file. Messages in this file are sorted by entrydate.2. Use the scroll bar to view the entire page.The system displays the current directory view information, if information exists, for this machine.3. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Remote Machine Parameters page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.
183! Print: Click this button to print the contents of the page.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > Maintenance > Reports > <strong>Administration</strong> reports> Viewing the Remote Machines ListViewing the Remote Machines ListThe Remote Machines List provides information on each remote machine administered in the system.To access the Remote Machines List:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine Lists > Remote Machines List.The system displays the Remote Machines List.2. Review the list. The list contains the following information for each remote machine:" Machine Name: Lists the names of each remote machine currently administered on the system, inalphabetical order." ID: Lists the ID of each remote machine currently administered on the system." Machine Type: Lists the machine type of each remote machine currently administered on thesystem." Conn Type: Lists the type of connection between each remote machine and the MessageNetworking system. The following connection types are supported:# TCP/IP (Aria Digital, AUDIX, Serenade Digital, VPIM, or SMTP/MIME)# AMIS# Octel Analog (Aria Analog, Serenade Analog, Octel 100, UM Analog)" Rate: Speed of the connection to this remote machine:# 9600 bps# 19200 bps# 56000 bps# 64000 bps" Chan: The number of the channel to which each remote machine is connected." Dial String: Lists the dial string or IP address for each remote machine." Subs: The number of subscribers on each remote machine." Bridged Machine: Indicates whether the remote machine is a bridged machine. This column doesnot appear if the Number of Bridged Machines on the Customer Options page is set to 500 (themaximum).The total number of remote machines, the total numbers of subscribers, and the number of bridgedmachines are listed beneath the machine list. The number of bridged machines is not included if theNumber of Bridged Machines on the Customer Options page is set to 500 (the maximum).
184The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Remote Machines List page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Export to File: Click this button to export the contents of the Remote Machines List to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_rep_remmach). When When a message asks if you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.! Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Message Networking as a remote machineAdministering Message Networking as a remote machineEach remote machine on the Message Networking network must administer the Message Networking system asa remote machine so that the two machines can communicate.You will need the following information about the Message Networking system before administering it as aremote machine:! The phone number that the new system must use to call Message Networking. As when MessageNetworking dials the new system, the phone number you enter must take into account whether the callswill occur over a private or public network. This, in turn, determines whether an outside access number(normally 9), a network access number (normally 8), and whether a long-distance number needs to beincluded.! The actual phone digits the remote machine receives to identify the Message Networking system. Whenthe remote machine calls Message Networking and Message Networking receives digits to identify theremote machine, the remote machine will receive digits identifying the Message Networking system. Theactual digits the new system receives, however, could be different than the Message Networking phonenumber, depending on how calls to the Message Networking system are routed.! The checklists for adding new remote machines to the Message Networking system list other informationyou need about the Message Networking system before you can administer it on each type of remotemachine.For information about administering Message Networking as a remote machine on your systems, see theadministration documentation associated with your systems.Top of page
185Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connectionAdministering the Message Networking switch connectionThis topic provides information on administering Message Networking for the connected switch. A switchconnection is required for analog systems.Administering the switch connection to the Message Networking system includes the following tasks:! Select the switch connected to the Message Networking system.! Perform switch administration. Switch administration is not required on all systems. For example, if youare connecting to an <strong>Avaya</strong> DEFINITY switch, you can use the system defaults and do not need toperform any additional administration.Before administering the switch connection, you must complete the following:! Verify that the PBX administration required to support the connection from Message Networking to thePBX has been completed.! Make the physical connections from the analog line interface card to the switch.! Install the appropriate switch software.! Administer the voice system.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Selecting the Message Networkingswitch connectionSelecting the Message Networking switch connectionThis topic provides information on selecting the switch connected to the Message Networking system. A switchconnection is required for analog systems.To select the switch connected to the Message Networking system:Note: Before administering the switch connection, you must make the physical connections from the analog lineinterface card to the switch, install the appropriate switch software, and administer the voice system.1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Switch Selection.The system displays the Switch Selection page.2. Select the appropriate switch and country from the drop-down list. The list varies depending on the switchsoftware package you installed.3. Click Save.The system displays a confirmation message and prompts you to stop and start the voice system.4. Stop and start the voice system.5. Test the switch connection by performing a test connect to an analog remote machine:" If the connection to the analog remote machine is successful, no further switch administration is
186required." If the connection to the analog remote machine is unsuccessful, you must continue withperforming switch administration.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking systemPerforming switch administration on the Message Networking systemThis topic provides information on performing switch administration on the Message Networking system. Theswitch administration parameters enable the Message Networking system to communicate with the switchconnected to the Message Networking system.Important! Depending on the switch connected to the Message Networking system, you might not be requiredto modify the switch administration parameters. If the test connection you performed after switch selection wassuccessful, you do not need to modify the switch administration pages. If the test connection was unsuccessful,use the switch administration pages to specify the settings required to connect to the installed switch.Switch administration involves configuring the interface parameters and call progress tones. Defaults areprovided for the interface parameters and call progress tones; however, you can modify them if necessary foryour system. If you know the information that needs to be modified, select one of the following links and followthe instructions to make the necessary changes:! Interface parameters! Call progress tonesIf you do not know which parameters require modification and you need to test the tones, complete theinstructions in Capturing call progress tones.Important: After changing the switch administration parameters, you must stop and start the voice system tohave the changes take effect.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking system > Configuring Interface ParametersConfiguring Interface ParametersThis topic provides information on configuring the interface parameters required by the Tip/Ring driver and theswitch.To configure interface parameters:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Switch <strong>Administration</strong> > Interface Parameters.The Interface Parameters page displays the current parameters for the selected switch. The Default
187column displays the defaults settings for the selected switch. The Current column displays the currentsettings. If you are administering this page for the first time, the Default settings and the Current settingsare identical.Note: When you modify the Interface Parameters, the previous values are discarded. Therefore, it ishighly recommended that you print the current settings in case they are required in the future.2. Modify the fields on the page as appropriate. The craft and dadmin logins can set values in any of theunrestricted fields. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration page to viewmore information.Note: To modify a restricted value, change the system's country assignment to OTHER on the SwitchSelection page. This setting removes the restrictions but prohibits the craft and dadmin logins fromchanging parameters.3. Click Save.A message asks you to verify that you want to save the changes.4. Click Save.5. Stop and start the voice system for the changes to take effect.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking system > Performing call progress tone administrationPerforming call progress tone administrationThis topic provides information on performing call progress tone administration on the Message Networkingsystem. Default tones are provided for each supported switch. However, you can use the Tones <strong>Administration</strong>pages to capture and evaluate tones, and to tune the default tones if necessary for your system.Note: Before performing tones administration, you must make the connections to the switch, install the switchsoftware, administer the voice system, and select the switch.There are multiple pages associated with Tones <strong>Administration</strong>:! Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page: The initial Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the current settings for eachof the defined tones. Each tone is specified in terms of Frequency 1 and/or 2, and the timing on and offcycles. You cannot modify the tone settings directly on this page.! Tone-specific pages: There is a separate page for each tone listed on the Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page.To access the tone-specific pages, click the name of the tone on the Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page. Forexample, to modify the Busy Tone settings, click BUSY TONE in the table on the Tones <strong>Administration</strong>page. You can use the tone-specific pages to modify the settings for each tone and to use the ToneCapture tool, which allows you to capture the actual tone to determine if you need to modify the systemdefaults for the tone.! Tone Capture settings page: The Tone Capture settings page lists the settings for the Tone Capturetool. Configure the Tone Capture tool settings if you want to capture any tones. To access the ToneCapture tool settings, click Capture Setting on the Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page. To launch the ToneCapture tool, click Capture on any of the tone-specific pages.Progress tone administration includes the following tasks:! Modifying existing tone settings! Defining new tones! Configuring tone capture settings
188! Capturing and analyzing tonesTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking system > Performing call progress tone administration > Modifying call progress tonesModifying call progress tonesThis topic provides information on modifying call progress tones. Default tones are provided for each supportedswitch. However, you can modify the default tones if necessary for your system.To modify existing tone settings on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Switch <strong>Administration</strong> > Tones <strong>Administration</strong>.The Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the current tone settings for the selected switch.2. Click the name of the tone you want to modify on the Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page.The tones-specific administration page displays.Note: If you do not know which parameters require modification, you can capture the tone to determinethe correct settings.3. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.4. Click Save.5. The system displays a message that the changes have been made and for you to stop and start themessaging system to accept the page settings.6. Click OK.7. Stop and start the voice system for the changes to take effect.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking system > Performing call progress tone administration > Defining additional call progress tonesDefining additional call progress tonesIn some cases, your circumstances might require that you assign more than one set of parameters for a certaincall progress tone. For example, if the switch connected to the Message Networking system and the switch atthe public telephone network office use different dial tone parameters, you might need to define both in theMessage Networking system.Use this procedure to set the frequencies and cadence the Message Networking system recognizes foradditional call progress tones. As many as three additional tones can be specified as either a busy tone, dialtone, reorder tone, or ring tone. As for the basic tones, each additional tone is made up of one or twofrequencies and consists of a series of on and off timing cycles (cadence). Unlike the basic tones (Dial, Busy orReorder), you cannot set any additional tone to be recognized as a disconnect signal.
189To define additional call progress tones on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Switch <strong>Administration</strong> > Tones <strong>Administration</strong>.The Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the current tone settings for the selected switch.2. Select one of the undefined tones:" First Add Tone" Second Add Tone" Third Add ToneThe page for the selected tone displays.3. Enter the appropriate values in the Frequency fields. You can click the field names or Help on the Webbasedadministration page to view more information.4. Type the tone name in the Report as: field that corresponds to the additional basic tone you are defining.For example, if you are defining an additional dial tone, type dial.5. Click Capture.Note: If you have not already configured the tone capture settings, the capture settings display.The Opcodes and Channels for the selected tone displays.6. Select the appropriate Opcodes and Channels. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-basedadministration page to view more information.7. Click Capture and Analysis.8. Click Save.The system displays a message that the changes have been made and for you to stop and start themessaging system to accept the page settings.9. Click OK.10. Stop and start the voice system for the changes to take effect.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking system > Performing call progress tone administration > Configuring tone capture settingsConfiguring tone capture settingsThis topic provides information on configuring the tone capture settings for Message Networking. The tonecapture tool allows you to capture tones for use in Message Networking switch administration. Default tones areprovided for each supported switch. You can use the tone capture tool to capture the actual tones anddetermine if you need to tune the system defaults.To configure the capture tone settings:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Switch <strong>Administration</strong> > Tones <strong>Administration</strong>.The Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the current tone settings for the switch.2. Click Capture Setting.The tone capture settings displays.3. Complete the fields on the page to configure the tone capture settings. You can click the field names orHelp on the Web-based administration page to view more information.4. Click Save.The Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.Top of page
190Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering the Message Networking switch connection > Performing switch administration onthe Message Networking system > Performing call progress tone administration > Capturing call progress tonesCapturing call progress tonesThis topic provides information on capturing tones for use in Message Networking switch administration. Defaulttones are provided for each supported switch. You can use the Tone Capture tool to capture the actual tonesand determine if you need to tune the system defaults.To capture tones:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Switch <strong>Administration</strong> > Tones <strong>Administration</strong>.The Tones <strong>Administration</strong> page displays the current tone settings for the switch.2. To capture a particular tone, click the name of the tone you want to modify on the Tones <strong>Administration</strong>page.The tones-specific administration page displays.3. Click Capture.Note: If you have not already configured the tone capture settings, the capture settings display.4. A message displays asking whether you want to use default commands to capture the tone.Note: The Dial Tone, Busy Tone, and Ring Tone have default Opcode commands that you can edit. TheReorder, First, Second, and Third Add Tones do not have default Opcode commands." If you click No, the capture proceeds with the current command sequence." If you click Yes, the current sequence of operation codes display. Use the drop-down lists tomodify the page. The following tables lists the Opcode Commands and the capture sequences fordial tone, ringback tone, and busy tone.
191Opcode CommandsCommandDescriptionOFFHK CH_No.ONHK CH_No.DIAL CH_No.digit_stringFLASH CH_No.durationLEARN andChannel numberWAIT CH_No.Seizes the specified line.Emulates an on-hook condition on the specified line (Idle).Dials out DTMF digits through the specified line.Performs hook flash on the channel for the specified number ofmsec.Captures the PCM data of the voice and performs an analysis ofthe Tone and displays the result.Duration Introduces a number of seconds of delay in execution ofthe next command. This command can be introduced anywhere inthe command sequence.The following table displays the opcode sequence used to capture a dial tone. Adjust the channelnumbers and the parameters to match the switch on which you are working.Dial Tone Capture SequenceOPCODE CH No. Parameter Command ResultOFFHK 10 Makes line 10 busy.LEARN 10 Performs the tone capture and analysis.ONHK 10 Releases line 10.The following table displays the opcode sequence used to capture a ringback tone. Adjust thechannel numbers and the parameters to match the switch on which you are working.Ringback Tone Capture SequenceOPCODE CHNo.Parameter Command ResultOFFHK 01 Makes line 01 busy.WAIT 01 4 Inserts a delay to accommodate silence or theconnect time.DIAL 01 1234 Dials the extension.LEARN 0 Captures the tone, and analyzes frequency andcadence.ONHK 01 Releases line 01.The following table displays the opcode sequence used to capture a a busy tone. Adjust thechannel numbers and the parameters to match the switch on which you are working.Busy Tone Capture SequenceOPCODE CHNo.Parameter Command ResultOFFHK 01 Makes line 01 busy.
192DIAL 01 1234 Dials extension 1234.LEARN 0 Captures the tone, and analyzes frequency andcadence.OFFHK 02 Causes the switch to inject a busy tone on line 02.DIAL 02 1234 Dials extension number of line 02.ONHK 01 Releases line 01.ONHK 02 Releases line 02.5. After you modify the opcodes, click Capture and Analysis. The results display on the tone-specific page.6. Stop and start the voice system for the changes to take effect.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribersAdministering subscribersThis topic provides information on subscriber administration for the Message Networking system. Each time asubscriber is added on a remote machine administered on the Message Networking system, the subscriberneeds to be registered on the Message Networking system to receive messages through Message Networking.This topic provides the following information:! Overview of adding and updating subscribers! Performing remote updates! Adding a subscriber mailbox manually! Modifying subscriber parameters manually! Deleting a subscriber mailbox manually! Displaying a subscriber mailbox! Administering subscribers in bulk! Self-registering subscribersThere are differences in subscriber functionality with Message Networking that you should be aware of beforeadministering remote subscribers. See Remote machine considerations for more information.Notes:! On UM for Lotus Notes Release 5.0 or later systems, remote subscribers must be administered as userson the Lotus Notes/Domino system. This allows subscribers on the local UM for Lotus Notes system tosend TUI messages to remote subscribers via Message Networking.! On UM for Exchange systems, remote subscribers must be administered as users on the Exchangesystem. This allows subscribers on the local UM for Exchange system to send TUI messages to remotesubscribers via Message Networking.Top of page
193Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Overview of adding and updating subscribersOverview of adding and updating subscribersThis topic describes in general terms how Message Networking and its administered remote machines populatesubscriber information on the Message Networking system and how the Message Networking system deliversthis information to other remote machines.Populating directories means adding, updating, or deleting subscribers in a messaging system database(directory). How each system performs these actions with the Message Networking system depends on the typeof messaging system. How much and what kind of subscriber information is exchanged between remotemachine and Message Networking also depends on the type of subscriber updates selected for that remotemachine (full, directory view, or dynamic).Important! There are considerations for configuring directory updates for <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging systemsthat you should be aware of before administering the MM systems on your network.The following information is provided:! Adding subscribers! Updating subscribers! Populating subscriber informationNotes:! When adding subscribers to the Message Networking system, do not attempt to add subscriberextensions beyond the range defined in the system's dial plan.! In addition to the methods listed in the following tables, you can also administer Message Networkingsubscribers via the system's secure LDAP interface.Adding subscribersWhen a new remote machine is added to the Message Networking network, Message Networking either pullsthe new subscriber information from the remote machine or the new subscriber information is pushed to theMessage Networking system from the remote machine (for AUDIX TCP/IP, Aria TCP/IP, Serenade TCP/IP, andModular Messaging with an MSS through LDAP). Once the subscriber information is retrieved from a remotemachine, that subscriber information can then be propagated to the other remote machines administered on theMessage Networking system.For those systems that cannot automatically send their subscriber directories, Message Networking supports thefollowing methods of adding subscribers to the Message Networking directory, in the recommended order ofpriority. Whether information is pulled or pushed depends on the remote machine involved in the messagingexchange:1. LDAP-based: LDAP is used to exchange subscriber information with Modular Messaging systems.Message Networking also supports a secure LDAP interface that allows third-party application access foradministering subscribers.2. Bulk subscriber administration by file: Subscribers can be added using FTP.3. Self-registration: Subscribers can self-register by sending a voice message (consisting of thesubscriber's voiced name) to the administrator-defined self registration ID network address.
1944. Sending a message through Message Networking: Subscribers who send messages throughMessage Networking are automatically added to the Message Networking directory.5. Subscriber Parameters <strong>Administration</strong>: Subscribers can be manually added through the MessageNetworking Subscriber Parameters <strong>Administration</strong> page (not supported for Modular Messaging remotemachines).6. Bulk subscriber administration by range: Subscribers can be added using the Message NetworkingAdd Subscribers from Range page.The following table describes how new remote machine subscribers are added to the Message Networkingsystem.New nodeAUDIX (DEFINITY ONE Release 2.0,INTUITY AUDIX Release 4.0 or later,IP600 9.2.1, INTUITY AUDIX LX, andInterchange Release 5.4)AMISOctel Analog NetworkingOctel Analog Networking with UnifiedMessengerAria DigitalSerenade DigitalVPIM v2What to doMessage Networking administrator uses DemandRemote Update.Use one of the following methods:! Initiate bulk add from the Message Networkingsystem.! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voicednames.! Send a message from the new subscriber.! Add via the administration page on theMessage Networking system.Use one of the following methods:! Use self-registration.! Prompt new Octel Analog Networking, AriaAnalog, and Serenade Analog subscriber tosend a message.! Add via the administration page on theMessage Networking system.! LDAP (customer must write LDAP Clientapplication).! Initiate name pull from Message Networking.Use the same methods as those of Octel AnalogNetworking nodes.Initiate NameSend from the Aria Digital.Initiate NameSend from the Serenade Digital.Use one of the following methods:! Use FTP to add subscribers.! Initiate bulk add from the Message Networkingsystem.! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voicednames.! Send a message from the new subscriber.! Add via the administration page on theMessage Networking system.
195! LDAP (customer must write LDAP Clientapplication).SMTP/MIME (LDAP-based)SMTP/MIME (non-LDAP)! Use LDAP either dynamically or through aDemand Remote Update (<strong>Avaya</strong> ModularMessaging with an <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Store andMessage Networking only).Use one of the following methods:! Use self-registration to add subscribers' voicednames.! Initiate bulk administration by file from theMessage Networking system.! Administer via the administration page.! Initiate bulk administration by range (with emaildefaulting to Network Address @ Domain).! LDAP (customer must write LDAP Clientapplication).Notes:! On UM for Lotus Notes Release 5.0 or later systems, remote subscribers must be administered as userson the Lotus Notes/Domino system. This allows subscribers on the local UM for Lotus Notes system tosend TUI messages to remote subscribers via Message Networking.! On UM for Exchange systems, remote subscribers must be administered as users on the Exchangesystem. This allows subscribers on the local UM for Exchange system to send TUI messages to remotesubscribers via Message Networking.Updating subscribersThe following table describes how Message Networking updates remote machine and remote machines updateMessage Networking.ProtocolAMISAUDIXWhen the remote machine updatesMN! Adds and changes are notsupported.! When Message Networkingattempts to deliver to anonexistent subscriber on anAMIS remote machine, it failsthe messages and deletes thatsubscriber from the MessageNetworking subscriberdirectory.! When a subscriber is added,changed, or deleted throughadministration, MessageNetworking is automaticallynotified.When MN updates the remotemachine! Updates are not supported.! When Message Networkingdetects a subscriber add,change, or delete, it pushes anupdate to the AUDIX remotemachine.Octel AnalogNetworking! When Message Networking ! When the remote machine
196Aria Digitaldelivers a message to theremote machine, it performs anASCII match on the recipient (ifASCII name check is set toyes).! If the recipient mismatches,Message Networking fails themessage and immediatelyrequests a pull from the remotemachine (when Updates In isset to yes on MessageNetworking and Updates Out isactivated on the remotemachine).! If the ASCII name is a defaulton the Message Networkingsystem, a comparison is notperformed by MessageNetworking, the message isdelivered, and the pull isimmediately requested (whenUpdates In is set to yes onMessage Networking andUpdates Out is activated onthe remote machine).! If the subscriber does not existon the remote machine butdoes exist on the MessageNetworking system, then themessage is failed andMessage Networking defaultsthe ASCII name and nulls thevoice name of the subscriber.! For any name pull to succeed,the remote machine must beset to Protocol Level 2 or 3.! When Message Networkingdelivers a message to theremote machine, it requeststhat the remote machineperform an ASCII match on therecipient.! If the recipient mismatches, theremote machine fails themessage and then MessageNetworking requests a pullfrom the remote machine.! If the ASCII name is a defaulton the Message Networkingsystem, a comparison is notrequested, the message isdelivered, and the pull isrequested.! If the subscriber does not existon the remote machine butdelivers a message toMessage Networking, itperforms an ASCII namematch on the recipient.! If the recipient mismatches, theremote machine fails themessage and deletes thesubscriber entry. The next timea message is sent to thatsubscriber, the remotemachine requests a pull fromMessage Networking.! If the ASCII name is a defaulton Message Networking,Message Networking alwaysaccepts the message (it doesnot perform a namecomparison), and the MessageNetworking system schedulesthe pull.! If a subscriber does not existon Message Networking andthat subscriber sends amessage through MessageNetworking, the MessageNetworking system adds thesubscriber as a default andthen a name pull is scheduled.! Also, when MessageNetworking detects asubscriber add or a change(not a delete), MessageNetworking pushes out anupdate.! When the remote machinedelivers a message toMessage Networking,Message Networking performsan ASCII match on therecipient.! If the recipient mismatches,Message Networking fails themessage and the remotemachine deletes the entry. Thenext time that a message issent to the subscriber, theremote machine requests apull from Message Networking.! Also, when MessageNetworking detects an add,change, or delete of asubscriber, it pushes out anupdate.
197Serenade DigitalVPIM v2does exist on the MessageNetworking system, then themessage is failed by theremote machine and theMessage Networking systemdefaults the ASCII name andnulls the voice name of thesubscriber.! Also, Aria Digital canautomatically push an add,change, or delete of asubscriber when the updateoccurs.! When the Serenade Digitalsystem delivers a message toMessage Networking, itautomatically pushes thesender's ASCII and spokenname (only when the spokenname exists).! The Serenade Digital canautomatically push an add orchange (but not a delete) of asubscriber when the updateoccurs.! When Message Networkingdelivers a message to theremote machine, it does anASCII name match on therecipient (if ASCII name matchis set to yes).! If the recipient mismatches,Message Networking fails themessage and defaults theASCII name and nulls thespoken name.! If the ASCII name is a defaulton Message Networking, acomparison is not performedand the message is delivered.! If the subscriber does not existon the remote machine butdoes on Message Networking,the message is failed andMessage Networking defaultsthe ASCII name and nulls thespoken name of thesubscriber.! When a VPIM sender sends amessage through MessageNetworking, that subscriber'srecord information is updatedon Message Networking if theASCII name/voice name has! When Message Networkingdelivers a message to theSerenade Digital system, itautomatically pushes thesender's ASCII and spokenname (only done when aspoken name exists).! When Message Networkingdetects a subscriber add orchange (but not a delete), itpushes out the update.! When the remote machinedelivers a message toMessage Networking, itperforms an ASCII match onthe recipient if addressedalphabetically.! If the recipient mismatches, theSerenade system fails themessage and deletes theentry.! When a Message Networkingsender sends a message to aVPIM system, that subscriber'srecord information is updatedon the receiving VPIM systemis the ASCII name/voice name
198SMTP/MIME(LDAP-based)SMTP/MIME(non-LDAP)changed and the sendingsystem supports thisinformation.! When a subscriber is added,changed, or deleted throughadministration, MessageNetworking is automaticallynotified.! When an SMTP/MIME sendersends a message throughMessage Networking, thatsubscriber's record informationis updated on MessageNetworking if the ASCII name(not voice name) has changedand the sending systemsupports this information.has changed and the receivingsystem supports thisinformation.! When Message Networkingdetects a subscriber add,change, or delete, it pushesout an update.! When Message Networkingsends a message to anSMTP/MIME system, thatsubscriber's record informationis updated on the receivingSMTP/MIME system, if theASCII name (not voice name)has changed and the receivingsystem supports thisinformation.Populating subscriber informationIf callers do not receive the recipient's voiced name or if they cannot use Dial-by-name, then the recipientsubscriber may or may not be available on the Message Networking system. The following tables explain whatactions can be taken to populate subscriber information on the Message Networking system and to transfersubscriber information from the Message Networking system to the remote machine requesting the update.The outcomes of these actions depend on proper configuration of both the Message Networking system and theremote machines.The following table describes the actions that can be taken to populate subscriber information on the MessageNetworking system.Remote machine typeAUDIXAMISOctel Analog NetworkingOctel Analog Networkingwith Unified MessengerAria DigitalSerenade DigitalVPIM v2ActionInitiate Demand Remote Update from the Message Networkingsystem to the AUDIX end node.Recipient needs to self-register for Dial-by-name; systemadministrator must manually add the ASCII name on the MessageNetworking system.! Initiate demand remote update from the Message Networkingsystem to the Octel Analog Networking end node.! Use bulk add utility where appropriate.Same as Octel Analog Networking.From the Aria Digital node, use NameSend to push the subscribername to the Message Networking system.From the Serenade Digital node, use NameSend to push thesubscriber name to the Message Networking system.Use one of the following methods:! Use bulk add utility where appropriate.
199! Enter subscriber information using the administration screens.! Recipient can self-register.! Have VPIM subscriber send a message.SMTP/MIMEUse one of the following methods:! Use bulk add utility where appropriate.! Enter subscriber information using the administration screens.! Recipient can self-register.! Initiate Demand Remote Update from the MessageNetworking system to the SMTP/MIME end node (LDAPbasedonly).The following table describes how subscriber information is populated from the Message Networking system toa remote machine.Remote MachineAUDIXAMISOctel AnalogNetworkingOctel AnalogNetworking withUnified MessengerAria DigitalSerenade DigitalVPIM v2SMTP/MIME (LDAPbased)SMTP/MIME (non-LDAP)ActionInitiate delta update to the Message Networking system.System administrator must administer subscriber information locally.From any mailbox on the Octel Analog Networking node (where thesubscriber information is not available), send a message to that addressusing digit addressing.Same as Octel Analog Networking.From any mailbox on the Aria Digital node (where the subscriberinformation is not available), send a message to that address using digitaddressing.The new subscriber (whose information is missing) must address amessage to any mailbox on the system missing that subscriberinformation.Send a message through the Message Networking system to the VPIMmachine; sender information on the VPIM machine is updated, if theVPIM machine stores and automatically updates subscriber information.Initiate delta update to the Message Networking system.Send a message through the Message Networking system to theSMTP/MIME machine; sender information on the SMTP/MIME machine isupdated, if the SMTP/MIME machine stores and automatically updatessubscriber information.Top of page
200Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updatesPerforming remote updatesThis topic provides information on performing remote updates, which you perform to send and receivesubscriber record updates from some remote machine types. Perform remote updates during initial systemadministration or after a significant number of subscribers have been added. Do not perform this procedureduring prime system hours.There are two types of remote updates:! Demand Remote Update allows subscriber records, including ASCII and voiced names, to be pulled overfrom INTUITY AUDIX, DEFINITY AUDIX, Serenade Analog, IP600, Aria Digital, DEFINITY ONE,Message Networking, and <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging remote machines on to the Message Networkingsystem. Demand Remote Updates are only used for INTUITY AUDIX, DEFINITY AUDIX, IP600, AriaDigital, and DEFINITY One systems. Demand Remote Updates are not supported for Serenade Digital,Unified Messenger, Aria Analog, AMIS Analog, VPIM V2, or other SMTP remote machines.! Demand Remote Push allows subscriber records, including ASCII and voiced names, to be pushed froman <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking to Octel Analog Networking or Aria Digital and Serenade Digital remotemachines. Demand Remote Push updates are not supported for Octel 100, VPIM v2, INTUITY AUDIX,and SMTP/MIME, including <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging and <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remotemachines.Note: NameSend is the recommended procedure to use for updating names in Aria Digital and SerenadeDigital. Names can be updated by range or by using the option for all.The following tasks are associated with remote updates:! Turning on remote updates! Performing a Demand Remote Update! Performing a Demand Remote Push! Monitoring AUDIX Digital remote updates! Monitoring analog remote updates! Monitoring Octel Analog Networking remote updates! Monitoring Aria Digital remote updates! Monitoring Serenade Digital remote updates! Monitoring SMTP port activityRemote updates are one method of updating subscriber records on the system. But, as noted earlier in thistopic, remote updates are not supported for all remote machine types. The following table summarizes thecases in which subscriber updates occur automatically for each type of remote machine.ProtocolRemote machine updatesMessage NetworkingMessage Networkingupdates remote machineAMIS! N/A for adds and changes.! When Message Networking attempts todeliver to a nonexistent subscriber on anAMIS remote machine, it fails themessages and deletes that subscriberfrom the Message Networking directory.N/A
201AUDIX DigitalOctel AnalogNetworkingAria DigitalWhen a subscriber is added, changed ordeleted through administration, the MessageNetworking system is automatically notified.! When Message Networking delivers amessage to the remote machine, it doesan ASCII match of the recipient (if ASCIIName Confirmation is set to Yes).! If the recipient does not match, it fails themessage and immediately requests a pullfrom the remote machine (when UpdatesIn is set to Yes for that remote machineon the Remote Parameters page inMessage Networking and the remoteremote machine itself is administered forremote updates).! If the ASCII name is a default on theMessage Networking system, acomparison is not performed by MessageNetworking, the message is delivered,and the pull is immediately requested(when Updates In is set to Yes for thatremote machine on the RemoteParameters page in Message Networkingand the remote machine itself isadministered for remote updates).! If the subscriber does not exist on theremote machine but does on theMessage Networking system, then themessage is failed. The MessageNetworking defaults the ASCII name andnulls the voiced name of the subscriber.! For any name pull to work, the remotemachine must be set to Protocol Level 2or 3.! When Message Networking delivers amessage to the remote machine, itrequests that the remote machineperform an ASCII match on the recipient.! If the recipient does not match, theremote machine fails the message, andMessage Networking requests a pull fromthe remote machine.! If the ASCII name is a default on theMessage Networking system, acomparison is not requested, themessage is delivered, and the pull isrequested.! If the subscriber does not exist on theremote machine but does on theMessage Networking system, then themessage is failed by the remote machine.Message Networking defaults the ASCIIWhen Message Networking detects anadd, change or delete of a subscriber, itpushes out the update to the AUDIXDigital remote machine.! When the remote machine deliversa message to the MessageNetworking system, it does anASCII match on the recipient.! If the recipient does not match, itfails the message and deletes theentry; the next time that subscriberis messaged, it requests a pull fromMessage Networking.! If the ASCII name is a default onthe Message Networking system,Message Networking alwaysaccepts the message (that is, itdoes not perform a namecomparison); the MessageNetworking system then schedulesa name pull.! If a subscriber does not exist on theMessage Networking system andthat subscriber sends a messagethrough Message Networking, theMessage Networking system addsthe subscriber as a default and thenschedules a name pull.! When Message Networking detectsan add or change (not a delete) of asubscriber, it pushes out theupdate.! When the remote machine deliversa message to Message Networking,the Message Networking systemdoes an ASCII match on therecipient.! If the recipient does not match,Message Networking fails themessage and the remote machinedeletes the entry; the next time thatsubscriber is sent a message, itrequests a pull from the MessageNetworking system.! When Message Networking detectsan add, change, or delete of asubscriber, it pushes out theupdate.
202SerenadeDigitalVPIM V2DigitalSMTP/MIME(LDAP-based)SMTP/MIME(non-LDAPbased)name and nulls the voiced name of thesubscriber.! Aria Digital can automatically push anadd, change, or delete of a subscriberwhen the update occurs.! When the Serenade Digital systemdelivers a message to the MessageNetworking system, it automaticallypushes the sender's ASCII and voicednames (if the voiced name exists).! The Serenade Digital system canautomatically push an add or change, butnot a delete, of a subscriber when theupdate occurs.! When Message Networking delivers amessage to the remote machine, it doesan ASCII match of the recipient (if theASCII Name Confirmation flag is set toYes).! If the recipient does not match, MessageNetworking fails the message, defaultsthe ASCII name, and then nulls thevoiced name.! If the ASCII name is a default on theMessage Networking system, acomparison is not performed, and themessage is delivered.! If the subscriber does not exist on theremote machine but does on theMessage Networking system, themessage is failed. Message Networkingthen defaults the ASCII name and nullsthe voiced name of the subscriber.Each time a VPIM sender sends a messagethrough Message Networking, the sender'srecord is updated on the Message Networkingsystem. Note that this update occurs only if theASCII name/voiced name has changed and thesending system supports this information.When the subscriber is added, changed ordeleted through administration, MessageNetworking is automatically notified.Each time an SMTP/MIME sender sends amessage through Message Networking, thatsubscriber's record is updated on MessageNetworking. Note that this update occurs only ifthe ASCII name (not voice name) has changedand the sending system supports thisinformation.! When Message Networking deliversa message to the Serenade Digitalsystem, it automatically pushes thesender's ASCII and voiced names(done only when a voiced nameexists).! When Message Networking detectsan add or change (not a delete) of asubscriber, it pushes out theupdate.! When the remote machine deliversa message to the MessageNetworking system, it does anASCII match on the recipient ifaddressed alphabetically.! If the recipient does not match, theSerenade fails the message anddeletes the entry.Each time a Message Networking sendersends a message to a VPIM system, thesender's record is updated on thereceiving VPIM system. Note that thisupdate occurs only if the ASCIIname/voiced name has changed and thereceiving system supports this information.When Message Networking detects anadd, change or delete of a subscriber, itpushes out the update to the LDAP-basedremote machine.Each time a Message Networking sendersends a message to an SMTP/MIMEsystem, the sender's record is updated onthe receiving SMTP/MIME system. Notethat this update occurs only if the ASCIIname (not voice name) has changed andthe receiving system supports this
203Note: LDAP updates (between Modular Messaging and Message Networking systems and between MessageNetworking systems) can impact system performance, including delay of administration page displays andreport results. Note that while the LDAP update is in progress between the two systems, messages are nottransmitted between them. The length of time to complete an LDAP update depends on:! The type of Modular Messaging system (Standard or High Availability)! The number of MASs in the system! The size of the system's databaseinformation.! The number of subscribers to be updated and the voice name message lengths! The number of updates occurring at the same time (multiple updates running slow the update rate)It is recommended that remote updates of more than approximately 4,000 subscribers with voiced names bescheduled during non-prime-time hours, and that remote updates of 50,000 subscribers or more be scheduledover a weekend.For Modular Messaging system updates, Standard Availability systems and systems with multiple MASs willtake longer to update. The following numbers are provided to help estimate the total time required for a remoteupdate. The update rate on a Standard Availability system with one MAS is approximately 4,000 subscribersupdated per hour. The update rate on a High Availability system with one MAS is approximately 9,000subscribers updated per hour.For Message Networking to Message Networking updates, the update rate for the S3210 server is from 5,000 to7,000 subscribers updated per hour. For Message Networking to Message Networking updates, the update ratefor the S3400-H server is from 14,000 to 15,000 subscribers updated per hour.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Turning on remote updatesTurning on remote updatesComplete the following procedure to turn on remote updates.To turn on remote updates between the digital remote machines and the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine Parameters.The system displays the Remote Machine Parameters page.2. From the drop-down menu, select a remote machine.The system displays the remote machine parameters for the selected remote machine.3. In the Updates In field, select Yes.4. In the Updates Out field, select Yes.5. In the Network Turnaround field, select Yes.Note: This field is only valid for the machine type INTUITY Release 4.0 or later.6. Click Save.7. Repeat Steps 2 through 6 above for each remote machine connected to the Message Networkingsystem.
2048. Verify that the updates have been completed successfully by accessing the Administrator's Log, eitherthrough the Subscriber List by remote machine name or the Remote Machines List.9. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Performing a Demand RemoteUpdatePerforming a Demand Remote UpdateDemand Remote Update allows subscriber ASCII and voiced names to be pulled from digital and Octel AnalogNetworking remote machines to the Message Networking system.If you are adding a new digital remote machine to an existing multi-Message-Networking environment, completeremote updates on the first Message Networking from the remote machine. Then, complete remote updatesfrom the other Message Networking to the first Message Networking.Caution! Do not execute more than two Demand Remote Updates from AUDIX Digital remote machines at onetime. A total of four LDAP updates can occur at one time.Serenade Octel Analog, Aria Digital, INTUITY AUDIX, and <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging remote machines arevalid remote machine choices. AMIS Analog, Serenade Digital, and VPIM are not valid remote machine choices.(Aria Digital and Serenade Digital machines have a NameSend command, which is the preferred method.) ASerenade remote machine does not transfer the ASCII name of a subscriber if the subscriber's mailbox on thatmachine does not have a recorded voiced name. For Serenade Octel Analog and Aria Digital machine types,you can use all or specific extension ranges.To run a Demand Remote Update:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Demand Remote Updates.The system displays the Demand Remote Updates page.2. From the drop-down menu, select a remote machine.3. For Octel users, enter the Start Extension and End Extension to indicate the range of addresses forwhich the update is to be executed.4. Click Update.If the attempt is successful, the message "Update queued" displays. If the attempt is unsuccessful, anerror message displays.During an update, the remote machine system updates the Message Networking system with any ASCIIor voiced names that have been added, deleted, or changed for the range of extensions on the remotemachine selected.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Verify the success of the Demand Remote Update by viewing the Administrator's Log.Top of page
205Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Performing a Demand RemotePushPerforming a Demand Remote PushThis topic provides information on performing a Demand Remote Push. Demand Remote Push allows MessageNetworking to push subscriber ASCII and voiced names to the Aria Digital, Serenade Digital, and Octel AnalogNetworking remote machines.Notes:! Demand Remote Push updates are not supported for Octel 100, VPIM v2, INTUITY AUDIX, andSMTP/MIME, including <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging and <strong>Avaya</strong> Message Networking remote machines.! The Microsoft Exchange database in Unified Messenger does not accept a Demand Remote Push.To demand a remote push:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Demand Remote Push.The system displays the Demand Remote Push page.2. Select a remote machine name from the drop-down list.3. Click the Push button.If the attempt is successful, the message "Demand Remote Push Triggered." displays. If the attempt isunsuccessful, an error message displays.During a Demand Remote Push, the Message Networking system updates the Octel remote machineswithin the network with any ASCII or voiced names that have been added, deleted, or changed on theMessage Networking system.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Verify the success of the Demand Remote Push through the remote machine subscriber reports. For moreinformation, see the corresponding Octel Analog Networking remote machine subscriber reports documentation.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Monitoring AUDIX Digital remoteupdatesMonitoring AUDIX Digital remote updatesThe process of adding, changing, or deleting subscribers on AUDIX Digital remote machines takes a variableamount of time based on the number of subscribers being updated. The AUDIX Port Monitor page allows you tomonitor the progress of the update. This page is also used for monitoring general port activity messages.To monitor an AUDIX Digital remote update:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > AUDIX Digital Monitor.The system displays the AUDIX Port Monitor page. See AUDIX Digital Monitor for information on thefields on the page.
2062. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Monitoring analog remoteupdatesMonitoring analog remote updatesThe process of adding, changing, or deleting subscribers on analog remote machines takes a variable amountof time based on the number of subscribers being updated. The Voice Channel Monitor page allows you tomonitor the progress of the update. This page is also used for monitoring general port activity messages.To monitor an analog remote update:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Analog Monitor.The system displays the Voice Channel Monitor page. For information on the fields on the page, clickHelp..2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Monitoring Octel AnalogNetworking remote updatesMonitoring Octel Analog Networking remote updatesThe process of adding, changing, or deleting subscribers on Octel Analog Networking remote machines takes avariable amount of time based on the number of subscribers being updated. The Octel Analog Update Monitordisplay page allows the system administrator to monitor the progress of the update.To monitor an Octel Analog Networking remote update:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Octel Analog Update Monitor.2. The system displays the Octel Analog Update Monitor page. See Octel Analog Update Monitor forinformation on the fields on the page.3. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Special considerations for Demand Remote UpdateKeep the following special considerations in mind when doing a Demand Remote Pull or Demand Remote Pushinvolving an Octel Analog Networking remote machine:! A remote Octel Analog Serenade system allows application mailboxes to receive messages. Thus, when
207you request a full system update from an Octel Analog Serenade remote machine, Message Networkingis updated with the application mailboxes as well as the subscriber mailboxes.! For example, if the Serenade Analog remote machine has 1000 subscriber mailboxes and 500application mailboxes residing on it, when doing a full system Demand Remote Update, MessageNetworking will have 1500 mailboxes administered on to it.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Monitoring Aria Digital remoteupdatesMonitoring Aria Digital remote updatesThe process of adding, changing, or deleting subscribers on Aria Digital remote machines takes a variableamount of time based on the number of subscribers being updated. The Aria Digital Monitor display page allowsyou to monitor the progress of the update. This page is also used for monitoring general port activity messages.To monitor an Aria Digital remote update:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Aria Digital Monitor.The system displays the Aria Digital Monitor page. See Aria Digital Monitor for information on the fieldson the page.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Monitoring Serenade Digitalremote updatesMonitoring Serenade Digital remote updatesThe process of adding, changing, or deleting subscribers on Serenade Digital remote machines takes a variableamount of time based on the number of subscribers being updated. The Serenade Digital Monitor page allowsyou to monitor the progress of the update. This screen is also used for monitoring general port activitymessages.To monitor a Serenade Digital remote update:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > Serenade Digital Monitor.The system displays the Serenade Digital Monitor page. See Serenade Digital Monitor for information onthe fields on the page.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
208Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Performing acceptance testing > Performing remote updates > Monitoring SMTP port activityMonitoring SMTP port activityYou use the SMTP Port Monitor page to track the use of the SMTP ports. Access this screen when you want toknow if there is any message activity taking place.Unlike the port monitor screens for AMIS, Octel, Aria, and Serenade, you cannot use the SMTP Port Monitor tomonitor subscriber update activity.To monitor SMTP port activity:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Remote Machine<strong>Administration</strong> > Port Monitors > SMTP Digital Monitor.The system displays the SMTP Port Monitor page. See SMTP Digital Monitor for information on the fieldson the page.2. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber administration > Adding a subscriber mailbox manuallyAdding a subscriber mailbox manuallyThis topic provides information on manually adding a subscriber mailbox to the Message Networking system.For additional information on adding and updating Message Networking subscribers, see Adding and updatingsubscribers.To add a subscriber mailbox to the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>.The Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.2. Enter the subscriber's mailbox extension in the Mailbox ID field, and click Validate.The Remote Machine drop-down menu displays.3. Select the remote machine to which the subscriber belongs from the Remote Machine drop-down menu.The parameter fields display.4. Complete the parameter fields. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.5. Click Save to save the subscriber to the system.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
209Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Modifying subscriber parameters manuallyModifying subscriber parameters manuallyThis topic provides information on modifying Message Networking subscriber parameters for an existingsubscriber.To modify subscriber parameters for an existing subscriber:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>.The Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.2. Enter the subscriber's mailbox extension in the Mailbox ID field, and click Validate.The Remote Machine drop-down menu displays.3. Select the remote machine to which the subscriber belongs from the Remote Machine drop-down menu.The current parameter settings for the subscriber display.4. Modify the fields that you want to change. For information on completing the fields, click the field namesor Help on the Web-based administration page.5. Click Save to save the updated subscriber parameters to the system.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Deleting a subscriber manuallyDeleting a subscriber manuallyThis topic provides information on deleting an individual subscriber.Notes:! You can also delete an individual subscriber by entering the same Starting Mailbox ID and EndingMailbox ID on the Delete Subscribers from Range page.! You cannot use this procedure to delete subscribers on INTUITY AUDIX or <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messagingremote machines.To manually delete a Message Networking system subscriber:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong>.The Subscriber Parameter <strong>Administration</strong> page displays.
2102. Enter the subscriber's mailbox extension in the Mailbox ID field and click Validate.The Remote Machine drop-down menu displays.3. Select the remote machine to which the subscriber belongs from the Remote Machine drop-down menu.The parameter fields display.4. Click Delete.A message box confirms the deletion.5. Click OK.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Displaying a subscriber mailboxDisplaying a subscriber mailboxThis topic provides information on displaying Displaying a subscriber mailbox.To display information about a subscriber:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber Parameter Display.The system displays the Subscriber Parameters Display screen.2. Enter the network address of the subscriber for which you want to view information and click Display.The system displays the Subscriber Parameter Display page. For information about the parameter fields,click a field or the Help button on the page.3. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulkAdministering subscribers in bulkMessage Networking allows you to add subscribers in bulk to the Message Networking system. The followingremote machine types support bulk subscriber administration:! AMIS Analog
211! Octel Analog Networking! VPIM! SMTP/MIME (all types except <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging)Bulk subscriber administration involves the following tasks:! Adding subscribers! Deleting subscribers! Changing subscribers from a fileTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Adding subscribers in bulkAdding subscribers in bulkMessage Networking allows you to add subscribers in bulk using the following methods:! Adding subscribers from a file! Adding subscribers from a rangeTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Adding subscribers in bulk >Adding subscribers from a fileAdding subscribers from a fileThis topic provides information on adding subscribers in bulk from a file using FTP.To bulk add subscribers from a file using FTP:1. Create an ASCII file with a text tool, such as Microsoft Notepad.2. Using the following format, type subscriber names and information into the file:remote machine name|extension|name|community ID|namenet type|userID|domain|language IDfor example (where blank indicates no change):internet|7325551212|Smith,John|1|u|jsmith|company.com|en-US
212orInternet|3035551212|Smith,Jane||||Notes:" The name, community ID, namenet type, and language ID are optional." The user ID and email domain are optional for non-SMTP subscribers. The user ID defaults to thenetwork address; the email domain defaults to the Message Networking domain." For each optional parameter that you do not use, you must substitute a "|" character, as shown inthe examples." The language ID defaults to 1 en-US (US English)." The community ID defaults to the default community ID administered for the remote machine." The namenet type defaults to the namenet type administered for the remote machine." The name defaults to: 1 xxxx ." Be sure that there are no blank spaces after the comma or at the beginning or end of each entry.Names are case-sensitive.3. Repeat Step 3 for each subscriber you want to add.Note: If the file to be used for bulk subscriber administration exceeds 100,000 subscribers, break downthe subscriber information into smaller files. Message Networking cannot process more than 100,000subscribers at one time.4. Save the file in the format .add to add subscribers.5. Upload the file to the Message Networking system using an FTP tool you are familiar with:1. In the tool, enter the IP address of the Message Networking system.2. Enter the user ID icftp and the corresponding password for the Message Networking iclog/icftpdirectory.3. Select the subdirectory and move the ftp file to the /sub directory.6. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Bulk Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> > Add Subscribers From File.The Add Subscribers From File page displays.7. Click Add.A confirmation box displays asking if you want to add subscribers from the file.8. Click OK.The system adds all subscriber names. The file created by this process can then be transferred to theMessage Networking system using the FTP process.9. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
213Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Adding subscribers in bulk >Adding subscribers from a rangeAdding subscribers from a rangeMessage Networking allows you to bulk add subscribers from a range.It is important to keep the following considerations in mind when adding subscribers within a range:! When using the Bulk Add by Range feature, you need to limit the range administered on the MessageNetworking system to the actual range (or subranges) used on the remote message server. The range ofmailbox IDs within which you can add subscribers is defined in the dial plan for the remote machine towhich you are adding the subscribers. In some cases, tens of thousands of default subscribers havebeen added for remote machines that actually have only a few hundred subscribers. Having thousands ofdefault subscribers can adversely affect system performance and create additional operational costs.Always use the minimum number of bulk-added subscribers.! Since Aria Digital and Serenade Digital systems support Demand NameSend and INTUITY AUDIXsystems support Demand Remote Update to initialize the Message Networking subscriber database, aBulk Add by Range is never used for these types of machines (nor is any of the other types of addmethods mentioned in this list). In addition, the digital system types notify Message Networking when anew subscriber has been added so that Message Networking can update its directory.! The name, community ID, and language ID are optional.! The user ID and email domain are optional for non-SMTP subscribers. The user ID defaults to thenetwork address; the email domain defaults to the incoming domain administered for the correspondingSMTP machine. It is important that you change the user IDs of SMTP subscribers to the subscribers'actual user IDs on the remote machine so that messages can be sent to and received by the subscribers.! The language ID defaults to en-US (US English).! The community ID defaults to the default community ID administered for the end node.! The name defaults to: 1 xxxx .To add subscribers in bulk from a range:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Bulk Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> > Add Subscribers From Range.The Add Subscribers From Range page displays.2. Select a remote machine from the drop-down list.3. Enter a Starting Mailbox ID and an Ending Mailbox ID. For information on completing the fields, click thefield names or Help on the Web-based administration page.4. Click Add.A confirmation box displays asking if you want to add subscribers from the range.5. Click OK.The system adds all subscribers within the specified range.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
214Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Deleting subscribers in bulkDeleting subscribers in bulkThis topic provides information on deleting subscribers in bulk.You can perform the following bulk delete tasks:! Deleting subscribers from a file! Deleting subscribers within a rangeTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Deleting subscribers in bulk >Deleting subscribers from a fileDeleting subscribers from a fileMessage Networking allows you to bulk delete subscribers from a file using FTP.To delete subscribers in bulk from a file using FTP:1. Create an ASCII file with a text tool, such as Microsoft Notepad.2. Using the following format, type subscriber names and information into the file:remote machine name|mailbox IDfor example:internet|73255512123. Repeat Step 2 for each subscriber you want to delete.Note: If the file to be used for bulk subscriber administration exceeds 100,000 subscribers, break downthe subscriber information into smaller files. Message Networking cannot process more than 100,000subscribers at one time.4. Save the file in the format .del to delete subscribers (for example, subs.del).5. Upload the file to the Message Networking system using an FTP tool you are familiar with:a. In the tool, enter the IP address of the Message Networking system.b. Enter the user ID icftp and the corresponding password for the Message Networking iclog/icftpdirectory.c. Select the subdirectory and move the ftp file to the /sub directory.6. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Bulk Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> > Delete Subscribers From File.The Delete Subscribers From File page displays.7. Click Delete.A confirmation box displays asking if you want to delete subscribers from the file.
2158. Click OK.9. The system deletes all subscriber names.Note: The following files are created during the FTP process:" .log is created through logging actions." .del.done file is created after execution (for example: dog.del.done file.)10. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Deleting subscribers in bulk >Deleting subscribers within a rangeDeleting subscribers within a rangeMessage Networking allows you to delete a range of subscribers at one time.To delete a range of subscribers:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Bulk Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> > Delete Subscribers From Range.The Delete Subscribers From Range page displays.2. Select a remote machine from the Remote Machine drop-down menu.3. Enter a Starting Mailbox ID and an Ending Mailbox ID. For information on completing the fields, click thefield names or Help on the Web-based administration page.4. Click Delete.A confirmation box displays asking if you want to delete subscribers from the range.5. Click OK.The system deletes all subscribers within the specified range.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
216Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Administering subscribers in bulk > Changing subscribers from afileChanging subscribers from a fileMessage Networking allows you to perform bulk changes to subscribers using FTP.To change subscribers in bulk from a file using FTP:1. Create an ASCII file with a text tool, such as Microsoft Notepad.2. Using the following format, type subscriber names and information into the file:remote machine name|extension|name|community ID|namenet type|userID|domain|language IDfor example (where blank indicates no change):internet|7325551212|Smith,John|1|u|jsmith|company.com|en-USorInternet|3035551212|Smith,Jane||||Notes:" The name, community ID, namenet type, and language ID are optional." The user ID and email domain are optional for non-SMTP subscribers. The user ID defaults to thenetwork address; the email domain defaults to the Message Networking domain." For each optional parameter that you do not use, you must substitute a "|" character, as shown inthe examples." The language ID defaults to 1 en-US (US English)." The community ID defaults to the default community ID administered for the remote machine." The namenet type defaults to the namenet type administered for the remote machine." The name defaults to: 1 xxxx ." Be sure that there are no blank spaces after the comma or at the beginning or end of each entry.Names are case-sensitive.3. Repeat Step 3 for each subscriber you want to change.Note: If the file to be used for bulk subscriber administration exceeds 100,000 subscribers, break downthe subscriber information into smaller files. Message Networking cannot process more than 100,000subscribers at one time.4. Save the file in the format .chg to add subscribers.5. Upload the file to the Message Networking system using an FTP tool you are familiar with:1. In the tool, enter the IP address of the Message Networking system.2. Enter the user ID icftp and the corresponding password for the Message Networking iclog/icftpdirectory.3. Select the subdirectory and move the ftp file to the /sub directory.6. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber<strong>Administration</strong> > Bulk Subscriber <strong>Administration</strong> > Change Subscribers From File.The Change Subscribers From File page displays.7. Click Change.A confirmation box displays asking if you want to change subscribers from the file.8. Click OK.The system changes the subscriber information.
2179. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering subscribers > Self-registering subscribersSelf-registering subscribersSubscribers on the following remote machine types can self-register on the Message Networking system byusing a specific network address defined on the Message Networking system to send a message containing avoiced name:! AMIS Analog! Octel Analog Networking! VPIMSMTP subscribers can also self-register (with the exception of <strong>Avaya</strong> Modular Messaging subscribers) bysending a voice message to the Message Networking system with their mailbox ID as the message subject andtheir voiced name as the message contents.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber administration > Adding and updating subscribers overview > Adding remotesubscribers as Lotus Notes usersAdding remote subscribers as Lotus Notes usersThis topic is for administrators on the UM for Lotus Notes 5.0 or later systems only.On Unified Messenger for Lotus Notes 5.0 or later systems, you must administer remote subscribers as userson the Lotus Notes/Domino system. This allows subscribers on the local UM for Lotus Notes system to send TUImessages from the UM system to remote subscribers via Message Networking. You must administer the remotesubscribers like other Lotus Notes users on the local UM system; however, the forwarding and Internet addressmust point to the remote network address via the Message Networking system.Note: The Import Text File option within Lotus Notes/Domino is a file upload utility that you can use to upload allthe remote subscribers. However, you must administer each user to edit their Person Record.To add a remote subscriber as a Lotus Notes user for addressing via the UM TUI:1. From Lotus Domino <strong>Administration</strong>, click the People & Groups tab.The contents of the People & Groups tab displays.2. Click Add Person. This option allows you to add a person with no login capability (a contact).The Person page displays
2183. Enter the following information about the new user:" First name: Type the first name of the user." MI: Type the middle initial of the user." Last name: Type the last name of the user." User Name: Type the user's name and then press Enter to create a new line in the field. In thenew line, type the user's numeric address (for example, UM_NUMERIC:3035551212).4. Click the Mail tab and either:" Select Other Internet System as the Mail System and then enter the Internet address in theForwarding address field (for example, 3035551212@my.company.com)." Select Other as the Mail System and enter the Internet address in the Other Address field.5. Click Save and Close.6. Wait a couple of minutes while the system updates the UM database.7. Using a telephone, log into a local UM mailbox, create a message, and send it to the new remotesubscriber mailbox using the network address (numeric address).If you hear the Text-to-Speech version of the ASCII name, the user was successfully added to thesystem.8. Repeat steps 2 through 7 for each person you need to add as a Lotus Notes user.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber administration > Adding and updating subscribers overview > Adding remotesubscribers as Microsoft Exchange usersAdding remote subscribers as Microsoft Exchange usersThis topic is for administrators on the UM for Microsoft Exchange 5.0 or later systems only.On Unified Messenger for Microsoft Exchange 5.0 or later systems, you must administer remote subscribers asusers on the Microsoft Exchange system. This allows subscribers on the local UM for Microsoft Exchangesystem to send TUI messages from the UM system to remote subscribers via Message Networking.To add a remote subscriber as a Microsoft Exchange user for addressing via the UM TUI:1. On the Microsoft Exchange Server, select Start > Programs > Microsoft Exchange > Active DirectoryUsers and Computers.The Active Directory Users and Computers window displays.2. In the left column, select Users.3. Select Action > New > Contact.The New Object - Contact dialog box displays.4. Enter the First name, Initials (middle initial), and Last name for the new user.The Full name is populated automatically.5. Enter the Display Name (usually the same as the Full Name).6. Click Next.7. Click Modify next to the E-mail address field.The New E-mail Address dialog box displays.
2198. From the New E-mail Address list, select SMTP Address.9. Click OK.The Internet Address Properties dialog box displays.10. On the General tab, enter the E-mail address, such as 2054856173@my.company.com.11. Select the Advanced tab.12. Select the Override Internet Mail Service settings for this recipient checkbox.13. In the MIME section, select Plain Text for Message Body.14. Click OK.15. Click Next.16. Click Finish.17. Wait a couple of minutes while the UM database is updated, then log into a real UM mailbox from atelephone, create a message, and send it to the new remote subscriber mailbox using dial by name.You should hear the Text-to-Speech version of the ASCII name.18. Repeat steps 3 through 17 for each remote subscriber.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise ListsAdministering Enterprise ListsThis topic provides information about administering Enterprise Lists on the Message Networking system. SeeEnterprise Lists overview for basic concepts and features of Enterprise Lists.You can use the following interfaces to administer Enterprise Lists:! The Message Networking Web-based administration interface.! An LDAP client that uses the Message Networking LDAP interface.! Enterprise List administration scripts, which provide a bulk administration tool to add and delete individualnetwork addresses to and from a specified Enterprise List using remote files.Administering Enterprise Lists involves the following tasks. The following procedures all use the Web-basedadministration interface. See LDAP Overview and Administering Enterprise Lists using administration scripts forinformation on the other ways you can administer Enterprise Lists.! Administering system parameters for Enterprise Lists! Administering subscriber permissions for Enterprise Lists! Managing Enterprise Lists" Creating a new Enterprise List" Modifying an Enterprise List" Deleting an Enterprise List" Assigning Enterprise List permissions" Managing Enterprise List membership
220" Sorting Enterprise lists! Generating Enterprise List reports! Running an Enterprise List auditTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Administering system parameters for Enterprise ListsAdministering system parameters for Enterprise ListsThis topic provides information about administering system parameters for Enterprise Lists. Parameters that youestablish on this page (such as ID ranges, subscriber permission definitions, and system delivery schedules)help list users and administrators effectively use Enterprise Lists and system resources. The EnterpriseSubscriber Permission Definition for LDAP client section of this page applies only to lightweight directory accessprotocol (LDAP) client access. Changes that you make on this page control system-wide Enterprise Listparameters.To administer system parameters for Enterprise Lists:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > System Parameters.The system displays the Enterprise Lists System Parameters page.2. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Help onthe Web-based administration page.3. Click Save.The system saves your changes.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Enterprise Lists System ParametersEnterprise Lists System ParametersUse this page to set system-wide parameters for Enterprise Lists. Parameters that you define on this page affectall of the Enterprise Lists in the Message Networking system.Note: You must administer the Enterprise List ID Ranges before you can create Enterprise Lists.This page contains the following fields.
221List ID Length: This field is a display-only field that contains the network address length of Enterprise List IDson the Message Networking system. The network address length is set on the Message Networking GeneralParameters page.Automatic Delivery Status: If the Delivery Status Report? field on the Create a New List page is set to Yes,you can specify when you want the system to automatically send status messages to the originator of themessage. Using 24-hour time, type the days, hours, and minutes that you want the system to wait beforeautomatically sending status messages.Automatic List Audit: Specify whether you want the system to perform automatic List Audits. The List Auditremoves members from Enterprise Lists or permissions lists when they no longer exist in the Enterprise Listmaster directory. Select Yes if you want the system to automatically audit lists. Select No if you do not want thesystem to automatically audit lists. The default for this field is Yes.If you select Yes, the system automatically runs the audit at the default time of 3:30 a.m. However, you canchange the audit time by typing the Hour and Minute (using 24-hour time) that you want to schedule theautomatic list audit. You can also run the audit manually from the List Audit page.<strong>Avaya</strong> recommends that you turn automatic audits off during the process of moving network mailboxes, toensure that subscribers whose mailboxes are being moved will keep the same mailbox ID and be retained inpredefined Enterprise Lists to which they belong.Enterprise List ID Ranges: Use the following fields to define valid ID ranges for Enterprise Lists on theMessage Networking system. You can define as many as ten Enterprise List ID ranges. You cannot create anyEnterprise Lists on the system until you administer this field.Start: Type a valid network address that begins the range of Enterprise List IDs that will be permitted on thesystem.End: Type a valid network address that ends the range of Enterprise List IDs that will be permitted on thesystem.Enterprise Subscriber Permission Definition for LDAP Client: Use the following fields to define permissionsthat you want to assign to Enterprise List members. Subscriber permissions are applicable only for systemsubscribers using an lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) client. If no LDAP clients are involved, you donot need to define permission IDs on this page. Once you define permissions on this page, you can assignthese permissions on the Enterprise Subscriber Permissions for LDAP Clients page.Permission ID: Type the permission ID number that you want to associate with this permission definition.Description: Type a description that you want to associate with this permission definition. When systemparameters are saved, this description is stored with the permission ID that you typed in the previous field.Create List?: Select Yes to allow Enterprise List members with this permission ID to create Enterprise Lists.Select No to deny them this permission.Note: Only those who administer Enterprise Lists through third-party applications via the Message NetworkingLDAP interface can create and update lists.Update List?: Select Yes to allow Enterprise List members with this permission ID to update lists. Select No todeny them this permission.View/Add Self to Subscription-based List?: Select Yes to allow Enterprise List members with this permissionID to view subscription-based lists, and allow them to add themselves to subscription-based lists. Select No todeny them this permission.View Other Members of Subscription-based List?: Select Yes to allow Enterprise List members with thispermission ID to view other members of subscription-based lists. Select No to deny them this permission.Max. Number of Lists: Type the maximum number of lists that you want to authorize Enterprise List memberswith this permission ID to create. This number must be lower than the maximum number of lists for the system.Max. Number of Members in List: Type the maximum number of members that you want to authorizeEnterprise List members with this permission ID to add to lists that they create. This number must be lower thanthe maximum number of members for the system.Report Access?: Select Yes to allow Enterprise List members with this permission ID access to Enterprise ListReports. Select No to deny Enterprise List members with this permission ID access to Enterprise List Reports.
222Enterprise List System Delivery Schedule: Use the following fields to define valid system-wide messagedelivery windows to avoid using the system during peak times. You can define up to three delivery windows. Asan alternative to this feature, you can schedule an Enterprise List message for future delivery to avoid using thesystem during peak times (especially for large lists). Delivery windows cannot overlap, nor can a window have astarting time that is later than the ending time. The default is one delivery window that encompasses all times ofthe day.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.Note: You can configure individual lists to ignore the system delivery schedule from the Change Attributes of AList page.From: Using 24-hour time, in the Hour and Minute fields, type the starting hour and minute for each deliverywindow that you want to define.To: Using 24-hour time, in the Hour and Minute fields, type the ending hour and minute for each deliverywindow that you want to define.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Save: Click this button to save changes you made to the system-wide parameters.! Cancel: Click this button to close this page without saving your changes.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Administering subscriber permissions for LDAP clientsAdministering subscriber permissions for LDAP clientsThis topic provides information about applying permissions to members that allow members to administer anduse Enterprise Lists. Message Networking allows an overall definition of system-level permissions for EnterpriseList members, which lets you customize the administrative permissions. These administrative permissions rangefrom having no permission to permissions to create lists and access list reports of individual subscribers. Youcan grant permissions to an individual or to a range of Enterprise List subscribers using network addresses ornumeric addresses.Note: Subscriber permissions are applicable only for system subscribers using an lightweight directory accessprotocol (LDAP) client. If no LDAP clients are involved, you do not need to assign permissions using this page.The only permission applicable to non-LDAP system subscribers is the Use permission, which is set on theEnterprise List Permissions page.Note: Members must be activated for a certain permission type at the system level before they can be grantedthe same permission at a particular list level.The Permission ID values are defined on the Enterprise List System Parameters page. Possible permissionsinclude:! None (no permission)
223! Create lists! Add/Change/Delete entries on an existing list (when granted permission for that list)! Maximum number of lists (for those granted permission to create lists)! Maximum number of members in list (for those granted permission to create lists)! General report access! View and add self to subscription-based lists (list id, name, number of other subscribers)! View other members of subscription-based listsTo assign permission IDs to subscribers:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Subscriber Permissions for LDAP Client.The system displays the Enterprise Subscriber Permissions for LDAP Client page.2. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.3. Click Save.The system saves your changes.4. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Enterprise Subscriber Permissions for LDAP ClientEnterprise Subscriber Permissions for LDAP ClientUse this page to grant a specific set of permissions (permission ID) to an individual or to a range of EnterpriseList subscribers by network addresses or numeric addresses. The permission IDs that are available from thispage are the ones created on the Enterprise Lists System Parameters page.Note: Subscriber permissions are applicable only for subscribers accessing the system through the MessageNetworking lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) interface. If no LDAP clients are involved, you do notneed to assign permissions using this page.This page contains the following fields.Start Address: Use this field to specify the start address for the address range to which you want to assignpermissions. To grant permissions to an individual, type the Enterprise subscriber address for that individual,and then type that same address in the following field.End Address: Use this field to specify the end address for the address range to which you want to assignpermissions. To grant permissions to an individual, type the same Enterprise subscriber address that you typedin the previous field.Numeric Address Format?: Specify whether you want to use numeric address format for the Start and Endfields. Select Yes if the Enterprise subscriber addresses are numeric addresses, or select No if the addressesare network addresses.Permission ID: Select the permission ID that you want to assign to this subscriber or range of subscribers. Thelisted IDs are the ones that you configure on the Enterprise Lists System Parameters page.
224Permission Description: This display-only field contains the description that corresponds to the Permission IDyou selected in the previous field. This description was associated with the Permission ID on the Enterprise ListsSystem Parameters page.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Save: Click this button to save changes you made to the permissions.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Administering Enterprise Lists using administration scriptsAdministering Enterprise Lists using administration scriptsThis topic provides information about administering Enterprise Lists using Enterprise Lists administration scripts.The Enterprise List administration scripts provide a bulk administration tool to add and delete individual networkaddresses or ranges of addresses to and from a specified Enterprise List.You must complete the following steps to administer Enterprise Lists using administration scripts:1. Create the Enterprise Lists if necessary2. Create the input files3. Transfer the input files to Message Networking4. Execute the administration scriptsCreate the Enterprise ListsIf you are adding subscribers to an Enterprise List, you must create the list, if it does not already exist, beforeproceeding. See Creating a new Enterprise List and complete the steps to create a list on the system.Creating the input filesTwo file formats are supported by Message Networking:! Format Option 1 by List ID: In this format, the filename indicates the ID of the list you want to add ordelete subscribers from, and the file lists the network addresses of the subscribers you want to add ordelete. Use this format when you want to add or delete subscribers to or from an individual EnterpriseList.! Format Option 2 by List ID and subscriber: In this format, the contents of the file specifies the EnterpriseLists IDs as well as the subscribers you want to add or delete from each of the specified lists. Use thisformat when you want to add or delete subscribers to or from multiple Enterprise Lists.
225Format Option 1 by List IDThe following ASCII file names are associated with the format by list ID:! .add to add members(Example: 1234567890.add)! .del to deleted members(Example: 1111112223.del)! .add.log or del.log is created logging list actions(Example: 1234567890.add.log)! .add.done or .del.done is a file created after execution of the script(Example: 1234567890.add or 111112223.del.done)The following is a sample ASCII file format by subscriber that adds an individual subscriber and a range ofsubscribers to a list:9085761111|90857655559085553232In this example, if you create an input file named 1234567890.add with the format listed above, you areinstructing the system to add the listed network addresses to the Enterprise List with the ID 1234567890. Thisformat allows one line for each subscriber or range of subscribers. The last line of the ASCII file format must be.Note: To delete all files within a list ID, the delete file must contain the following:ListID.delallYou must place all on a separate line.Format Option 2 by List ID and List subscriberThe following ASCII file names are associated with the format by string:! .add to add subscribers(Example: cat.add)! .del to delete subscribers(Example: cat.del)! .log is created logging list actions(Example: cat.log)! .add.done or .del.done, which is a file created after execution of the script(Example: cat.add.done or cat.del.done)The following is a sample ASCII file format by list ID and list subscriber:4444444444|73281722225555555555|61486311115555555555|9085761111|9085765555In the example, you specify the ID of the Enterprise List, followed by the subscriber or range of subscribers thatyou want to add or delete. This format allows one line for each subscriber. The last line of the ASCII file formatmust be .
226Transferring the input files to Message NetworkingAfter you create the input files, use FTP to transfer the files from the customer-supplied FTP application installedon a remote system to the /iclog/icftp/elist directory of the Message Networking system. Message Networkingprompts you for the icftp login and password to establish a connection with the customer-supplied FTPapplication software. For information on how to use your FTP application software, see the documentation thatcame with your FTP application software.Executing the Enterprise List administration scriptsComplete the following steps to execute the Enterprise List administration scripts using the input files yougenerated to add or delete subscribers from an Enterprise List:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Execute List <strong>Administration</strong> Script.The system displays the Execute List <strong>Administration</strong> Scripts page, which lists all files inthe /iclog/icftp/elist directory with the .add or .del extension.Note: If the system does not find any files with the proper extensions in the /iclog/icftp/elist directory, thesystem displays a message that no loading files are available.2. Click Execute to implement the changes specified in the input files.The system displays a message when it finishes executing the files and prompts you to transfer the .logfile for additional details.3. Transfer the .log file from the /iclog/icftp/elist directory of the Message Networking system to thecustomer-supplied FTP application. When prompted, enter the icftp login and password.4. Review the file to ensure that the operation completed successfully.5. View the List Detail Report for the Enterprise Lists you modified to verify the membership changes to thelist.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List <strong>Administration</strong> > Execute List <strong>Administration</strong> ScriptsExecute List <strong>Administration</strong> ScriptsUse this page to administer Enterprise Lists using Enterprise Lists administration scripts. The Enterprise Listadministration scripts provide a bulk administration tool to add and delete individual network addresses or arange of network addresses to and from a specified Enterprise List.Before you can execute the Enterprise List administration scripts, you must:1. Create the Enterprise Lists you want to modify if they do not already exist.2. Create the input files that specify the network addresses to be added or deleted from particular EnterpriseLists. See Administering Enterprise Lists using administration scripts for detailed information.3. After you create the input files, you must use FTP to transfer the files from the customer-supplied FTPapplication to the /iclog/icftp/elist directory of the Message Networking system. When prompted, enter the
227icftp login and password.Complete the following steps to execute the Enterprise List administration scripts using the input files yougenerated to add or delete subscribers from an Enterprise List:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Execute List <strong>Administration</strong> Script.The system displays the Execute List <strong>Administration</strong> Scripts page, which lists all files inthe /iclog/icftp/elist directory with the .add or .del extension.Note: If the system does not find any files with the proper extensions in the /iclog/icftp/elist directory, thesystem displays a message that no loading files are available.2. Click Execute to implement the changes specified in the input files.The system displays a message when it finishes executing the files and prompts you to transfer the .logfile for additional details.3. Use FTP to transfer the .log file from the /iclog/icftp/elist directory of the Message Networking system tothe customer-supplied FTP application. When prompted, enter the icftp login and password.4. Review the .log file to ensure that the operation completed successfully.5. View the List Detail Report for the Enterprise Lists you modified to verify the membership changes to thelist.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of this page.! Back: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Execute: Click this button to execute the Enterprise List administration scripts, using the input files youcreated.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Manage Enterprise Lists > Creating a new Enterprise ListCreating a new Enterprise ListThis topic provides information about creating Enterprise Lists that can be used to send messages tosubscribers on the Message Networking system.When you create an Enterprise List, Message Networking assigns a unique virtual mailbox ID to that list. Thismailbox ID remains associated with the Enterprise List and information about the list, such as its name, owner,and other important administrative and usage attributes, are stored as part of the list. Subscribers can use thismailbox ID to forward multimedia messages to other Enterprise List members.The mailbox also has an ASCII list name to facilitate administration and usage. In addition, this mailbox has avoice name that only the list owner has permission to record.To create a new Enterprise List:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists
2282. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page, click Create a New List.The system displays the Create a New List page.3. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.4. Click Save.The system saves the list you created.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Create a New List or Change Attributes of a ListCreate a New List or Change Attributes of a ListUse the Create a New List page to create a new Enterprise List. You must administer Enterprise List ID rangesbefore you can create any Enterprise Lists.Use the Change Attributes of a List page to modify an existing Enterprise List.Note: After you have created or edited an Enterprise List, run a List Detail report to verify the list contents.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This field contains a unique network address that subscribers use to send messages to an EnterpriseList. For an existing list, this field displays the network address for that Enterprise List. When you are creating anew list, use one of the following methods to assign a network address:! Type the network address to assign to this Enterprise List. The length of this network address mustmatch the List ID length on the Enterprise Lists System Parameters page." If the ID length is valid, the system checks whether the ID is already associated with an existingEnterprise List." If the input duplicates an existing network address, the following message is displayed: "xxxx Is anexisting subscriber! Do you want to use the system picked value xxxxx for List ID?" Click OK toaccept this list ID.! Leave this field blank and allow the system to assign a valid List ID. The following message is displayed:"Do you want to use the system picked value xxxxx for List ID?" Click OK to accept this list ID.Note: Do not use 0000000000 to 0000000009 as Enterprise List IDs as these can be reserved for systemmailboxes on some remote machines.Voice Name Recorded: This display-only field indicates whether a voice name has been recorded for thisEnterprise List. The list owner, who must be a valid subscriber on the Message Networking system, is the onlyperson who can record the voice name. To record a voice name for the list, record a priority message for thevoice name mailbox for the Enterprise List.List Name: Use this field to define a name for this Enterprise List. List names can be a maximum of 30characters, including numbers, letters, commas, colons, underscores, and apostrophes.Owner: Type the name or partial name for the subscriber that you want to specify as the owner of thisEnterprise List. If the following Numeric Address Format field is set to Yes, type the numeric address for thesubscriber. Click Look Up. In the following Subscriber Name field, the system displays a list of subscribers,including their subscriber name, network address, and remote machine name.Subscriber Name: This field displays a partial entry from either the Owner or Moderator fields on this page.
229When you click Look Up on the Create a New List or Change Attributes of a List pages, the system displays allsystem subscribers that match the partial entry. From that list, select the subscriber that you want to designateas the owner or moderator, and then click Select. The network address for that subscriber displays in theappropriate field.Note: The owner, who must be a valid subscriber on the Message Networking system, is the only person whocan change the voice name, which is enabled from this page.Numeric Address Format?: This format allows an alternate method for Modular Messaging systems toaddress messages to subscribers on other remote systems. Use this format if members of this list aresubscribers on another remote system. Select Yes to allow system address entries in numeric format for bothowner and moderator. Select No to allow system address entries in network format only for both owner andmoderator.Voice Name ID Active?: If you want to use a voice name for this Enterprise List, select Yes. If you select Yes inthis field, the system requires you to assign a voice name ID in the field that follows. Select No if you do notwant to use a voice name for this Enterprise List.Note: The default voice name for an Enterprise List is the voice name that the list owner has recorded. Torecord a new voice name for the list, record a priority message for the voice name mailbox for the EnterpriseList.Voice Name ID: If the Voice Name field is set to Yes, the system requires a voice name ID for this EnterpriseList. You can assign a network address or allow the system to assign one automatically. Use one of thefollowing methods to define the network address for the voice name mailbox:! Type a valid voice name ID. The system validates the ID length." If the ID length is valid, the system checks whether the ID is already associated with an existingEnterprise List." If the ID you typed duplicates an existing ID, the following message is displayed: "xxxxx Is anexisting subscriber! Do you want to use the system picked value xxxxx for Voice Name ID?" ClickOK to accept this voice name ID.! Leave this field blank and allow the system to assign a valid voice name ID. The following message isdisplayed: "Do you want to use the system picked value xxxxx for Voice Name ID?" Click OK to acceptthis voice name ID.Subscription Based?: Use this field to define whether lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) clients canrequest being added to the list. Select Yes to allow or No to deny LDAP clients the ability to request beingadded to this list.Reply Enable?: Use this field to define whether this list is enabled for replies and the type of replies to allow:! No Reply: When you select this option, message recipients cannot send a reply. When Reply Enable? isset to No Reply, the sender of the Enterprise List message is a system mailbox on the MessageNetworking system, and a no reply earcon is included in the voice message. If a recipient does reply, thereply is sent back to the system mailbox and is deleted.Note: For Modular Messaging, no reply is offered to the recipient.! Reply: When you select this option, message recipients can send a reply to the originator. When ReplyEnable? is set to Reply, the sender of the Enterprise List message is the original sender.! Reply To All: When you select this option, message recipients can send a reply to all recipients of themessage. When Reply Enable? is set to Reply to All, the sender of the Enterprise List message is the listitself, and the option to reply to all is included in the the voice message.Note: Be very careful when using Reply To All. Set this parameter to Yes only if the list size is relatively small.For example, if you send a message to a list comprising 1,000 recipients and this field is set to Reply To All,1,000,000 messages would be generated if everyone replied.Delivery Failure Message?: Use this field to specify whether you want the system to notify message senderswhen recipients do not receive a message. On this page, you can also choose the format for these messages:voice, fax, or text. Voice and text notifications can be delivered in the language that the message senderprefers. However, fax notifications are U.S. English only. Select Yes if you want the system to notify the senderwhen recipients of this Enterprise List do not receive a message. Select No if you do not want the system tonotify the sender when recipients of this Enterprise List fail to receive a message.
230The default for this field is No.Delivery Status Message?: Use this field to specify whether you want the system to notify message senders ofthe status of their messages (sent, delivered, failed, or accessed). On this page, you can also choose the formatfor notifying message senders: voice, fax, or text. Voice and text notifications can be delivered in the languagethat the message sender prefers. However, fax notifications are U.S. English only. Select Yes if you want thesystem to generate delivery status messages for senders who use this Enterprise List. Select No if you do notwant the system to generate delivery status messages for senders who use this Enterprise List.The default for this field is No.Voice?: Use this field to generate delivery failure and delivery status messages in voice format, which can be inthe language that the user prefers. Select Yes if you want the system to generate delivery failure and deliverystatus messages in voice format for this Enterprise List. Select No if you do not want the system to delivermessages in voice format.Fax?: Use this field to generate delivery failure and delivery status messages in fax format. Messagesgenerated in fax format are U.S. English only. Select Yes to generate delivery failure and delivery statusmessages for this Enterprise List in fax format. Select No if you do not want the system to deliver messages infax format.Text?: Use this field to generate delivery failure and delivery status messages in text format, which can be inthe language that the user prefers. Select Yes if you want the system to generate delivery failure and deliverystatus messages in text format for this Enterprise List. Select No if you do not want the system to delivermessages in text format.ELA Filter?: This filter prevents members from receiving duplicate messages when they are referenced in boththe Enterprise List and Enhanced List Application (ELA) lists (INTUITY AUDIX and Modular Messaging with an<strong>Avaya</strong> Message Store systems). Select Yes if you want to apply the ELA filter to this Enterprise List. Select No ifyou do not want to apply the ELA filter. The default for this field is No.Moderator Active?: Use this field to specify whether you want to activate a moderator for this Enterprise List.When a moderator is active, messages sent to that Enterprise List are delivered to the moderator for approvalbefore being sent to the list members. Select Yes if you want to activate a moderator for this Enterprise List.Select No if you do not want to activate a moderator for this Enterprise List.Note: The moderator role is only supported for simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP) or multipurpose Internetmail extension (MIME) systems. A moderator must be a valid subscriber on an SMTP remote machine, such asModular Messaging.Moderator: If the Moderator Active field is set to Yes, type the name or partial name of the subscriber that youwant to specify as the moderator for this Enterprise List. If the following Numeric Address Format field is set toYes, type the numeric address of the subscriber. Click Look Up. In the following Subscriber Name field, thesystem displays a list of subscribers, including their subscriber names, network addresses, and remote machinenames.Subscriber Name: This field displays a partial entry from either the Moderator or Owner fields on this page.When you click Look Up on the Create a New List or Change Attributes of a List pages, the system displays allsystem subscribers that match the partial entry. From that list, select the subscriber that you want to designateas the moderator, and then click Select. The network address for that subscriber displays in the Moderator field.Numeric Address Format?: Select Yes if the address for the moderator is in numeric format. Select No if theaddress for the moderator is in network format.System Delivery Override?:! Select Yes to override the system-wide delivery schedule for this Enterprise List and send messagesimmediately. The system-wide delivery schedule is set on the Enterprise Lists System Parameters page.! Select No to maintain the set system-wide delivery schedule for this Enterprise List.The default for this field is No.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.Creator: This display-only field contains one of the following:! Login ID (if a system administrator created the list)
231! Subscriber network address (if a subscriber created the list through an external third-party LDAP client)Last Updated Time: On the Change Attributes of a List page, this display-only field contains one of thefollowing:! Date and time the Enterprise List was created! Date and time the Enterprise List was most recently modified (this field is populated when you first savethe list, and then updated each time you modify it)The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise Lists page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Save: Click this button to save or update an Enterprise List.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Modifying an Enterprise ListModifying an Enterprise ListThis topic provides information about modifying the settings for an existing Enterprise List, such as changing thelist name or how the list functions in the Message Networking system.To modify an existing Enterprise List:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.2. On the Manage Enterprise List page, select the Enterprise List that you want to modify.3. Click Change Attributes of Selected List.The system displays the Change Attributes of A List page.4. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.5. Click Save.The system saves your changes to the list.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Deleting Enterprise Lists
232Deleting Enterprise ListsThis topic provides information about deleting Enterprise Lists from the Message Networking system.To delete Enterprise Lists:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise List page, select one or more lists that you want to delete. Select contiguouslists by clicking while pressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous lists by clicking while pressing theControl key.3. Click Delete Selected List.4. Click OK to approve this deletion.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Assigning Enterprise List permissionsAssigning Enterprise List permissionsThis topic provides information about managing permissions for Enterprise Lists. Permissions are assigned as asecurity feature to control access to and use of Enterprise Lists. One permission is applicable for systemsubscribers not using the lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) interface:! Use: Lets members send messages using Enterprise Lists, but does not allow members to update lists.The following two permissions are available for use by remote LDAP clients:! All: Gives members all permissions.! Update: Lets members send messages using Enterprise Lists and allows members to update lists.Note: When the Subscription Based parameter on the Enterprise List attributes page is set to Yes for this list,the following two permissions are also available:! Subscribe: Lets members who are LDAP clients add themselves to subscription-based lists.! View: Lets members who are LDAP clients view existing members of subscription-based lists.How you assign permissions differs depending on the interface a system subscriber uses and the role of thatsubscriber in the system.! For system subscribers not using the LDAP interface, the only available list permission is Use. Otherpermissions are restricted for use by remote LDAP clients.! LDAP client subscribers must be administered for a permission at the system level before they can beassigned the same permission at the list level.! List owners have All permission by default.! List moderators have the Use permission by default. Use permission is the minimum level of permissionthat a moderator must have.You can manage permissions for an Enterprise List by:! Range of network address
233! Range of numeric addressTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Administering Enterprise List Permissions > Enterprise ListPermissions By Range Of Network AddressEnterprise List Permissions By Range Of Network AddressUse this page to assign permissions to a selected Enterprise List by a range of network addresses. You canalso delete permissions that have been previously assigned.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.New Network Address Ranges: Under New Network Ranges, define network addresses for the Enterprise Listmembers to whom you want to assign permissions.From: Type the beginning network address for the range of addresses to which you want to assign permissions.To: Type the ending network address for the range of addresses to which you want to assign permissions.Permissions: Select the permissions you want to assign to members.After you enter the ranges of network addresses for the subscribers and chosen their permissions, click Add tovalidate the ranges of network addresses and apply the permissions to the subscribers. You can assignpermissions for up to 10 ranges of network addresses at one time.Existing Permissions by Network Address Ranges: This table lists the current permissions assignments fornetwork address ranges. If you want to delete the permissions assigned to selected ranges of networkaddresses, select an address range and click Delete.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: Click this button to add permissions for new network address ranges entered on this page.! Delete: Click this button to delete permissions for selected existing address ranges.! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List Permissions page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | Close
234Getting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Administering Enterprise List Permissions > Enterprise ListPermissions By Range Of Numeric AddressEnterprise List Permissions By Range Of Numeric AddressUse this page to assign permissions to a selected Enterprise List by a range of numeric addresses. You canalso delete permissions that have been previously assigned.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.New Numeric Address Ranges: Under New Numeric Address Ranges, define the network addresses of theEnterprise List members to whom you want to assign permissions.From: Type the beginning numeric address for the range of addresses to which you want to assign permissions.To: Type the ending numeric address for the range of addresses to which you want to assign permissions.Permissions: Select the permissions you want to assign to members.After you enter the ranges of numeric addresses and chosen their permissions, click Add to validate the rangesof numeric addresses and apply the permissions to the subscribers. You can assign permissions for up to 10ranges of numeric addresses at one time.Existing Permissions by Numeric Address Ranges: This table lists the current permissions assignments fornumeric address ranges. If you want to delete the permissions assigned to selected ranges of numericaddresses, select an address range and click Delete.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: Click this button to add permissions for new numeric address ranges entered on this page.! Delete: Click this button to delete permissions for selected existing address ranges.! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List Permissions page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membershipManaging Enterprise List membershipThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to Enterprise Lists. The systemalso allows you to change the delivery priority for an existing member or delete existing members from a list.Delivery prioritization determines which list members get a message processed or delivered first by remote
235machine or range of network addresses for each Enterprise List. Depending on such things as message size,current traffic, and list size, messages sent to Enterprise Lists can sometimes take a long time to deliver. Thisfeature helps administrators control who on an Enterprise List receives a message first, for example all remotemachines at headquarters.Message Networking provides ten criteria by which to administer delivery priority and Enterprise Listmembership. A dynamic record of the membership of each Enterprise List is stored in the system according tothe different criteria used to add members to that list. At the time a message is sent using an Enterprise List, thesystem assembles the appropriate recipients for that list based on its current record of membership criteria.You can add system subscribers or other Enterprise Lists to an Enterprise List using any of the following tencriteria:! Individual network address! Individual numeric address! Subscriber name! Name match! Range of network address! Range of numeric address! Email address! Remote machine name! Community ID! Language IDNote: While you can add another Enterprise Lists as a member of a list, Enterprise Lists can be a maximum oftwo levels. This means that only one level of embedded lists is supported. For example, if List B is embeddedwithin List A, then List B cannot include any embedded lists.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by individual network addressAdding Enterprise List members by individual network addressThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirindividual network addresses. You can also delete existing list members or change their message deliverypriority.A network address is a value that is fixed in length and formulated from the dial plan mapping of a subscriber’smailbox ID.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using individual network addresses:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select the existing
236Enterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Individual Network Address.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Individual Network Address page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new network addresses.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing network addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Individual Network Address page, select one or more networkaddresses from the Existing Network Addresses as List Members table. Select contiguous networkaddresses by clicking while pressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous network addresses by clickingwhile pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The network addresses are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing network addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Individual Network Address page, select one or more networkaddresses from the Existing Network Addresses as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Individual Network AddressEnterprise List Members By Individual Network AddressUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List by their individual networkaddresses. From this page, you can also delete existing list members or change their message delivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.New Network Addresses: Under New Network Addresses, define the network addresses of subscribers thatyou want to add to this Enterprise List.Address: Type the individual network address of the subscriber that you want to add to this Enterprise List. You
237can add up to ten individual network addresses at a time.Priority: Delivery priority levels define the order in which Enterprise List members receive messages. Memberswith high delivery priority receive messages first.! Select Normal to set the delivery priority for each individual network address to normal.! Select High to set the delivery priority for each individual network address to high.The default for this field is Normal.Existing Network Addresses As List Members: This table lists the existing members of the selectedEnterprise List by their individual network address and their assigned delivery priority. Any additional networkaddresses that you add to the selected Enterprise List are also displayed here. You can delete or change thedelivery priority of existing network addresses using the Delete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of thepage.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have entered the network addresses for the subscribers and selected their deliverypriority, click this button to validate individual network addresses and add subscribers with those networkaddresses as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete selected existing individual network addresses from this Enterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for existingindividual network addresses that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by individual numeric addressAdding Enterprise List members by individual numeric addressThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirindividual numeric addresses. You can also delete existing list members or change their message deliverypriority.A numeric address is an alternate method for Modular Messaging systems to address messages to subscriberson other remote systems.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using individual numeric addresses:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select the existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.
2383. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Individual Numeric Address.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Individual Numeric Address page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new numeric addresses.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing numeric addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Individual Numeric Address page, select one or more numericaddresses from the Existing Numeric Addresses as List Members table. Select contiguous numericaddresses by clicking while pressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous numeric addresses by clickingwhile pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The numeric addresses are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing numeric addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Individual Numeric Address page, select one or more numericaddresses from the Existing Numeric Addresses as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Individual Numeric AddressEnterprise List Members By Individual Numeric AddressUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List by their individual numericaddresses. From this page, you can also delete existing list members or change their message delivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.New Numeric Addresses: Under New Numeric Addresses, define the numeric addresses of subscribers thatyou want to add to this Enterprise List.Address: Type the individual numeric address of the subscriber that you want to add to this Enterprise List. Youcan add up to ten individual numeric addresses at a time.
239Priority: Delivery priority levels define the order in which Enterprise List members receive messages. Memberswith high delivery priority receive messages first.! Select Normal to set the delivery priority for each individual numeric address to normal.! Select High to set the delivery priority for each individual numeric address to high.The default for this field is Normal.Existing Numeric Addresses As List Members: This table lists existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by their individual numeric address and their assigned delivery priority. Individual numeric addresses thatyou add to the selected Enterprise List are also displayed here. You can delete or change the delivery priority ofexisting numeric addresses using the Delete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have entered the numeric addresses for the subscribers and selected their deliverypriority, click this button to validate individual numeric addresses and add subscribers with those numericaddresses as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete selected existing individual numeric addresses from this EnterpriseList.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for existingindividual numeric addresses that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists >Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by subscriber nameAdding Enterprise List members by subscriber nameThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirindividual subscriber names. You can also delete existing list members or change their message deliverypriority.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using individual subscriber address:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, existing members of the selected Enterprise List are displayed by
240each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes under CurrentList Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Subscriber Name.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Subscriber Name page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new members.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing Enterprise List members:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Subscriber Name page, select one or more system subscribernames from the existing list members table. Select contiguous subscriber names by clicking whilepressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous subscriber names by clicking while pressing the Controlkey.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The system subscribers are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing Enterprise List members:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Subscriber Name page, select one or more system subscribernames from the existing list members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Subscriber NameEnterprise List Members By Subscriber NameUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List by their individualsubscriber names. From this page, you can also delete existing list members or change their message deliverypriority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address of the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.Enter Subscriber Name: Complete this field in one of the following ways:! Type the full or partial subscriber name that you want to add to the list, and then click Display. After thefollowing Subscriber Name field, the system displays a list of matching system subscribers, including theirsubscriber name, network address, numeric address, and remote machine name.! Type the name (full or partial) of other Enterprise Lists to embed them in this list.Note: Partial subscriber and Enterprise List names can include ? and *.
241! The question mark represents one character.! The asterisk can represent multiple characters.For example, if you enter only alpha characters as a partial entry, the system will only find matches fornames that start with that exact string. If you enter a string that includes a question mark, the system willfind matches for that string, including all variables for the question mark. If you enter a string preceded byan asterisk, the system will find all names that include that string.Existing Subscriber Names as List Members: This table lists current members of the selected Enterprise Listand includes their subscriber names, network and numeric addresses, remote machine names, and deliverypriority. When you add new members to this Enterprise List, their information is added to this table.Subscriber Name: This field displays a partial entry from the Enter Subscriber Name field on this page. Whenyou click Display, the system displays a list of all subscribers that match the partial entry. From that list, selectone or more subscribers that you want to add to the list, and then click Add. The system updates the page toshow the new list members.Add: After you have selected one or more subscribers, click this button to validate subscriber names and addvalid subscribers as members of the selected Enterprise List.Cancel: Click this button if you do not want to add any of the subscribers from the Subscriber Name list asmembers of the selected Enterprise List.The following buttons appear on this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Delete: Click this button to delete selected members from this Enterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for selectedmembers of this Enterprise List.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by name matchAdding Enterprise List members by name matchThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirnames. You can also delete existing name match strings or change their message delivery priority.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using name match strings:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.
2423. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Name Match.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Name Match page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new members.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing Enterprise List members:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Name Match page, select one or more system subscriber namesfrom the existing list members table. Select contiguous subscriber names by clicking while pressing theShift key; select non-contiguous subscriber names by clicking while pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The system subscribers are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing Enterprise List members:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Name Match page, select one or more system subscriber namesfrom the existing list members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Name MatchEnterprise List Members By Name MatchUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using name match strings.From this page, you can also delete existing name match strings or change their message delivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.Name Match String: Type a partial or whole name match string for the subscribers that you want to add to thisEnterprise List. You can add up to ten name match strings at a time.Note: Name match strings can include ? and *.! The question mark represents one character.
243! The asterisk can represent multiple characters.Priority: Delivery priority levels define the order in which Enterprise List members receive messages. Memberswith high delivery priority receive their messages first.! Select Normal to set the delivery priority to normal for each name match string.! Select High to set the delivery priority to high for each name match string.The default for this field is Normal.Existing name match strings of the selected Enterprise List and their assigned delivery priority are displayed inthe table on this page. Name match strings that you add to the selected Enterprise List will also be displayedhere. You can delete or change the delivery priority of existing Name match strings using the Delete and TogglePriority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have entered name match strings for subscribers and selected their delivery priority, clickthis button to validate name strings and add subscribers with valid name strings as members of theselected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete the existing name match strings that you selected from this EnterpriseList.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for the existingname match strings that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! View List Detail: Click this button to see all Enterprise List members that have been added to thisEnterprise List by name match. The View List Details page contains the following fields:" Subscriber Name" Network Address" Numeric Address" Email Address! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of page
244Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by range of network addressAdding Enterprise List members by range of network addressThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirnetwork addresses. You can also delete existing network address ranges or change their message deliverypriority.Note: You cannot embed existing lists in an Enterprise List using ranges of network addresses. Existing listscan only be embedded in an Enterprise List using individual addresses. Enterprise Lists can be a maximum oftwo levels, meaning that only one level of embedded lists is supported. For example, if List B is embeddedwithin List A, then List B cannot include any embedded lists.A network address is a value that is fixed in length and formulated from the dial plan mapping of a subscriber’smailbox ID.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using range of network address:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Range of Network Address.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Range of Network Address page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new network address range or ranges.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing ranges of network addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Range of Network Address page, select one or more networkaddress ranges from the Existing Network Address Ranges as List Members table. Select contiguousranges of network addresses by clicking while pressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous ranges ofnetwork addresses by clicking while pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The network address ranges are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing ranges of network addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Range of Network Address page, select one or more networkaddress ranges from the Existing Network Address Ranges as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.
2453. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Range Of Network AddressEnterprise List Members By Range Of Network AddressUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using a range of networkaddresses. From this page, you can also delete existing network address ranges or change their messagedelivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.New Network Address Ranges: Under New Network Address Ranges, define the network addresses ofsubscribers that you want to add to this Enterprise List. You can add up to ten ranges of network addresses at atime.Note: You cannot embed existing lists in an Enterprise List using ranges of network addresses. Existing listscan only be embedded in an Enterprise List using individual addresses.From: Type the beginning network address for the range of subscribers that you want to add to this EnterpriseList.To: Type the ending network address for the range of subscribers that you want to add to this Enterprise List.Priority: Delivery priority levels define the order in which Enterprise List members receive their messages.Members with high delivery priority receive their messages first.! Select Normal to set the delivery priority to normal.! Select High to set the delivery priority to high.The default for this field is Normal.Existing Network Address Ranges As List Members: This table lists existing network address ranges of theselected Enterprise List along with their assigned delivery priority. Network address ranges that you add to theselected Enterprise List will also be displayed here. You can delete or change the assigned delivery priority ofexisting network address ranges using the Delete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have entered the ranges of network addresses for the subscribers and selected theirdelivery priority, click this button to validate address ranges and add subscribers within those addressranges as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete the existing network address ranges that you selected from thisEnterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for existingnetwork address ranges that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.
246! View List Detail: Click this button to see all Enterprise List members that have been added to thisEnterprise List by range of network address. The View List Details page contains the following fields:" Subscriber Name" Network Address" Numeric Address" Email Address! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by range of numeric addressAdding Enterprise List members by range of numeric addressThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirnumeric addresses. You can also delete existing numeric address ranges or change their message deliverypriority.Note: You cannot embed existing lists in an Enterprise List using ranges of numeric addresses. Existing listscan only be embedded in an Enterprise List using individual addresses.A numeric address is an alternate method for Modular Messaging systems to address messages to subscriberson other remote systems.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using range of numeric address:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, existing members of the selected Enterprise List are displayed byeach of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes under CurrentList Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Range of Numeric Address.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Range of Numeric Address page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new numeric address range or ranges.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing ranges of numeric addresses:
2471. From the Enterprise List Members By Range of Numeric Address page, select one or more numericaddress ranges from the Existing Numeric Address Ranges as List Members table. Select contiguousranges of numeric addresses by clicking while pressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous ranges ofnumeric addresses by clicking while pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The numeric address ranges are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing ranges of numeric addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Range of Numeric Address page, select one or more numericaddress ranges from the Existing Numeric Address Ranges as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Range Of Numeric AddressEnterprise List Members By Range Of Numeric AddressUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using a range of numericaddresses. From this page, you can also delete existing numeric address ranges or change their messagedelivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.New Numeric Address Ranges: Under New Numeric Address Ranges, define the numeric addresses ofsubscribers that you want to add to this Enterprise List. You can add up to ten ranges of numeric addresses at atime.Note: You cannot embed existing lists in an Enterprise List using ranges of numeric addresses. Existing listscan only be embedded in an Enterprise List using individual addresses.From: Type the beginning numeric address for the range of subscribers that you want to add to this EnterpriseList.To: Type the ending numeric address for the range of subscribers that you want to add to this Enterprise List.Priority: Delivery priority levels define the order in which Enterprise List members receive messages. Memberswith high delivery priority receive their messages first.! Select Normal to set the delivery priority to normal.! Select High to set the delivery priority to high.The default for this field is Normal.Existing Numeric Address Ranges As List Members: This table lists existing numeric address ranges of the
248selected Enterprise List along with their assigned delivery priority. Numeric address ranges that you add to theselected Enterprise List will also be displayed here. You can delete or change the assigned delivery priority ofexisting numeric address ranges using the Delete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have entered the ranges of numeric addresses for the subscribers and selected theirdelivery priority, click this button to validate address ranges and add subscribers within those addressranges as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete selected existing numeric address ranges from this Enterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for the existingnumeric address ranges that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! View List Detail: Click this button to see all Enterprise List members that have been added to thisEnterprise List by range of numeric address. The View List Details page contains the following fields:" Subscriber Name" Network Address" Numeric Address" Email Address! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by email addressAdding Enterprise List members by email addressThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theiremail addresses. You can also delete existing list members or change their message delivery priority.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using email addresses:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.
2494. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Email Address.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Email Address page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new members.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing email addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Email Address page, select one or more email addresses from theexisting list members table. Select contiguous email addresses by clicking while pressing the Shift key;select non-contiguous email addresses by clicking while pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The email addresses are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing email addresses:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Email Address page, select one or more email addresses from theexisting list members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Email AddressEnterprise List Members By Email AddressUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using email addresses.From this page, you can also delete existing list members or change their message delivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise ListEmail Address: Type the email addresses of the subscribers that you want to add to this Enterprise List. Youcan add up to ten email addresses at a time.Priority: Delivery priority levels define the order in which Enterprise List members receive their messages.Members with high delivery priority receive their messages first.! Select Normal to set the delivery priority to normal.! Select High to set the delivery priority to high.The default for this field is Normal.Existing Email Addresses As List Members: This table lists existing members of the selected Enterprise Listby their email addresses and assigned delivery priority. Any members that you add to the selected EnterpriseList will also be displayed here. You can delete or change the delivery priority of existing list members using the
250Delete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have entered email addresses for subscribers and selected their delivery priority, click thisbutton to validate email addresses and add subscribers with those email addresses as members of theselected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete the existing members that you selected from this Enterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for existingmembers that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by remote machine nameAdding Enterprise List members by remote machine nameThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List usingremote machine names. You can also delete existing remote machine names or change their message deliverypriority.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using remote machine names:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select the existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Remote Machine Name.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Remote Machine Name page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new remote machine names.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing remote machines:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Remote Machine Name page, select one or more remote machine
251names from the Existing Remote Machines as List Members table. Select contiguous machine names byclicking while pressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous machine names by clicking while pressing theControl key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The remote machines are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing remote machines:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Remote Machine Name page, select one or more remote machinenames from the Existing Remote Machines as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Remote Machine NameEnterprise List Members By Remote Machine NameUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using remote machinenames. From this page, you can also delete existing remote machine names or change their message deliverypriority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.Remote Machine List: Select the remote machine that you want to use to add members to this Enterprise List.Existing Remote Machines As List Members: This table lists existing remote machine names of the selectedEnterprise List along with their assigned delivery priority. Remote machine names that you add to this EnterpriseList will also be displayed here. You can delete or change the delivery priority of existing remote machinenames using the Delete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have selected remote machine names, click this button to validate remote machinenames and add valid remote machine names as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete the existing remote machines that you selected from this EnterpriseList.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for the existingremote machines that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.
252Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by community IDAdding Enterprise List members by community IDThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theircommunity IDs. You can also delete existing community IDs or change their message delivery priority.A community is a group of telephone users administered with special send-and-receive messaging capabilities.Typically, a community consists of people who need full access to each other by telephone on a frequent basis.If a remote machine supports community IDs, you can use these IDs to add subscribers from that remotemachine as members of an Enterprise List.To add Enterprise List members using community IDs:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Community ID.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Community ID page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new community IDs.7. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing community IDs:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Community ID page, select one or more community IDs from theExisting Community ID as List Members table. Select contiguous community IDs by clicking whilepressing the Shift key; select non-contiguous community IDs by clicking while pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The community IDs are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing community IDs:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Community ID page, select one or more community IDs from theExisting Community ID as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default value
253is Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Community IDEnterprise List Members By Community IDUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using community IDs.From this page, you can also delete existing community IDs or change their message delivery priority.A community is a group of telephone users administered with special send-and-receive messaging capabilities.Typically, a community consists of people who need full access to each other by telephone on a frequent basis.If a remote machine supports community IDs, you can use these IDs as a criteria for adding subscribers fromthat remote machine as members of an Enterprise List.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.Community ID List: Select the community IDs that you want to use to add members to this Enterprise List.Existing Community ID As List Members: This table lists existing members of the selected Enterprise List bytheir community ID number and assigned delivery priority. Community IDs that you add to this Enterprise Listwill also be displayed here. You can delete or change the delivery priority of existing community IDs using theDelete and Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have selected community IDs, click this button to validate community IDs and add validcommunity IDs as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete selected existing community IDs from this Enterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either high or normal for existingcommunity IDs that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of page
254Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List membership > Adding Enterprise Listmembers by language IDAdding Enterprise List members by language IDThis topic provides information about adding Message Networking subscribers to an Enterprise List by theirlanguage IDs. You can also delete existing list members or change their message delivery priority. Language IDspecifies the language that a subscriber uses.Note: <strong>Avaya</strong> strongly recommends that messages for large lists be sent during off-peak times. This is especiallytrue when the lists involve analog connectivity due to its slower performance.To add Enterprise List members using language IDs:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > EnterpriseList <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, select an existingEnterprise List for which you want to manage membership.3. Click Manage Memberships of Selected List.The system displays the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.Note: Under Current List Definitions, the system displays existing members of the selected EnterpriseList by each of the criteria that have been used to add members. You can click in any of the boxes underCurrent List Definitions to go directly to the page for administering members by that specific criteria.4. From the Add List Members By Criteria menu, select By Language.The system displays the Enterprise List Members By Language ID page.5. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.6. Click Add. The system updates the page to display the new language IDs.7. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.To delete existing language IDs:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Language ID page, select one or more language IDs from theExisting Language ID as List Members table. Select contiguous language IDs by clicking while pressingthe Shift key; select non-contiguous language IDs by clicking while pressing the Control key.2. Click Delete.3. Click OK. The language IDs are deleted from the selected list.4. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.To change the message delivery priority of existing language IDs:1. From the Enterprise List Members By Language ID page, select one or more language IDs from theExisting Language ID as List Members table.2. Click Toggle Priority to change the assigned delivery priority to either Normal or High. The default valueis Normal.3. Click Back to return to the Add List Members by Criteria page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
255Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Managing Enterprise List Membership > Enterprise ListMembers By Language IDEnterprise List Members By Language IDUse this page to add Message Networking subscribers to the selected Enterprise List using Language IDs.Language IDs specify the language that a subscriber uses. From this page, you can also delete existing listmembers or change their message delivery priority.This page contains the following fields.List ID: This display-only field contains the network address for the selected Enterprise List.List Name: This display-only field contains the name associated with the selected Enterprise List.Available Language ID List: Select the language IDs that you want to use to add members to this EnterpriseList.Existing Language ID As List Members: This table lists existing members of the selected Enterprise List bytheir language ID number and assigned delivery priority. Language IDs that you add to this Enterprise List willalso be displayed here. You can delete or change the delivery priority of existing language IDs using the Deleteand Toggle Priority buttons at the bottom of the page.The following buttons appear on this page:! Add: After you have selected language IDs, click this button to validate language IDs and add validlanguage IDs as members of the selected Enterprise List.! Delete: Click this button to delete selected existing language IDs from this Enterprise List.! Toggle Priority: Click this button to change the delivery priority to either High or Normal for the existinglanguage IDs that you selected.! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise List Membership page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Sorting Enterprise ListsSorting Enterprise ListsThis topic provides information about sorting existing Enterprise Lists. Sorting Enterprise Lists changes theorder in which they appear on the Manage Enterprise Lists page and makes it easier to find the lists you want toadminister.To sort existing Enterprise Lists on the Message Networking system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise
256List <strong>Administration</strong> > Manage Enterprise Lists.The system displays the Manage Enterprise Lists page.2. On the Manage Enterprise Lists page under Total Number of Enterprise Lists, click Sort Lists.The system displays the Sort Enterprise Lists page.3. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.4. Click Save.The system saves your changes and displays the new sort order on the Manage Enterprise Lists page.Note: Default settings are restored if you do not access the system for one day.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Sort Enterprise ListsSort Enterprise ListsUse this page to sort Enterprise Lists that are displayed on the Manage Enterprise Lists page by selectedcriteria.This page contains the following fields.Sort Order: Use this menu to select the sorting order, either ascending or descending, for both the primary andsecondary sort keys.List Name: Select either the Primary or Secondary sort key to sort by Enterprise List names.List ID: Select either the Primary or Secondary sort key to sort by the network address of each Enterprise List.Owner's Name: Select either the Primary or Secondary sort key to sort by the owner of each Enterprise List.Owner's Address: Select either the Primary or Secondary sort key to sort by the network address of theEnterprise List owner.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Manage Enterprise Lists page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Save: Click this button to save the new sort order. The new sort order is saved for one day. The new sortorder is then displayed on the Manage Enterprise Lists page.Note: Default settings are restored if you do not access the system for one day.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of page
257Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reportsGenerating Enterprise List reportsThis topic provides information about generating Enterprise List reports, which provide helpful information formaintaining and administering Enterprise Lists.Report results can be viewed on the system or saved to a file and later downloaded to remote machines usingFTP.You can generate the following Enterprise List reports.! Delivery Status Report: Provides a status of the delivery, failure, or access of a particular message. Thereport includes information about who sent the message and when it was sent. It also identifies thenumber of intended recipients, how many of those recipients received or accessed the message, and thenumber of recipients to whom the system was unable to deliver the message.! List Detail Report: Generates a list of members who have been defined for a particular Enterprise List.For each member in the list, the report provides a network address, that member's subscriber name, thecommunity ID associated with this subscriber, and the remote machine name associated with the networkaddress.! List Permissions Report: Creates a list of members that have permission to use or administer a particularEnterprise List. For each member in the list, the report includes the subscriber name, network or numericaddress, community ID, the remote machine name associated with the network address, and languageID (which identifies the member's preferred language).! List Summary Report: Summarizes all of the Enterprise Lists that exist on the system. For eachEnterprise List, the report includes its network address, name, owner and network address, mailbox IDassociated with the voice name for the list, number of subscribers, when the list was last used, andwhether a voice name has been recorded.! Subscriber Membership Report: Identifies the lists (by network address and list name) of which asubscriber is a member.! Subscriber Permissions Report: Identifies the Enterprise Lists (by List ID and List Name) that asubscriber has permission to use or administer.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reports > Delivery Status ReportDelivery Status ReportUse the Delivery Status Report page to view the status of the delivery of messages using either the networkaddress of the sender or an Enterprise List ID. This report includes the number of delivered, failed, andaccessed messages. The list below describes the information that this report generates.To generate a Delivery Status Report:
2581. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List<strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List Reports.The system displays the Enterprise List Reports page.2. On the Enterprise List Reports page, click Delivery Status Report.The system displays the Delivery Status Report page.3. Complete the fields on the page:" Sending Network Address: Type the network address of the sender for whom you want togenerate a Delivery Status report. The default for this field is ALL." List ID: Select the list for which you want to generate a Delivery Status Report. The default for thisfield is ALL LIST IDS.4. Click Display. The system displays the Delivery Status Report.The report page contains the following fields.Sending Network Address: Displays the network address of the sender for whom this report was generated.To generate another Delivery Status Report, type the network address of the sender for whom you want togenerate a report. The default for this field is ALL. Be sure to also select the list ID for which you want togenerate a report in the following field.List ID: Displays the list ID for this report. To generate another Delivery Status Report, after you have typed thenetwork address of the sender in the previous field, select the list ID for which you want to generate a report,and then click Display. The default for this field is ALL LIST IDS.The following list describes each item in the report:! List Name: Name associated with this Enterprise List.! List ID: Network address for this Enterprise List.! Used By: Name of the sender of the message.! Network Address: Network address associated with the sender of the message.! Date/Time Used: Date and time when this Enterprise List was last used.! Message ID: Unique numeric identifier assigned to this message by the system.! Intended Recipients: Number of recipients that this Enterprise List designates.! Delivered: Number of messages delivered.! Accessed: Number of messages that message recipients have accessed.Note: Accessed message status is available only for INTUITY AUDIX endpoints.! Failed: Number of messages that Message Networking was unable to deliver.! The following recipients failed to receive this message: Name, network address, and message statefor recipients who have failed to receive the message.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of the Delivery Status Report page:! Back: Click this button to return to Enterprise List Reports page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the Delivery Status Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_delstat). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
259Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reports > List Detail ReportList Detail ReportUse the List Detail Report page to view a list of current members for an Enterprise List. The table belowdescribes the information that this report generates.You can also sort the results of the List Detail Report.To generate a List Detail Report:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List<strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List Reports.The system displays the Enterprise List Reports page.2. On the Enterprise List Reports page, click List Detail Report.The system displays the List Detail Report page.3. Select the List ID, which specifies the list for which you want to generate a List Detail Report.4. Click Display. The system displays the List Detail Report.The report page contains the following fields.List ID: Displays the list ID for this report. To generate another List Detail Report, select the list for which youwant to generate a report, and then click Display.List Name: Displays the name of the Enterprise List for this report.Number of Subscribers: Displays the number of current members for the selected Enterprise List.The following table describes each item in the report.ItemNetworkAddressSubscriberNameNumericAddressCommunity IDRemoteMachineLanguageEmail AddressDescriptionNetwork address associated with the list member.Name associated with the network address of the list member.Numeric address associated with the list member.The identifier for the group of telephone users to which the listmember belongs.Name of the remote machine associated with the networkaddress of the list member.Preferred language of the list member.Email address associated with the list member.You can sort the results of the List Detail Report by clicking Sort at the bottom of the page. The Sort page forthe List Detail Report contains the following fields:Sort Order: Use this menu to select the sorting order, either ascending or descending, for both the primary andsecondary sort keys.Network Address: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by networkaddress.Subscriber Name: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by subscribername.Numeric Address: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by numeric
260address.Community ID: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by community ID.Remote Machine: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by remote machine.Language: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by language.Email Address: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by email address.You can click Save to save the sort order that you selected and return to the List Detail Report results. The newsort order is saved for one day. Click Back to return to the List Detail Report results.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of the List Detail Report page:! Back: Click this button to return to Enterprise List Reports page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Sort Report: Click this button to sort the results of the List Detail Report.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the List Detail Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_list_det). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reports > List Permissions ReportList Permissions ReportUse the List Permissions Report page to view a list of the system subscribers that have permission to use oradminister a selected Enterprise List. The table below describes the information that this report generates. Youcan also sort the results of the List Permissions Report.To generate a List Permissions Report:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List<strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List Reports.The system displays the Enterprise List Reports page.2. On the Enterprise List Reports page, click List Permissions Report.The system displays the List Permissions Report page.3. Select the List ID, which specifies the list for which you want to generate a List Permissions Report.4. Click Display. The system displays the List Permissions Report.The report page contains the following fields.List ID: Displays the list ID for this report. To generate another List Permissions Report, select the list for whichyou want to generate report, and then click Display.List Name: Displays the name of the Enterprise List for this report.The following table describes each item in the report.
261ItemPermissionNetworkAddressSubscriberNameNumericAddressCommunity IDRemoteMachineLanguageDescriptionThe Enterprise List permission assigned to a system subscriber.The network address of the system subscriber.The name of the system subscriber.The numeric address of the subscriber, if applicable.The identifier for the group of telephone users to which thesystem subscriber belongs.Name of the remote machine associated with the networkaddress of the system subscriber.The subscriber's preferred language.You can sort the results of the List Permissions Report by clicking Sort at the bottom of the page. The Sort pagefor the List Permissions Report contains the following fields:Sort Order: Use this menu to select the sorting order, either ascending or descending, for both the primary andsecondary sort keys.Permission: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by subscriber permissiontype.Network Address: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by networkaddress.Subscriber Name: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by subscribername.Numeric Address: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by numericaddress.Community ID: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by community ID.Remote Machine: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by remote machine.Language: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by language.You can click Save to save the sort order that you selected and return to the List Permissions Report results.The new sort order is saved for one day. Click Back to return to the List Permissions Report results.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of the List Permissions Report page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List Reports page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Sort Report: Click this button to sort the results of the List Permissions Report.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the List Permissions Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_list_perm). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
262Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reports > List Summary ReportList Summary ReportUse the List Summary Report page to view a summary of all of the Enterprise Lists currently defined on aMessage Networking system. The table below describes the information that this report generates.Note: This report is generated at 9 p.m. each night. So the report for the current day does not reflect changesmade after 9 p.m. the previous day.To generate a List Summary Report:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List<strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List Reports.The system displays the Enterprise List Reports page.2. On the Enterprise List Reports page, click List Summary Report.The system displays the List Summary Report page.The report page contains the following fields.Report Date: Displays the date and time that you generated the List Summary Report.The following table describes each item in the report.ItemList IDList NameVoiced Name IDOwner IDNumber ofSubscribersLast Used TimeVoiced NameDescriptionNetwork address for the Enterprise List.Name associated with the Enterprise List.Mailbox ID associated with the voice name for theEnterprise List.Network or numeric address associated with the owner ofthe Enterprise List.Number of subscribers on the Enterprise List.Date and time when the Enterprise List was last used.Indicates whether a voiced name is being used for this list.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of the List Summary Report page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List Reports page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the List Summary Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_list_sum). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
263Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reports > Subscriber MembershipReportSubscriber Membership ReportUse the Subscriber Membership Report page to view the Enterprise Lists of which a selected system subscriberis a member. The table below describes the information that this report generates. You can also sort the resultsof the Subscriber Membership Report.To generate a Subscriber Membership Report:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List<strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List Reports.The system displays the Enterprise List Reports page.2. On the Enterprise List Reports page, click Subscriber Membership Report.The system displays the Subscriber Membership Report page.3. Complete the fields on the page:" Enter Address: Type the network address of the subscriber for whom you want to generate aSubscriber Membership Report." Numeric Address Format? Select Yes if the address for the selected subscriber is in numericformat. Select No if the address is in network format.4. Click Display. The system displays the Subscriber Membership Report.The report page contains the following fields:Enter Address: Displays the network address for the system subscriber in this report. To generate anotherSubscriber Membership Report, type the network address of the subscriber for whom you want to generate areport, designate whether or not the subscriber's address is in numeric format, and then click Display.Numeric Address Format? Displays whether or not the selected subscriber's address is in numeric format.Subscriber Name: Displays the name of the system subscriber for this report.The following table describes each item in the report.ItemList IDListNameDescriptionNetwork address for an Enterprise List of which the selected systemsubscriber is a member.Name associated with the Enterprise List.You can sort the results of the Subscriber Membership Report by clicking Sort at the bottom of the page. TheSort page for the Subscriber Membership Report contains the following fields:Sort Order: Use this menu to select the sorting order, either ascending or descending, for both the primary andsecondary sort keys.List ID: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by Enterprise List IDs.List Name: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by Enterprise List names.You can click Save to save the sort order that you selected and return to the Subscriber Membership Reportresults. The new sort order is saved for one day. Click Back to return to the Subscriber Membership Reportresults.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of the Subscriber Membership Report page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List Reports page.
264! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Sort Report: Click this button to sort the results of the Subscriber Membership Report.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the Subscriber Membership Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_sub_mem). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Generating Enterprise List reports > Subscriber PermissionsReportSubscriber Permissions ReportUse the Subscriber Permissions Report page to view the Enterprise Lists that a selected subscriber haspermission to use. The table below describes the information that this report generates. You can also sort theresults of the Subscriber Permissions Report.To generate a Subscriber Permissions Report:1. From the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List<strong>Administration</strong> > Enterprise List Reports.The system displays the Enterprise List Reports page.2. On the Enterprise List Reports page, click Subscriber Permissions Report.The system displays the Subscriber Permissions Report page.3. Complete the fields on the page:" Enter Address: Type the network address for the system subscriber for whom you want togenerate a Subscriber Permissions Report." Numeric Address Format? Select Yes if the address for the selected subscriber is in numericformat. Select No if the address is in network format.4. Click Display. The system displays the Subscriber Permissions Report.The report page contains the following fields.Enter Address: Displays the network address for the system subscriber in this report. To generate anotherSubscriber Permissions Report, type the network address for the system subscriber for whom you want togenerate a report, designate whether or not the subscriber's address is in numeric format, and then clickDisplay.Numeric Address Format? Displays whether or not the selected subscriber's address is in numeric format.Subscriber Name: Displays the name of the system subscriber for this report.The following table describes each item in the report.ItemList IDDescriptionNetwork address for an Enterprise List the selected systemsubscriber has permission to use.
265List Name Name associated with the Enterprise List.Permission The Enterprise List permission assigned to a system subscriber.You can sort the results of the Subscriber Permissions Report by clicking Sort at the bottom of the page. TheSort page for the Subscriber Permissions Report contains the following fields.Sort Order: Use this menu to select the sorting order, either ascending or descending, for both the primary andsecondary sort keys.List ID: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by Enterprise List IDs.List Name: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by Enterprise List names.Permission: Select either the Primary or Secondary Sort key to sort the report results by subscriber permissiontypes.You can click Save to save the sort order that you selected and return to the Subscriber Permissions Reportresults. The new sort order is saved for one day. Click Back to return to the Subscriber Permissions Reportresults.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of the Subscriber Permissions Report page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List Reports page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Sort Report: Click this button to sort the results of the Subscriber Permissions Report.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the Subscriber Permissions Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_sub_perm). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > Running an Enterprise List auditRunning an Enterprise List auditThis topic provides information about running a manual audit of an Enterprise List. Enterprise List audits removefrom a list or permissions list members who no longer exist in the Message Networking master subscriberdirectory. Enterprise List audits delete only those subscribers that have been individually referenced in anEnterprise List. They do not affect subscribers within a range.You can also enable or disable automatic audits from the Enterprise List System Parameters page. <strong>Avaya</strong>recommends that you turn automatic audits off during the process of moving network mailboxes, to ensure thatsubscribers whose mailboxes are being moved will keep the same mailbox ID and be retained in predefinedEnterprise Lists to which they belong.To run an audit on an Enterprise List:1. From the Message Networking Main Menu, select Enterprise List <strong>Administration</strong> > List Audit.The system displays the List Audit page.2. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administration
266page to view more information.3. Click Audit to run the audit on the list you selected.4. Review the contents of the List Audit Report that displays on the page.5. Click Export to File to save the contents of the List Detail Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_list_audit). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the report, click OK.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Enterprise Lists > List AuditList AuditUse this page to run an Enterprise List Audit, which removes members from a list or permissions list who nolonger exist in the Message Networking master subscriber directory. This function deletes only thosesubscribers that have been individually referenced in an Enterprise List. It does not affect subscribers within arange.The audit does not delete Message Networking Enterprise Lists, even if the list contains no members. If asubscriber sends a message to another subscriber who no longer exists in the Message Networking mastersubscriber directory, the sender receives a “Recipient Not Found” message until this audit is executed and thenonexistent subscriber is removed from the network.Note: When the Automate List Audit? field on the Enterprise List System Parameters page is set to Yes, thesystem automatically runs the audit at the default time of 3:30 a.m. You can change the audit time on theSystem Parameters page by typing the hour and minute (using 24-hour time) that you want to schedule theautomatic list audit.This page contains the following field:List ID: Select the list ID of the Enterprise List for which you want to execute the audit from the list of IDsadministered on the system.The following buttons are displayed at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Enterprise List <strong>Administration</strong> page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Audit: Click this button to run the list audit.! Export to File: Click this button to save the contents of the List Audit to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_list_audit). When a message asks whether you want to overwrite any previousversion of the audit, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about this page.Top of page
267Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Call Detail RecordingAdministering Call Detail RecordingThis topic provides information on Call Detail Recording (CDR), which is used to help manage messagenetworks using Message Networking. Administering Call Detail Recording involves the following tasks:! Performing a CDR file transfer! Generating a CDR Subscriber Detail reportNote: CDR is an optional feature. To determine if CDR is enabled on your Message Networking system, seeVerifying feature options.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Call Detail Recording > Performing a CDR File TransferPerforming a CDR file transferThis topic provides information on performing a Call Detail Recording (CDR) file transfer. You can use CDR tocreate a data file that can be downloaded, using the FTP process, from the Message Networking server on toanother system for analyzing and reporting purposes. For more information on FTP, see Message NetworkingFTP <strong>Support</strong>.The Message Networking CDR feature writes a call detail record for each of the following:! Successful delivery of a message from one subscriber to another, including digital, AMIS Analog, andOctel Analog Networking message transfers! Failed delivery of a message from one subscriber to another, including digital, AMIS Analog, and OctelAnalog Networking message transfersOne week's worth of data, on average, is stored on the Message Networking system. The exact length of timefor which this data is to be stored is determined by the value entered in the CDR Retention field on the GeneralParameters page. For a detailed list of the CDR records in format, you can generate a CDR Subscriber Detailreport.Message Networking provides an interface that allows a system to copy CDR data from a CDR file on theMessage Networking system to another system. CDR file transfer is done by using FTP.Complete the following steps to create a CDR file to be used for transferring:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Call DetailRecording > Unload CDR Data.The system displays the Unload CDR Data page.2. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Display.If you previously unloaded the CDR data, a message asks if you want to overwrite the existing CDR data:
268" Click Yes to overwrite the data and display the Unload CDR Data page." Click No if you do not want to continue.Once a CDR file has been transferred from Message Networking to your machine, to verify that thetransfer has taken place, run a cdr directory list on your machine and compare the file (for example, filesize) to the cdr subdirectory under the ICFTP_DIR (iclog/icftp/cdr) directory list on the MessageNetworking system.4. Click Return to Main.CDR file fieldsThe following table provides a description of the fields contained in the CDR file.FieldLength DescriptionRecord Length 3 Length of the call detail record in bytes, including this field (leadingzeroes), but not including line feed. This field provides informationabout the record itself and is not actually stored in the database (193).Record Type 2 Message delivery detail. This field provides information about therecord itself and is not actually stored in the database (04).Record Version 2Version of this record. This field provides information about the recorditself and is not actually stored in the database (04).MessageNetworkingName14 Name of the Message Networking machine generating this record; notactually stored in the database.Message ID 10 Unique number assigned to every message sent within a MessageNetworking system; a combination of message ID, sending date/time,and sending mailbox ID guarantees uniqueness; numbered in chunksof 256 (511-256, etc.).This ID remains unique across Message Networking reboots andserver updates. Numbering is recycled after 10 billion.Delivery Result 2 Indicates the delivery status. See the Delivery Status Codes table for alist of delivery status codes.Number ofDeliveryRetries2 Number of retries to deliver a message (right justified; leading zeroes).Received Date 8 Date when message was received by Message Networking (in theformat yyyymmdd).Received Time 6 Time when message was received by Message Networking (in theformat hhmmss).Sending Date 8 Date when successful delivery or failure occurs (in the formatyyyymmdd).Sending Time 6 Time when successful delivery or failure occurs (in the formathhmmss).SendingNetworkAddress30 Network address of the sending machine.Receiving 30 Network address of the receiving machine.
269NetworkAddressSendingMachine NameReceivingMachine Name24 Name of the sending machine.24 Name of the receiving machine.Voice Size 5 Voice component size in seconds (leading zeroes).Fax Size 3 Fax component size in pages (leading zeroes).Text Size 5 Text component size in KB (leading zeroes).Binary Size 5 Binary component size in KB (leading zeroes).AnnotationSize1 Annotation component size in KB (leading zeroes); the Subject line.Priority 1 Indicates whether the message was sent as a priority message:! 0 - no! 1- yesPrivate 1 Indicates whether the message was sent as a private message:! 0 - no! 1 - yesLine Feed 1 Line feed for record. This is field is not actually stored in the database.Delivery status codesThe following table lists the delivery status codes for the CDR report.Delivery codeDescriptionSuccessful delivery00 Successful delivery60 Extended absence greeting warning61 Reply to previous message (reserved)62 Forwarded message (reserved)Failed delivery01 Connection failure02 Mailbox is full03 Nonexistent subscriber04 Invalid message attributes (message header corrupted, and so on.)05 Permissions failure (recipient is call-answer only)06 Sending restrictions07 Miscellaneous delivery failure
27008 Multimedia delivery failure09 Unsupported media type11 AMIS message length is too long15 Extended absence greeting block16 Message size is too large17 Future delivery failure18 Future expire19 Message component delivery failure20 Message Networking error21 Insufficient disk capacity22 Destination is not accepting calls23 Duplicate subscriberTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Call Detail Recording > Unload CDR DataUnload CDR DataUse the Unload CDR Data page to unload the CDR data.This page contains the following fields.From Date: Type the beginning date, in mm/dd/yy format, to be used for reporting purposes. The default for thisfield is the current date.To Date: Type the ending date, in mm/DD/yy format, to be used for reporting purposes. The default for this fieldis the current date.From Hour: Select the start time, from 0 to 23, to be used for reporting purposes.To Hour: Type the ending time, from 0 to 23, to be used for reporting purposes.The following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Call Detail Recording page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to unload the CDR data and view the output.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of page
271Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > Maintenance > Generating reports > Generating a Call Detail Recording Subscriber Detail reportGenerating a Call Detail Recording Subscriber Detail reportThe Call Detail Recording (CDR) Subscriber Detail report provides traffic information about the voice messagessent by and received by subscribers. This report, which can be used for monitoring, marketing, and billingpurposes, can provide information about:! All the messages a particular subscriber sent during a specified report period! Messages that a particular subscriber sent to a particular recipient! All messages sent to a particular recipient! All messages sent from all subscribers to all recipientsTo access the CDR Subscriber Detail report:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Message Networking <strong>Administration</strong> > Call DetailRecording > Subscriber Detail Report.The system displays the Subscriber Detail Report page.2. Complete the fields on the page. For information on completing the fields, click the field names or Helpon the Web-based administration page.3. Click Display.The system displays the Subscriber Detail Report. The following table provides a description of each fieldcontained in the report.FieldSendingReceivingMessageIDReceivingDate/TimeSendingDate/TimeSize(sec)DescriptionSending network address or mailbox ID specified for reporting. All messages sent bythis subscriber during the date and hour range specified are displayed.Receiving network address or mailbox ID specified for reporting. All messagesreceived by this subscriber during the date and hour range specified are displayed.Unique numeric identifier assigned by the Message Networking for this message.Date (mm/dd/yy) and time (hh:mm) that the message was received (for example,10/01/96 15:35).Date (mm/dd/yy) and time (hh:mm) that the message was sent (for example,10/01/96 12:00).Length of the received or delivered list:! 1 - no list received
272! 2 to 999 - length (in seconds) of a list received by or delivered to MessageNetworking; includes the Message Networking recipient or sender! Indicates whether this message was sent as a priority message.PStatusIndicates whether this message was sent as a private message.Indicates the status of the message.! ok: successful! compo: message component delivery failure (reserved)! conn: failed message because of a connection failure! dfull: insufficient disk capacity! dup: duplicate subscriber! eag_b: subscriber has extended absence greeting block! eag_w: extended absence greeting warning! erfu: destination that is not accepting calls! full: failed message because mailbox is full! futuex: future expire (reserved)! fwd: forwarded message (reserved)! inval: failed message because message contains invalid message attributes(message header corrupted, and so on.)! futur: failed future delivery! II-II: upstream Message Networking error! >len: message size is too large! Len: AMIS message length too long! misc: failed message because of a miscellaneous error! mmed: failed message because subscriber does not support message mediatype! mmfail2: failed message due to an unknown media type! nosub: failed message because subscriber does not exist! nosup: feature not supported (annotation only to AMIS, and so on)! perm: failed message because of a permissions failure! prm: permanent failure! refu: destination is not accepting calls! reply: reply to previous message (reserved)! rest: sending restrictions (community IDs)! restr: failed message because of sending restrictions! tmp: temporary failure4. Click Export to File if you want to export the contents of the Subscriber Detail Report to a file(/iclog/icftp/reports/pr_cdr_subdet). When a message asks if you want to overwrite any previous versionof the report, click OK.5. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
273Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Call Detail Recording > Subscriber Detail ReportSubscriber Detail ReportUse the Subscriber Detail Report page to view the Subscriber Detail report, which provides traffic informationabout the voice messages sent by and received by subscribers. This report, which can be used for monitoring,marketing, and billing purposes, can provide information about:! All the messages a particular subscriber sent during a specified report period! Messages that a particular subscriber sent to a particular recipient! All messages sent to a particular recipient! All messages sent from all subscribers to all recipientsThis page contains the following fields.From Date: Type the beginning date to be used for reporting purposes, in mm/dd/yy format. The default for thisfield is the current date.To Date: Type the ending date to be used for reporting purposes, in mm/dd/yy format. The default for this fieldis the current dateFrom Hour: Select the start time to be used for reporting purposes, from 0 to 23.To Hour: Select the ending time to be used for reporting purposes, from 0 to 23.Sending Network Address: Type a network address, up to 24 digits, to see all the messages received fromthat address. Leave this field at the default setting, ALL, to see all of the messages.Receiving Network Address: Type a network address, up to 24 digits, to see all the messages sent to thisaddress. Leave this field at the default setting, ALL, to see all of the messages.Click Display to generate the report. The following table provides a description of each field contained in thereport.FieldSendingReceivingMessageIDReceivingDate/TimeSendingDate/TimeSize(sec)DescriptionSending network address or mailbox ID specified for reporting. All messages sent by thissubscriber during the date and hour range specified are displayed.Receiving network address or mailbox ID specified for reporting. All messages received by thissubscriber during the date and hour range specified are displayed.Unique numeric identifier assigned by the Message Networking system for this message.Date (mm/dd/yy) and time (hh:mm) that the message was received (for example, 10/01/9615:35).Date (mm/dd/yy) and time (hh:mm) that the message was sent (for example, 10/01/96 12:00).Length of the received or delivered list:! 1: no list received! 2 to 999: length (in seconds) of a list received by or delivered to the Message Networking
274system; includes Message Networking recipient or sender!P Indicates whether this message was sent as a priority or private message:! !: priority message! P: private messageStatusIndicates the status of the message:! ok: successful! compo: message component delivery failure (reserved)! conn: failed message because of a connection failure! dfull: insufficient disk capacity! dup: duplicate subscriber! eag_b: subscriber has extended absence greeting block! eag_w: extended absence greeting warning! erfu: destination that is not accepting calls! full: failed message because mailbox is full! futuex: future expire (reserved)! fwd: forwarded message (reserved)! inval: failed message because message contains invalid message attributes (messageheader corrupted, and so on)! futur: failed future delivery! II-II: upstream Message Networking error! >len: message size is too large! Len: AMIS message length too long! misc: failed message because of a miscellaneous error! mmed: failed message because subscriber does not support message media type! mmfail2: failed message due to an unknown media type! nosub: failed message because subscriber does not exist! nosup: feature not supported (annotation only to AMIS, and so on)! perm: failed message because of a permissions failure! prm: permanent failure! refu: destination is not accepting calls! reply: reply to previous message (reserved)! rest: sending restrictions (community IDs)! restr: failed message because of sending restrictions! tmp: temporary failureThe following buttons appear at the bottom of this page:! Back: Click this button to return to the Call Detail Recording page.! Return to Main: Click this button to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.! Display: Click this button to display the report results.! Export to File: Click this button to export the contents of the Subscriber Detail report to a file. When
275When a message asks if you want to overwrite any previous version of the report, click OK.! Help: Click this button to get information about completing this page.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Using the File Transfer ProtocolUsing the File Transfer ProtocolThe File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a user interface used to transfer files to and from remote network sites.Message Networking provides authenticated FTP access for specific applications, including the following:! Subscriber imports! Enterprise List administration! Report exports! CDR exports! Downloadable service packs (software updates)! Transfer of private MIB for SNMP supportMessage Networking establishes a connection with the customer-supplied FTP application software and uses itwith your remote machine. For information on how to use your FTP application software, see the documentationthat came with your FTP application software.Before you use FTP with Message Networking, you must understand the prerequisites for using FTP and the filenames used with FTP for Message Networking.Note: Message Networking systems are shipped with the FTP feature deactivated by default. If you activateFTP to use it for a task, such as exporting a report, it is recommended that you deactivate it when you completethe task.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Using the File Transfer Protocol > Prerequisites for using FTPPrerequisites for using FTPBefore you can use FTP for Message Networking, you must:! Set the Activate FTP field on the General Parameters page to Yes! Change the default password for the icftp login. Message Networking allows FTP access for the loginname icftp; it does not allow shell access.
276To reset the FTP system password, complete the following:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Password<strong>Administration</strong> > Assign/Change Password.The system displays the Assign/Change Password page.2. Select icftp from the Login menu.3. Type the new password in the New Password field.4. Type the new password again in the Re-enter New Password field.5. Click Save.The password for the FTP process has now been updated.6. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Using the File Transfer Protocol > Message Networking file names for FTPMessage Networking file names for FTPFile Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a user interface used to transfer files to and from remote network sites. MessageNetworking establishes a connection using your FTP application software and uses it with your remote machine.FTP application software is provided by the customer. For information on how to use your FTP applicationsoftware, see the corresponding FTP application software documentation.Message Networking files that use the FTP process are contained in a directory called iclog (/iclog/icftp). Youonly have access to the /iclog/icftp directories and their subdirectories.SubdirectoriesThe subdirectories in the iclog directory contain the Message Networking files that can be transferred.! The subdirectory for subscriber files for AMIS Analog, Octel Analog Networking, VPIM v2, andSMTP/MIME is sub. These files are uploaded to the Message Networking system for bulk administrationby using FTP (and the icftp login) to transfer files.! The subdirectory for Enterprise List files is elist.! The subdirectory for Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) files is mibs.The mibs subdirectory contains Message Networking private MIB definitions for SNMP versions 2c and 3.! The subdirectory for Call Detail Recording (CDR) files is cdr.! The subdirectory for reports for Message Networking administration and Message Networking networkingtraffic report files is reports. These reports are generated by clicking Print on the report pages.Note: To list the iclog subdirectories and files, use the ls -l command. Also, the current working directory isrepresented by a slash (/). The complete path does not display.Subscriber file namesMessage Networking supports the following formats for subscriber files using FTP:! .add to add subscribers
277! .del to delete subscribers! .chg to change subscribers! .add to add Enterprise List subscribers! .del to delete Enterprise List subscribersOnce the system has completed transferring the subscriber files by FTP, the file formats are displayed as:! .add.done! .del.done! .chg.doneThe system also creates a log file using the format .log.Enterprise List File NamesThe following table lists the names of files that Message Networking uses for downloading Enterprise List reportfiles. The directory is /iclog/icftp/reports.Report NameSubscriber Membership ReportSubscriber Permissions ReportList Summary ReportList Detail ReportDelivery Status ReportList Permissions ReportList Audit ReportFile Namepr_sub_mempr_sub_permpr_list_sumpr_list_detpr_delstatpr_list_permpr_list_auditSNMP Files NamesThe following table lists the names of MIB files that Message Networking uses. The directory is /mibs/:! mnMib.txt! avaya_snmp_mib.txt! avaya_oam_mib.txtCDR file namesThe following table lists the names of files that Message Networking uses to download these CDR files.Function/report nameCDR UnloadSubscriber DetailcdrFile namepr_cdr_subdet<strong>Administration</strong> file namesThe following table lists the names of files that Message Networking uses to download Message Networkingadministration report files.
278Report nameFile nameSubscriber ListBy Network AddressBy Mailbox IDBy Remote MachineBy Subscriber NameDynamic Directory ListRemote Machine Listspr_sub_addpr_sub_mboxpr_sub_machpr_sub_namepr_dyn_machpr_rem_machRemote Machine Dial Plan List pr_dialplanNetworking Traffic reports file namesThe following table lists the names of files that Message Networking uses to download Message Networkingintegrated traffic report files.Report nameNetwork LoadPort UtilizationNetwork StatusFile namepr_inteloadpr_inteportpr_intestatTop of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMPAdministering SNMPThis topic provides information on administering the SNMP feature on the Message Networking system. SeeSimple Network Management Protocol overview for information on basic SNMP concepts and features.Before you attempt to administer SNMP Network Management Stations (NMSs) for queries on the MessageNetworking system, make sure that your remote network and the Message Networking system are both TCP/IPenabled. See Administering TCP/IP LAN connectivity for administration procedures.If you want to perform alarm notification via SNMP, you must administer the NMS to which Message Networkingsends alarm notification. See your SNMP NMS application documentation for details about how to complete thistask and confirm communication between the NMS and managed elements.The tasks you must complete to administer SNMP on the Message Networking system depend on the version ofSNMP you are using.Notes:! If you want to use SNMP for alarm notification, you must first transfer the appropriate MIBs to the NMSsyou administer to receive alarm notification.
279! For SNMP versions 1 and 2c, access to SNMP queries is controlled by communities and NMSaddresses. For SNMP version 3, access to SNMP queries is controlled by user IDs.For SNMP versions 1 and 2c, complete the following tasks in the following recommended order:1. Start and enable the SNMP Service2. Configuring MIB-II parameters3. Administering SNMP communities4. Administering SNMP NMSs for queries, if you choose to use SNMP for queries5. Administering SNMP NMSs for alarms (secondary NMS), if you choose to use SNMP for alarms6. Administering the alarm management, if you choose to administer alarm management via SNMP (primaryNMS)For SNMP version 3, complete the following tasks in the following recommended order:1. Start and enable the SNMP Service2. Configuring MIB-II parameters3. Administering SNMP users, if you choose to use SNMP for queries4. Administering SNMP communities, if you choose to use SNMP for alarms5. Administering SNMP NMSs for alarms (secondary NMS), if you choose to use SNMP for alarms6. Administering the alarm management, if you choose to administer alarm management via SNMP (primaryNMS)Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Configuring MIB-II parametersConfiguring MIB-II parametersThis topic provides information about configuring the parameters of the SNMP MIB-II to use it for SNMP servicein the system. The SNMP service must be started in order for the read-only System Descriptor, System ObjectID and System Name fields on this page to display. If the SNMP service is not started, you can start it byclicking Start SNMP Service on this page.To configure the SNMP MIB-II:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> >SNMP MIB-II Parameters.The system displays the SNMP MIB-II Parameters page.2. Complete the System Location and System Contact fields on the page. You can click the field names orclick Help on the Web-based administration page to view more information.3. Click Save.The system saves your changes.4. Click OK to confirm the MIB-II parameters settings.5. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
280Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Transferring <strong>Avaya</strong> MIBs to network management stationsTransferring <strong>Avaya</strong> MIBs to network management stationsThis topic provides information about transferring <strong>Avaya</strong>-provided Management Information Base (MIB) filesfrom the Message Networking system to the appropriate network management stations (NMSs). See SimpleNetwork Management Protocol MIBs for information on the MIBs used by Message Networking.You must use your FTP software to transfer the MIB files to the NMSs. For information on how to use your FTPapplication software, see the corresponding FTP application software documentation. See Message NetworkingFile Transfer Protocol <strong>Support</strong> for information on Message Networking's FTP support.To transfer the <strong>Avaya</strong> MIBs to an NMS:1. Start your FTP software.2. Request access to your Message Networking system via FTP. You will be prompted for the icftppassword. See Administering passwords for information on setting up the icftp login.3. Change to the mibs directory.4. Locate the MIB files you want to transfer in the mibs directory.5. Transfer the appropriate MIB files.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs for queriesAdministering SNMP NMSs for queriesThis topic provides information on administering SNMP NMSs to be used for system queries. You mustadminister NMSs for queries if the NMS from which you want to query the system is running SNMP version 1 or2c. Before administering NMS for queries, you must administer communities. Each NMS configured to query thesystem must be associated with a valid existing community.For SNMP versions 1 and 2c, access to SNMP queries is controlled by communities and NMS addresses. ForSNMP version 3, access to SNMP queries is controlled by user IDs.You can perform the following administrative tasks for SNMP NMSs for queries:! Add an SNMP NMS to the system for queries! Modify an existing SNMP NMS for queries! Delete an existing SNMP NMS for queriesTop of page
281Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering Alarm Management > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs forqueries > Adding a new SNMP NMS for queriesAdding a new SNMP NMS for queriesThis topic provides information about adding new SNMP network management stations (NMSs) for queries ofsystem information. Complete this procedure if you are performing SNMP queries from an NMS running SNMPversion 1 or 2c.Note: You must administer communities before you administer NMSs for queries. Each NMS configured toquery the system must be associated with a valid existing community.To add a new SNMP NMS for queries of system information:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries page.2. Click Add.The system displays the Add New SNMP NMS for Queries page.3. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or click Help on the Web-basedadministration page to view more information.4. Click Save.The system saves your changes.5. Click OK to confirm your changes.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries page with an updated list of NMSscapable of system queries.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs for queries > Modifying an SNMP NMS forqueriesModifying an SNMP NMS for queriesThis topic provides information about modifying an existing SNMP network management station (NMS) forquerying the system.The only modification you can make to an existing NMS for queries it to select a different community. Youcannot change the IP Address or Host Name field of an existing NMS for queries. If you want to change the IPaddress or host name of an NMS for queries, you must delete the NMS for queries and then add it back with thenew IP address or host name.To modify an existing SNMP NMS for queries:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP
282<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for QueriesThe system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries page.2. Select the existing NMS for queries that you want to associate with a different community.3. Click Change.The system displays the Change An Existing SNMP NMS for Queries page.4. Select the community to associate with the selected NMS for queries. You can click the field name orclick Help on the Web-based administration page to view more information.5. Click Save. The system saves your changes.6. Click OK to confirm your changes. The system displays the updated SNMP NMS for Queries page.7. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs for queries > Deleting an SNMP NMS forqueriesDeleting an SNMP NMS for queriesThis topic provides information about deleting an SNMP network management station (NMS) for queries fromthe system.To delete an SNMP NMS for queries from the system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries page.2. Under Allow Access To, select the NMS for queries that you want to delete.3. Click Delete.4. Click OK to confirm this deletion.The system deletes the selected SNMP NMS for queries.5. Click OK to acknowledge the deletion.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Queries page with an updated list of NMSscapable of system queries.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> menu, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of page
283Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs for alarmsAdministering SNMP NMSs for alarmsThis topic provides information about administering SNMP Network Management Stations (NMSs) to monitorsystem alarms. Customer NMSs that are used to monitor system alarms are also referred to as secondaryNMSs.Note: Up to 32 NMSs can be configured to receive (but not to acknowledge) <strong>Avaya</strong> alarm and eventnotifications.If you are administering alarm management via SNMP, see Administering alarm management to set up yourprimary NMS for alarm notification and acknowledgement. You can administer secondary NMSs even if you donot administer Alarm Management to send notification via SNMP.You can perform the following administrative tasks for an SNMP NMS to monitor alarms in the system:! Add an SNMP NMS for alarms to the system.! Modify an existing SNMP NMS for alarms.! Delete an existing SNMP NMS for alarms.! Configuring the minimum alarm severity and alarm suppression for NMSs for queries.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs for alarms > Modifying existing SNMP NMSsfor alarmsModifying existing SNMP NMSs for alarmsThis topic provides information about modifying the community selected for existing SNMP networkmanagement stations (NMSs) capable of monitoring alarms in the system. NMSs can be configured to monitor(but not to acknowledge) alarm and event information in the system.To modify an existing SNMP NMS for alarms in the system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Alarms.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Alarms page.2. In the table on this page, select the SNMP NMS for alarms that you want to modify.3. Click Change.The system displays the Change An Existing SNMP NMS for Alarms page.4. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or Help on the Web-based administrationpage to view more information.5. Click Save.The system saves your changes.
2846. Click OK to confirm changes to the selected community.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Alarms page with an updated list of existingNMSs capable of monitoring system alarms.7. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> menu, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP NMSs for alarms > Deleting SNMP NMSs for alarmsDeleting SNMP NMSs for alarmsThis topic provides information about deleting existing SNMP Network Management Stations (NMSs) capable ofmonitoring alarms in the system. Customer NMSs are referred to as secondary NMSs in the system.To delete an existing SNMP NMS for alarms in the system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Alarms.The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Alarms page.2. In the table on this page, select the SNMP NMS for alarms that you want to delete.3. Click Delete.4. Click OK to confirm this deletion.The system deletes the selected SNMP NMS for alarms.5. Click OK to acknowledge the deletion. The system displays the SNMP NMS <strong>Administration</strong> for Alarmspage with an updated list of NMSs capable of monitoring system alarms.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> menu, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Controlling the SNMP serviceControlling the SNMP serviceThis topic provides information about controlling the SNMP service on the Message Networking system. Fromthis page you can start the SNMP service, you can enable the SNMP service so that it automatically restartswhenever the system is rebooted, and you can disable the SNMP service so that it does not automaticallyrestart when the system is rebooted. The SNMP service allows queries from remote network managementstations (NMSs) via SNMP.The other SNMP service used by Message Networking is SNMPTRAPD. You can view the status of this servicefrom the SNMP Service Control page, but whether the service is running depends on the setting of the
285Acknowledgement Type field on the Alarm Management page.Note: SNMP is a service of the Linux operating system. As long as the SNMP service is enabled on theMessage Networking system, SNMP is available even if Message Networking is disabled or not running.To control the SNMP service:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> >SNMP Service Control.The system displays the SNMP Service Control page.2. In the Select a Service field, select one of the available options:" Stop SNMP Service: Select this option to stop the SNMP service." Start SNMP Service: Select this option to start the SNMP service." Restart SNMP Service: Select this option to restart the SNMP service." Enable SNMP Service: Select this option if you want the SNMP service to automatically restartwhen the system is rebooted." Disable SNMP Service: Select this option if you do not want the SNMP service to automaticallyrestart when the system is rebooted.You can click the field names or click Help on the Web-based administration page to view moreinformation.3. Click Invoke Service.If you stop, start, or enable the service, the system prompts whether you really want to make therequested service change.4. Click OK to confirm the change.If you selected stop, start, or enable, the system displays a message confirming the service change.5. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP communitiesAdministering SNMP communitiesThis topic provides information about administering SNMP communities. The system uses SNMP communitiesas follows:! To authenticate SNMP requests received from NMSs running SNMP version 1 or SNMP version 2c! When sending alarm notifications to NMSsYou can perform the following administrative tasks for SNMP communities:! Add an SNMP community to the system! Modify an existing SNMP community! Delete an existing SNMP community
286Message Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP communities > Adding a new SNMP communityAdding a new SNMP communityThis topic provides information about adding new SNMP communities to the system. The system uses SNMPcommunities as follows:! To authenticate SNMP requests received from NMSs running SNMP version 1 or SNMP version 2c! When sending alarm notifications to NMSsTo add a new SNMP community to the system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. Click Add.The system displays the Add New SNMP Community page.3. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or click Help on the Web-basedadministration page to view more information.4. Click Save.The system saves your changes.5. Click OK to confirm addition of the new community.The system displays the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> page with an updated list of existingcommunities.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP communities > Modifying an SNMP communityModifying an SNMP communityThis topic provides information about modifying the permission assigned to existing SNMP communities.Note: If you change the permission for an existing community, the community no longer has access to thesystem information that it had prior to the change. For example, a community originally set to trap is being usedwith an NMS for alarm management; if you change the community to read-only, the system lets you do it, eventhough the NMS is now assigned a community that does not have access for alarm management.To modify an existing SNMP community:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. In the table on this page, select an SNMP community that you want to modify.
2873. Click Change.The system displays the Change An Existing SNMP Community page.4. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or click Help on the Web-basedadministration page to view more information.5. Click Save. The system saves your changes.6. Click OK to confirm your changes. The system displays the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> page withan updated list of existing SNMP communities.7. Click Back to return to the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> menu, or click Return to Main to return tothe <strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP communities > Deleting an SNMP communityDeleting an SNMP communityThis topic provides information about deleting existing SNMP communities. You can delete any existingcommunity, however you need to be careful to only delete communities that aren't being used by the system.To delete an existing SNMP community:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. In the table on this page, select the SNMP community that you want to delete.3. Click Delete.4. Click OK to confirm the deletion.The system deletes the selected SNMP community.5. Click OK to acknowledge the deletion. The system displays the SNMP Community <strong>Administration</strong> pagewith an updated list of existing SNMP communities.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> menu, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP usersAdministering SNMP usersThis topic provides information about administering SNMP users. You can add SNMP users to the system andgive them secure access to network management stations (NMSs) so that they can make use of Message
288Networking SNMP information.Note: Valid SNMP users can access Message Networking through any NMS that supports SNMP version 3.You can perform the following administrative tasks for SNMP users:! Add an SNMP user to the system! Delete an existing SNMP userMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP users > Adding a new SNMP userAdding a new SNMP userThis topic provides information about adding new SNMP users to the system. Complete this procedure if youare performing SNMP queries from an NMS running SNMP version 3.To add a new SNMP user to the system:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP User <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SNMP User <strong>Administration</strong> page.2. Click Add.The system displays the Add New SNMP User page.3. Complete the fields on the page. You can click the field names or click Help on the Web-basedadministration page to view more information.4. Click Save.The system saves your changes.5. Click OK to confirm addition of the new user.The system displays the SNMP User <strong>Administration</strong> page with an updated list of existing users.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> page, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering SNMP > Administering SNMP users > Deleting an SNMP userDeleting an SNMP userThis topic provides information about deleting existing SNMP users from the system.To delete an existing SNMP user:1. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and then select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP<strong>Administration</strong> > SNMP User <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the SNMP User <strong>Administration</strong> page.
2892. In the table on this page, select the SNMP user that you want to delete.3. Click Delete.4. Click OK to confirm the deletion.The system deletes the selected SNMP user.5. Click OK to acknowledge the deletion. The system displays the SNMP User <strong>Administration</strong> page with anupdated list of existing users.6. Click Back to return to the SNMP <strong>Administration</strong> menu, or click Return to Main to return to the<strong>Administration</strong> menu.Top of pageMessage Networking HelpHome | SearchPrint | Back | Fwd | CloseGetting Started Admin Maintenance ReferenceHome > <strong>Administration</strong> > Administering alarm managementAdministering alarm managementWhen you activate alarm origination, the system sends notification of alarms that occur on the MessageNetworking system to a remote location that you specify, such as the remote service center. MessageNetworking supports alarm notification via SNMP or modem. For Message Networking systems running on theS3400-H server, notification via modem can only occur if the maintenance modem for the RMB is installed andactive.If you are administering alarm management via SNMP, use the Alarm Management page to set up your primarynetwork management station (NMS) for alarm notification. If you want to set up additional NMSs to receivealarm notification, see Administering network management stations for alarms.To set up alarm management:1. Clear all alarms. See Overview of Message Networking alarms for more information.2. Start at the <strong>Administration</strong> menu, and select Basic System <strong>Administration</strong> > Alarming <strong>Administration</strong>.The system displays the Alarm Management page.3. Type the Product ID for the system. See the completed Message Networking planning forms for thisnumber.Caution! The product ID is always a 9-digit number beginning with the number 2. Do not continue withoutthe correct product ID number.4. Verify that Alarm Suppression is set to INACTIVE.Note: You can use the default settings for Alarm Level and Clear Alarm Notification.5. Specify the type of alarm notification to use on this system:" For INADS alarming, set Alarm Origination to INADS. Continue with Step 6." For SNMP alarming, set Alarm Origination to SNMP Continue with Step 7.Note: If you select SNMP in the Alarm Origination field, make sure that you administer SNMP on thesystem.6. If you selected INADS in Step 5, type the Alarm Destination telephone number. Click the field name orHelp to see a complete field description.7. If you selected SNMP in Step 5, complete the Network Management Station, SNMP Community(Context), and Acknowledgement Type fields. Click the field names or Help to see complete fielddescriptions.
290Note: If you are sending Message Networking alarm notifications via SNMP to an <strong>Avaya</strong> Fault andPerformance Manager (FPM), you must select ping surround in the Acknowledge Type field.8. Click Save.9. Click Return to Main to return to the <strong>Administration</strong> menu.10. Run the Alarm Origination Test to verify that alarm origination is functioning properly.Notes: If you are setting up alarm notification via the modem:! Alarm origination via modem can be set only up on COM2, so the COM2 port must be activated beforeyou perform alarm management.! If you purchase the <strong>Avaya</strong> Communication Manager Fault and Performance Manager, you mustconfigure the Install Modem/Terminal Software page to comply with the MFPM modem as follows:" Select Other in the Modem Type field." Select 9600 in the Speed field" In the Modem Init String field, type the following (entry is case-sensitive and all 0s are zeros) :AT&F&M0Q2&C1&D2&R1&H0&U2&N2&K0S0=0S13=1Y0&W0Top of page