Download - Yemen Humanitarian Response | YEMEN
Download - Yemen Humanitarian Response | YEMEN
Download - Yemen Humanitarian Response | YEMEN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
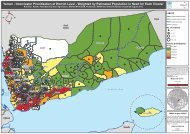
In the mountain, significantly low proportion of stunting were found among children inhouseholds where caretakers reported practicing hand washing before meal (X 2 :10.298,p=0.001). This result may suggest that children in households where caretakers not practicinghand washing before meal suffered from longer and repeated episodes of childhood illnessesincluding diarrhea which is detrimental to their long-term nutritional status. It is, therefore,important to share and act on information about the importance of hand washing using soapbefore meal.The proportion of households defecating in the open field was also high, especially in Lowlandzone suggesting the need for active campaign for behavioral change communication. Hygienepromotion is a key intervention contributing to health and eventually better nutrition wellbeingof the population5.6. Education of caregiversEducation is one of the most important resources that enable women to provide appropriatecare for their children, which is an important determinant of children’s growth anddevelopment. Many studies show a decreased incidence of malnutrition among young childrenwith an increase in the level of mothers' education. However, there was not significantassociation found between education level of care givers’ and all the nutrition indices in Lahjsurvey.5.7. Cross Cutting Issues (Gender)Highly significant (p=0.000) gender disparity has been observed in the prevalence of acutemalnutrition between boys and girls. The prevalence of acute malnutrition in Lowland zone wassignificantly higher among boys than girls. Therefore, sex-related parental care giving behaviorneeds further exploration.6. CONCLUSIONOf the two ecological surveyed, Lowland presented a critical nutrition situation with GAM at23.0% and SAM estimated at 4.5%. The Mountainous zone presented a serious nutritionsituation with GAM and SAM estimates of 14.3% and 2.8%, respectively and in the presence ofaggravating factors such as acute food insecurity, suboptimal vitamin A supplementationcoverage, and childhood morbidity considered as high.52