Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual - Acme Fluid Handling
Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual - Acme Fluid Handling
Installation, Operation & Maintenance Manual - Acme Fluid Handling
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
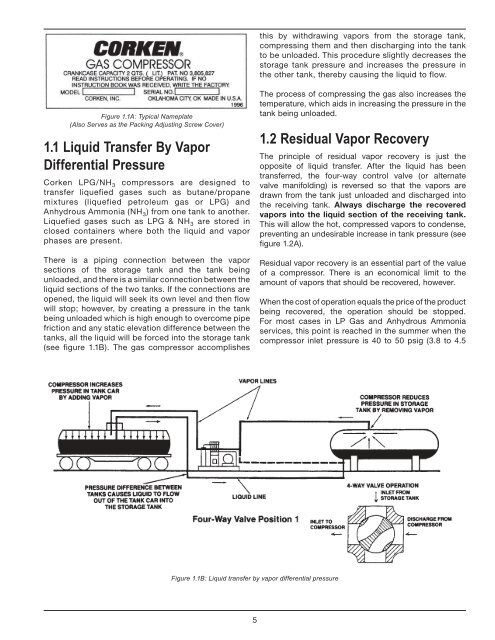
this by withdrawing vapors from the storage tank,compressing them and then discharging into the tankto be unloaded. This procedure slightly decreases thestorage tank pressure and increases the pressure inthe other tank, thereby causing the liquid to flow.Figure 1.1A: Typical Nameplate(Also Serves as the Packing Adjusting Screw Cover)1.1 Liquid Transfer By VaporDifferential PressureCorken LPG/NH 3 compressors are designed totransfer liquefied gases such as butane/propanemixtures (liquefied petroleum gas or LPG) andAnhydrous Ammonia (NH 3 ) from one tank to another.Liquefied gases such as LPG & NH 3 are stored inclosed containers where both the liquid and vaporphases are present.There is a piping connection between the vaporsections of the storage tank and the tank beingunloaded, and there is a similar connection between theliquid sections of the two tanks. If the connections areopened, the liquid will seek its own level and then flowwill stop; however, by creating a pressure in the tankbeing unloaded which is high enough to overcome pipefriction and any static elevation difference between thetanks, all the liquid will be forced into the storage tank(see figure 1.1B). The gas compressor accomplishesThe process of compressing the gas also increases thetemperature, which aids in increasing the pressure in thetank being unloaded.1.2 Residual Vapor RecoveryThe principle of residual vapor recovery is just theopposite of liquid transfer. After the liquid has beentransferred, the four-way control valve (or alternatevalve manifolding) is reversed so that the vapors aredrawn from the tank just unloaded and discharged intothe receiving tank. Always discharge the recoveredvapors into the liquid section of the receiving tank.This will allow the hot, compressed vapors to condense,preventing an undesirable increase in tank pressure (seefigure 1.2A).Residual vapor recovery is an essential part of the valueof a compressor. There is an economical limit to theamount of vapors that should be recovered, however.When the cost of operation equals the price of the productbeing recovered, the operation should be stopped.For most cases in LP Gas and Anhydrous Ammoniaservices, this point is reached in the summer when thecompressor inlet pressure is 40 to 50 psig (3.8 to 4.5Figure 1.1B: Liquid transfer by vapor differential pressure5