Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
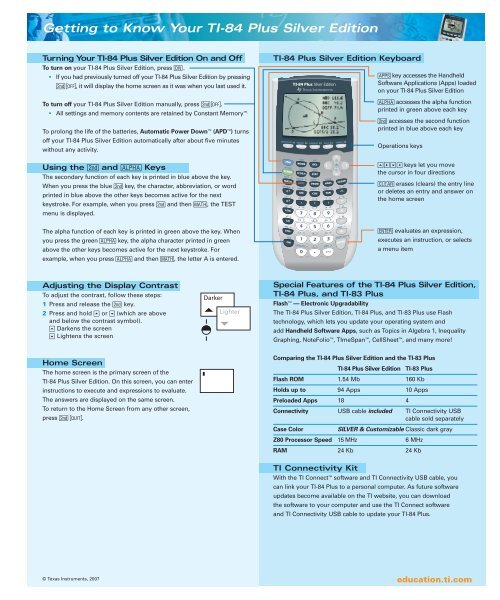
Getting to Know Your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionTurning Your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition On and OffTo turn on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition, press ….■If you had previously turned off your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition by pressingy M, it will display the home screen as it was when you last used it.To turn off your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition manually, press yM.■All settings and memory contents are retained by Constant Memory .To prolong the life of the batteries, Automatic Power Down (APD ) turnsoff your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition automatically after about five minuteswithout any activity.Using the y and É KeysThe secondary function of each key is printed in blue above the key.When you press the blue y key, the character, abbreviation, or wordprinted in blue above the other keys becomes active for the nextkeystroke. For example, when you press y and then ç, the TESTmenu is displayed.<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition Keyboardåkey accesses the HandheldSoftware Applications (Apps) loadedon your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionÉ accesses the alpha functionprinted in green above each keyy accesses the second functionprinted in blue above each keyOperations keys}~Ü| keys let you movethe cursor in four directionsë erases (clears) the entry lineor deletes an entry and answer onthe home screenThe alpha function of each key is printed in green above the key. Whenyou press the green É key, the alpha character printed in greenabove the other keys becomes active for the next keystroke. Forexample, when you press É and then ç, the letter A is entered.Õ evaluates an expression,executes an instruction, or selectsa menu itemAdjusting the Display ContrastTo adjust the contrast, follow these steps:1 Press and release the y key.2 Press and hold } or Ü (which are aboveand below the contrast symbol).} Darkens the screenÜ Lightens the screenDarkerLighterSpecial Features of the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition,<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus, and <strong>TI</strong>-83 PlusFlash — Electronic UpgradabilityThe <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition, <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus, and <strong>TI</strong>-83 Plus use Flashtechnology, which lets you update your operating system andadd Handheld Software Apps, such as Topics in Algebra 1, InequalityGraphing, NoteFolio , <strong>TI</strong>meSpan , CellSheet , and many more!Home ScreenThe home screen is the primary screen of the<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition. On this screen, you can enterinstructions to execute and expressions to evaluate.The answers are displayed on the same screen.To return to the Home Screen from any other screen,press y5.Comparing the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition and the <strong>TI</strong>-83 Plus<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition <strong>TI</strong>-83 PlusFlash ROM 1.54 Mb 160 KbHolds up to 94 Apps 10 AppsPreloaded Apps 18 4Connectivity USB cable included <strong>TI</strong> Connectivity USBcable sold separatelyCase ColorSILVER & Customizable Classic dark grayZ80 Processor Speed 15 MHz 6 MHzRAM 24 Kb 24 Kb<strong>TI</strong> Connectivity KitWith the <strong>TI</strong> Connect software and <strong>TI</strong> Connectivity USB cable, youcan link your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus to a personal computer. As future softwareupdates become available on the <strong>TI</strong> website, you can downloadthe software to your computer and use the <strong>TI</strong> Connect softwareand <strong>TI</strong> Connectivity USB cable to update your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus.© Texas Instruments, 2007education.ti.com
Getting Started Using Your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition Edit KeysKeystroke Result~ or | Moves the cursor within an expression.} or Ü Moves the cursor from line to line within an expression thatoccupies more than one line. On the top line of an expressionon the home screen, } moves the cursor to the beginning ofthe expression. On the bottom line, Ü moves the cursor tothe end of the expression.y| Moves the cursor to the beginning of an expression.y~ Moves the cursor to the end of an expression.Õ Executes an instruction and/or an expression.ë On a line with text on the home screen, clears the current line.On a blank line on the home screen, clears everything on thehome screen. In an editor, clears the expression or valuewhere the cursor is located.{ Deletes a character at the cursor.y 6 Changes the cursor to an underline (__) and inserts charactersin front of the underline cursor; to end insertion, pressy6,or press |}~or Ü.y Changes the cursor to ; the next keystroke performs a2nd operation (in blue above a key); to cancel 2nd,press y again.É Changes the cursor to ÿ; the next keystroke pastes an alphacharacter (in green above a key); to cancel É pressÉ again, or press |}~or Ü.y7 Changes the cursor to ÿ; sets alpha-lock; subsequentkeystrokes paste alpha characters; to cancel alpha-lock, pressÉ. If you are prompted to enter a name for a group or aprogram, alpha-lock is set automatically.Ñ Pastes an X in Func mode, a T in Par mode, a in Pol mode,or an n in Seq mode with one keystroke.Display CursorsIn most cases, the appearance of the cursor indicates what will happenwhen you press the next key.Cursor Appearance Effect of next keystrokeEntry Solid rectangle A character is entered at the cursor;$ any existing character is overwritten.Insert Underline A character is inserted in front of the__cursor location.Second Up arrow A 2nd character (blue on the keyboard)} is entered or a 2nd operation is executed.Alpha Reverse A An alpha character (green on the keyboard)ÿis entered or SOLVE is executed.Full Checkerboard No entry; the maximum number ofrectangle # characters has been entered at a promptor memory is full.© Texas Instruments, 2007Using a <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition MenuYou can access most <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition operations using menus.When you press a key or key combination to display a menu, one ormore menu names appear on the top line of the screen.■The menu name on the left side of the top line is highlighted.Up to seven items in that menu are displayed, beginning with item 1,which is also highlighted.■A number or letter identifies each menu item’s place in the menu.The order is 1 through 9, then 0, then A, B, C, and so on.■When the menu continues beyond the displayed items, a down arrow( ) replaces the colon next to the last displayed item.■When a menu item ends in an ellipsis (...), selecting the item willdisplay a secondary menu or editor.Displaying a MenuWhile using your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition, you will oftenneed to access items from its menus. When you pressa key that displays a menu, that menu temporarilyreplaces the screen where you are working.Example: Calculate 5 + 9 31. 5 + 9 Enter the expression in the home screen2. Press ç3. Press 3 to choose the correct item from the menu4. Press Õ to calculateKeystrokes: 2T6 ç 0 Õ 734Moving Between MenusSome of the keys on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Editionaccess more than one menu. When you press sucha key, the names of all accessible menus aredisplayed on the top line. When you highlight amenu name, the items in that menu are displayed.Press ~ and | to highlight each menu name.Setting ModesMode settings control how your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition displays andinterprets numbers and graphs. Mode settings are retained by theConstant Memory feature when you turn off your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.All numbers, including elements of matrices and lists, are displayedaccording to the current mode settings.To display the mode settings on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition, pressz . The current settings will be highlighted. Default settings arehighlighted below.Normal Sci Eng Numeric notationFloat 0123456789 Number of decimal placesRadian DegreeUnit of angle measureFunc Par Pol Seq Type of graphingConnected DotWhether to connect graph pointsSequential Simul Whether to plot simultaneouslyReal a+bi re i Real, rectangular complex, or polar complexFull Horiz G-TFull screen, two split-screen modesChanging Mode SettingsTo change mode settings:1 Press Ü or } to move the cursor to the line of the setting you want.2 Press ~ or | to move the cursor to the setting you want.3 Press Õ.education.ti.com
<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition Expressions, Menus, and GraphingEntering Expressions and InstructionsWhat is an Expression?An expression is a group of numbers, variables, or functions andtheir arguments, or a combination of these elements. An expression1evaluates to a single answer. For example, ( ) 2 3is an expression. On the<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition, you enter an expression in the same order asyou would write it on paper. You can enter anexpression on the home screen to calculatean answer.Entering an ExpressionTo create an expression, you enter numbers, variables, and functionsfrom the keyboard and menus on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition. Anexpression is completed when you press Õ, regardless of thecursor location. The entire expression is evaluated according toEquation Operating System (EOS ) rules (see General Math page),and the answer is displayed. When an entry isexecuted on the home screen, the answer isdisplayed on the right side of the next line.The mode settings control the way the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition interpretsexpressions and displays answers. If an answer, such as a list or matrix,is too long to display entirely on one line, anellipsis (...) is displayed to the right or left.Press ~ or | to display the rest of the answer.To display the MATH menu, press çMATH NUM CPX PRB1: Frac Displays answer as a fraction2: Dec Displays answer as a decimal3: 3 Calculates cube4: 3 √ ( Calculates cube root5: x √ Calculates xth root6: fMin( Finds minimum of a function7: fMax( Finds maximum of a function8: nDeriv( Computes numeric derivative9: fnInt( Computes integral of a function0: Solver... Displays equation solverTo display the MATH NUM menu, press ç ~MATH NUM CPX PRB1: abs( Computes absolute value2: round( Rounds value to specified decimal place3: iPart( Calculates integer part4: fPart( Calculates fractional part5: int( Finds greatest integer less than or equal to number6: min( Finds minimum value7: max( Finds maximum value8: lcm( Calculates least common multiple9: gcd( Calculates greatest common divisorTo display the MATH PRB menu, press ç |MATH NUM CPX PRB1: rand Generates random number between 0 and 12: nPr Computes number of permutations3: nCr Computes number of combinations4: ! Calculates factorial5: randInt( Generates random integer in specified range6: randNorm( Generates random # from Normal distribution7: randBin( Generates random # from Binomial distributionDefining or Editing a Function for GraphingTo Define or Edit a Function1 Press o to display the Y= editor.2 Press Ü to move the cursor to thefunction you want to define or edit.To erase a function, press ë.3 Enter or edit an expression to definethe function.Displaying a New GraphTo display a graph of the selected function,press s. TRACE, ZOOM, and CALCoperations display the graph automatically.As the graph is plotted, the busy indicator ison, and the X and Y values are updated.Free-Moving CursorWhen you first display the graph, no cursor is visible. You must press|~}or Ü for the cursor to move from the center of the viewingwindow. Continue pressing | ~}or Ü to move the cursor around.Tracing a FunctionUse the TRACE operation to move the cursor from one plotted pointto the next along a function. To begin, press r. The TRACE cursoris on the first selected function in the Y= editor, centered horizontallyon the screen. The cursor coordinates are displayed at the bottom ofthe screen if CoordOn format is selected. The Y= expression is displayedin the top left corner of the screen if ExprOn format is selected.Moving the TRACE CursorTo move the TRACE cursorDo this:To the previous or next plotted point Press | or ~Five plotted points on a function Press y | or y ~(Xres affects this)To any valid X value on a function Enter a value & press ÕFrom one function to anotherPress } or ÜTo alter the viewing area of the graph, press qZOOM MEMORY1: ZBox Draws a box to define the viewing window2: Zoom In Magnifies the graph around the cursor3: Zoom Out Views more of a graph around the cursor4: ZDecimal Sets X and Y to 0.15: ZSquare Sets equal-size pixels on the X and Y axes6: ZStandard Sets the standard window variables7: ZTrig Sets the built-in trig window variables8: ZInteger Sets integer values on the X and Y axes9: ZoomStat Sets the values for current stat plots0: ZoomFit Fits Ymin and Ymax between Xmin and XmaxTo display the CALCULATE menu, press y /CALCULATE1: value Calculates a function Y value for a given X2: zero Finds a zero (x-intercept) of a function3: minimum Finds a minimum of a function4: maximum Finds a maximum of a function5: intersect Finds an intersection of two functions6: dy/dx Finds a numeric derivative of a function7: ∫f(x)dx Finds a numeric integral of a functionTo return to the Home Screen from any other screen, press y 5.© Texas Instruments, 2007education.ti.com
All About Apps for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionIf you’ve ever wondered...So what is that little å key on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Editionfor, anyway?Handheld Software Applications, or Apps, are pieces of software youcan add on to your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition or <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus, in the sameway you would add software to your computer. This allows you tocustomize your <strong>TI</strong> handheld to meet your class needs and update itfrom one year to the next. Pretty cool, huh?The <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition comes preloaded with lots of Apps ––StudyCards , Probability Simulation, CBL /CBR , Conic Graphing,Cabri Jr., Organizer, CellSheet , Puzzle Pack, Science Tools, CatalogHelp, Vernier EasyData , to name a few! The <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus comespreloaded with StudyCards, Probability Simulation, CBL/CBR, CatalogHelp, and other Apps. Some of the coolest Apps for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus SilverEdition and <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus are:To access the Apps on your<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionAll you have to do is press the å key, scroll down the list to the Appyou‘d like to explore, and press Õ. If you get stuck using an App,visit education.ti.com/guides to download the FREE instruction guide.But that’s not all…We also have dozens of other Apps you can download, and all ofthem are FREE! Visit the <strong>TI</strong> website at education.ti.com/apps to findout more information on all of the Apps you can download.So how do you get these free Apps?First, you’ll need a <strong>TI</strong> Connectivity USB cable – one is included withthe <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition and is available as an accessory with the<strong>TI</strong>-83 Plus model. You can purchase a <strong>TI</strong> Connectivity USB cable at aretail store or the <strong>TI</strong> Online Store. USB and serial cables are availablefor both Windows ® PCs and Macintosh ® computers.Cabri Jr.Add a new dimension to your learning experiencewith Cabri Jr., our interactive Geometry App.Construct, analyze and transform mathematicalmodels and geometric diagrams. Then altergeometric objects on the fly to see patterns, makeconjectures and draw conclusions.Inside the <strong>TI</strong> Connectivity kit (and <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition) package,you will find a CD with <strong>TI</strong> Connect link software, which allowsyour computer to communicate with your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Editionhandheld. Follow the directions to install the software from the CDinto your computer.OrganizerKeep track of where you’re going and whereyou’ve been. Put your future and your friends atyour fingertips when you input contacts and tasks.CellSheet You have a spreadsheet to your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus SilverEdition! Create graphs, including pie charts, andfill a range of cells with formulas. You can evenimport and export files to and from Excel ® .© Texas Instruments, 2007StudyCards Create electronic flash cards to use as a study tool forquiz or test review. Download ready made StudyCardstacks for the SAT * and ACT from our collectionat education.ti.com/studycards. Create and sharestacks with other students from all over theworld.NoteFolio Easily type notes for all your classes with the<strong>TI</strong> Keyboard. Select, cut, copy, paste, deleteand insert text in your notes. Best of all, usethe NoteFolio Creator PC utility to transfernotes to and from Word ® files.Topics in Algebra 1Walk, run or ride a bicycle through basic conceptsin algebra. You can be the envy of all your friendsby grasping this mystical subject with this fun andeasy tutorial.Next, visit education.ti.com/apps to browse through the FREE Appsthat are available for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus and <strong>TI</strong>-83 Plus families of graphingcalculators. All Apps are FREE to download – simply follow the stepsonline. Just be sure to save the file in a location you’ll remember.Now it’s time to transfer the App from your computer to your<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition. This is the easy part! Just plug your USBcable into your computer and your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition,launch the <strong>TI</strong> Connect software, and click on Device Explorer.<strong>TI</strong> Connect will automatically detect your device. All you have to dois find the App file you saved, drag it to the Device Explorer window,drop it, and wait for it to transfer. Voilà! Press the å key to see yournewly transferred App! Good luck and happy downloading!We know you’ll have an Appsolute blast!® Excel, Word, Windows, and Macintosh are registered trademarks of their respective owners.* SAT & AP are registered trademarks of the College Entrance Examination Board.PSAT/NMSQT is a registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board andNational Merit Scholarship Corporation. ACT is a registered trademark of ACT, Inc. None ofthese were involved in the production of nor do they endorse this product.Policies subjectto change. Visit www.collegeboard.com and www.act.org.education.ti.com
General Math with the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionArithmetic Operations and PropertiesArithmetic Operations with the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionAddition: valueA + valueB Returns valueA plus valueB √Subtraction: valueA - valueB Subtracts valueB from valueA πMultiplication: valueA x valueB Returns valueA times valueB ØDivision: valueA ÷ valueB Returns valueA divided by valueB •Properties of Addition & MultiplicationCommutative property of additionCommutative property of multiplicationAssociative property of additionAssociative property of multiplicationDistributive property of multiplication over additionDistributive property of multiplication over subtractionNumbersPrime NumbersA whole number with only two factors: itself and 1EXAMPLES: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17a+b = b+aab = baa+(b+c) = (a+b)+ca(bc) = (ab)ca(b+c) = ab+aca(b–c) = ab–acCommon FactorsA number that divides exactly into two or more given numbersEXAMPLES: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 are factors of 12Greatest Common FactorThe greatest number that is a factor of two or more numbersEXAMPLE: 4 is the greatest common factor of 12 and 16.To calculate the greatest common factor on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition,press ç ~ 9:gcd(. This will compute the greatest common factor ofvalueA and valueB, which can be real numbers or lists.Least Common MultipleThe smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbersEXAMPLE: 12 is the least common multiple of 2, 3, 4 and 6.To calculate the least common multiple on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition,press ç ~ 8:lcm(. This will compute the least common multiple ofvalueA and valueB, which can be real numbers or lists.Order of OperationsGeneral Rules1 Do all operations within parentheses2 Do all powers and roots3 Do multiplication and division in order from left to right4 Do addition and subtraction in order from left to rightEquation Operating System (EOS ) for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionEOS defines the order in which functions and expressions are entered andevaluated. EOS evaluates the functions in an expression in this order:1 Functions that precede the argument, such as √ (, sin(, or log(2 Functions that are entered after the argument, such as 2 , -1 , !, °, or r ,and conversions3 Powers and roots, such as 2 5 or 5 √324 Permutations (nPr) and combinations (nCr)5 Multiplication, implied multiplication, and division6 Addition and subtraction7 Relational functions, such as > or ≤8 Logic operator and9 Logic operators or and xorWithin a priority level, EOS evaluates functions from left to right.Calculations within parentheses are evaluated first.Math SymbolsTo access many math symbols,go to the TEST Menu on your<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition, by pressingy : .Powers and RootsSquare: value 2 The ° key returns a value multiplied by itself.The value can be a real or complex number,expression, or list.Square root: √ (value) y C returns the square root of a realor complex number, expression, or list.Common Squares and Rootsn n 2 √n1 1 1.02 4 1.4143 9 1.7324 16 2.05 25 2.2366 36 2.4497 49 2.6468 64 2.828Cube: value 3 Press ç. 3: 3 Returns the cube of a real orcomplex number, expression, list, or square matrix.Cube root: 3 √ (value) Press ç. 4: 3 √ ( Returns the cube root of areal or complex number, expression, or list.x th root: x √ value Press ç. 5: x √ ( Returns xth root of a value.Power: value^power The õ key returns a value raised to a power. Valuecan be a real or complex number or expression.Power of 10: 10^(value) Press y G. Returns 10 raised to the value power.Value can be a real or complex number or expression.Fractions, Decimals and Percents1 = 1.0 = 100%1 /2 = 0.5 = 50%1 /3 = 0.333 = 33.3%1 /4 = 0.25 = 25%1 /5 = 0.2 = 20%1 /6 = 0.166 = 16.7%1 /8 = 0.125 = 12.5%1 /9 = 0.111 = 11.1%1 /10 = 0.1 = 10%1 /12 = 0.083 = 8.3%2 /3 = 0.666 = 66.7%3 /4 = 0.75 = 75%value ➧Decvalue ➧Fracn n 2 √n9 81 3.010 100 3.16215 225 3.87320 400 4.47225 625 5.0100 10,000 10.01 /2 1 /4 0.7071 /4 1 /16 1 /2Press ç. 2: ➧Dec Displays a real or complexnumber, expression, list or matrix in decimal format.Press ç. 1: ➧Frac Displays a real or complexnumber, expression, list or matrix as a fractionsimplified to its simplest terms.© Texas Instruments, 2007education.ti.com
Algebra with the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionLaw of Exponents & RadicalsFormulas Examples Keystrokes(where a=3, b=2, P=5,Q=6, r=4, s=2)a r x a s = a r + s 3 4 x 3 2 = 3 4 + 2 0 G D 1 T / E Õ 729Graphing Inequalitiesa ra s = a r – s 3 43 2 = 3 4 – 2 0 G D 1 U / E Õ 9a p a q3 5 x 3 6The intersection of y ≤ 2x-3a –r 1= (a ≠ 0) 3 -4 =1. W 0 G 1 Õ .0123a r3 4= a p + q – r 3 4 = 3 5 + 6 – 4 0GD2T3U1EÕ 2187the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition is and y > .5x 2 -7 is shaded.used here to enter the equations(ab) r = a r b r (3 x 2) 4 = 3 4 x 2 4 0 G 1 V / G 1 Õ1296y ≤ 2x-3 and y > .5x 2 -7.a r a( r3 3b )= b r (b ≠ 0) ( 2 ) 4Solving Linear Systems by Graphing= 2 40 G 1 W / G 1 Õ 5.0625The intersection of two functions is the solution to the system.r sa s = √a r 2 49 4 = √9 2 1 ç 2 D 6 G / E Õ3Graphing provides a quick and powerful way to solve linear systems.a 0 = 1 (a ≠ 0) 3 0 = 1 0 G 7 Õ 1Binomial Expansiona (b + c) = ab + ac(a + b) (c + d) = ac + ad + bc + bd(a + b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2(a – b) 2 = a 2 – 2ab + b 2(a + b) 3 = a 3 + 3a 2 b + 3ab 2 + b 3(a – b) 3 = a 3 – 3a 2 b + 3ab 2 – b 3(a + b) 4 = a 4 + 4a 3 b + 6a 2 b 2 + 4ab 3 + b 4(a + b) 5 = a 5 + 5a 4 b + 10a 3 b 2 + 10a 2 b 3 + 5ab 4 + b 5Factoringa 2 – b 2 = (a + b) (a – b)a 2 + 2ab + b 2 = (a + b) 2a 2 – 2ab + b 2 = (a – b) 2a 3 + b 3 = (a + b) (a 2 – ab + b 2 )a 3 b – ab = ab (a + 1) (a – 1)a 3 – b 3 = (a – b) (a 2 + ab + b 2 )Factorialn! = n (n-1) (n-2) ... (2) (1)Example: 5! = 5 (4) (3) (2) (1)Keystrokes: 5! = 2 ç | 4 Õ 1201 Enter equations in the o editor.2 Press s to graph both equations.(You may need to adjust the viewing window.)3 Press y / 5: intersect to find the point of intersection.4 Press Õ to select the 1st curve and again to select the 2nd curve.5 Enter your best guess and press Õ.Quadratic FormulaIf a ≠ 0, the roots of ax 2 + bx + c = 0 areExample: 3x 2 + 2x - 4x = –b ± √b2 - 4ac2a(where a=3, b=2, c=-4)x = -2 ± √2 2 - 4(3)(-4)2(3)KeystrokesStep 1 2 2 - 4(3)(-4) / F U 1 V 0 V M 1 Õ 52Step 2 -2 + √52 M / T % b 2 / E Õ 5.211-2 - √52 M / U % b 2 / E Õ -9.211Step 3 5.211 28/..WD/V0EÕ 0.8692(3)-9.211 M68/..WD/V0EÕ -1.5352(3)Using the Equation SolverUse the Equation Solver on your <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition to solve for anyvariable in an equation. In this example, the Solver is being used to findone of the roots of the polynomial x 2 - 5x + 6.Logarithms ´ µ Jy = log a x means a y = x log a x r = r log a x log x = log 10 xlog a xy = log a x + log a y log a 1 = 0xlog a = log a x – log a y log a a = 1 log a x = log 10 xylog 10 aIn x = log e x ln e = 1© Texas Instruments, 20071 Press ç 0: Solver…2 Enter equation (must be in form where equation is set equal to 0)and press Õ.3 Place cursor next to variable for which you would like to solve.4 Enter a guess for the value.5 Press É \ to see a solution.education.ti.com
More Algebra with the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionDefinition of SlopeThis section uses the Topics in Algebra 1 App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Editionto help define slope.m = vertical change = rise = y 2 – y 1The Distance FormulaThe Distance Formula is used to calculate the distance between two points.d(P 1 , P 2 ) = √(x 2 – x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 – y 1 ) 2Example: Find the distances between the points P 1 (2, 5) and P 2 (-3, 1).d(P 1 , P 2 ) = √(-3 – 2) 2 + (1 – 5) 2 = √(-5) 2 + (-4) 2= √25 + 16 = √41 ≈ 6.403Keystrokes- z £ M [ T Z E 6 \ D Y T R E 6 E b ≈ 6.403<strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition:horizontal change run x 2 – x 1Quadratic FunctionsTo draw the line segment between (-3, 1) and (2, 5) on youry< 2:Line M ¬ ¢ ¿ ¢ ¡ ¢ § ÕEquations of LinesThis section features the Topics in Algebra 1 App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.This section features the Conic Graphing App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.Ax + By = CStandard form — graph using interceptsy = mx + bSlope-intercept form — graph using m and (0,b)y – y 1 = m(x – x 1 ) Point-slope form — graph using m and (x 1 , y 1 )Equation of a circle: (x – H) 2 + (y – k) 2 = R 2Values are entered for the center and the radius. The Conic Graphing Appproduces a circle you can now trace.Standard form exampleGiven 3x + 2y = 6, find intercepts:3(0) + 2y = 6 3x + 2(0) = 6 x y2y = 6 3x = 6 0 3y = 3 x = 2 2 0Equation of a parabola: (x – H) 2 = 4P(y – k)Values are entered for the vertex (H, K) and the distance (P) betweenthe directrix and the vertex. The Conic Graphing App produces aparabola you can now trace.Point-slope form exampleGiven m=3 and (2,-3)Equationy – (-3) = 3(x-2)y + 3 = 3x – 6y = 3x – 9The Transformation Graphing App allows you to see what happens to agraph as you change its coefficient(s).Keystrokeso ë ¬ Ñ π Æ q _© Texas Instruments, 2007education.ti.com
Geometry with the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionLinesPolygonsThe information in this section is presented using screen shots from theStudyCards and Cabri Jr. Apps for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.Creation of primitive geometric objectsas Points, Lines, Line Segments and manyothers is fun and easy using the Cabri Jr. App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.TrianglesThis section features the Cabri Jr. App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.Equilateral: all sides and angles equalIsosceles: two sides and angles equalRight: one 90 degree angleExample: Draw an Isosceles Triangle1 23 4AnglesPythagorean Theorem1. Create a segment2. Find the middle ofthe segment3. Trace aperpendicularline crossing themiddle point4. Trace a triangleusing the twoexisting points ofthe segment anda point on theperpendicular lineCirclesThis section features the Cabri Jr. App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Edition.Diameter = 2*(radius)Circumference = π*(diameter)Circle Area = π*(radius) 2DiameterChordAreaCircle’sEquationGeometric FormulasAll PerimetersP = a+b+c+SquarePerimeterAreaRectanglePerimeterAreaCircleCircumferenceArea...P = 4sA = s 2P = 2l+2wA = lwC =A = πr 2 TriangleParallelogramPerimeterAreaTrapezoidArea2πr© Texas Instruments, 2007Perimeter P = a+b+cArea A = 1 bh2P = a+b+c+dA = bhPerimeter P = a+b+c+dA = (a+b)h2Rectangular PrismSurface S = 2(hl+lw+hw)Volume V = lwhSphereSurface S = 4 πr 2Volume V = 4 πr 33Right Circular CylinderLateralSurface S = 2πrhTotalSurface S = 2πrh + 2πr 2Volume V = πr 2 hRight Circular ConeLateralSurface S = πr √r 2 +h 2TotalSurface S = πr √r 2 +h 2 +πr 2Volume V = 1 πr 2 h3Frustum of a ConeVolume V =1πh(r 2 +rR+R 2 )3Circular SectorArea A =1r 2 Circular RingArea A = π(R 2 –r 2 )education.ti.com/CabriJr2
Trigonometry with the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver EditionhypoppTrigonometric hypFunctionsopp Special Values of Trigonometric FunctionsAcute Anglesadj ò sin = opp / hyp csc = hyp /hyp(degrees) (radians) sin cos tan cot sec csc oppô cos = adj / hyp sec = hyp hypadjopp0° 0 0 1 0 – 1 –y/ adjoppö tan = opp / adj cot = adj π 1 √3 √32√3(a,b)/ opp adj30° 2y6 2 2 3√3hyp3adjopprArbitrary Anglesx(a,b)π √2 √245° 1 1sin = b / rcsc = r y4 2√2 √22/bradjcos = a / rsec = r y xπ √3 1√32√3(a,b)60° √32/ a3 2 233tan = b / acot = a (a,b) y / ryb x90° π 1 0 – 0 – 1(x,y)r2x(a,b)Real Numberst y(1,0)sin t = ycsc t = 1 rxx / (x,y)ycos t = xsec t = 1 y t Inverse Trigonometric Functionst radians/ x(1,0)Function Domain Rangetan t = y / xcot t = x y(x,y)x/ y(x,y) t y ? y = sin -1 πx y –1 ≤ x ≤ 1 – ≤ y ≤πt radians(1,0)2 2x(x,y)Special Triangles(1,0)y @ y = cos -1 xt–1 ≤ x ≤ 1 0 ≤ y ≤πx(1,0)πt radians3 =60°y A y = tan -1 xπ πx All real numbers – < y
Math <strong>Reference</strong>sPrefix Symbol MagnitudeMetric PrefixesPrefix Symbol Magnitudedeka- da 10 1 atto- a 10 -18Exa- E 10 18deci- d 10 -1Peta- P 10 15centi- c 10 -2Tera- T 10 12milli- m 10 -3Giga- G 10 9micro- ∝ 10 -6Mega- M 10 6nano- n 10 -9kilo- k 10 3pico- p 10 -12hecto- h 10 2femto- f 10 -15Greek AlphabetUpper Lower Name Upper Lower Name Upper Lower NameΑ α alpha Ι ι iota Ρ ρ rhoΒ β beta Κ κ kappa Σ σ sigmaΓ γ gamma Λ λ lambda Τ τ tau∅ δ delta Μ ∝ mu Υ υ upsilonΕ ε epsilon Ν ν nu Φ φ phiΖ ζ zeta Ξ ξ xi Χ χ chiΗ η eta Ο ο omicron Ψ ψ psiΘ θ theta Π π pi Ω ω omegaWeights and MeasuresAnnular and Circular Measure60 seconds = 1 minute90 minutes = 1 degree90 degrees = 1 right angle180 degrees = 1 straight angle360 degrees = complete angleApothecaries’ Fluid Measure60 minims = 1 fluid dram8 fluid drams = 1 fluid ounce16 fluid ounces = 1 pint2 pints = 1 quart4 quarts = 1 gallonApothecaries’ Weight20 grains = 1 scruple3 scruples = 1 dram8 drams = 1 ounce12 ounces = 1 poundAvoirdupois Weight27 11 / 32 grains = 1 dram16 drams = 1 ounce16 ounces = 1 pound100 pounds = 1 short cwt.1 short ton = 2,000 poundsCubic Measure1728 cubic inches = 1 cubic foot27 cubic feet = 1 cubic yard1000 cu. millimeters = 1 cu. cm.1000 cu. centimeters = 1 cu. dcm.1000 cu. decimeters = 1 cu. meterLinear Measure12 inches = 1 foot3 feet = 1 yard5 1 / 2 yards = 1 rod40 rods = 1 furlong5,280 feet = 1 mile10 millimeters = 1 centimeter10 centimeters = 1 decimeter10 decimeters = 1 meter10 meters = 1 dekameter10 dekameters = 1 hectometer10 hectometers = 1 kilometerLiquid Measure4 gills = 1 pint2 pints = 1 quart4 quarts = 1 gallon31 1 / 2 gallons = 1 barrel2 barrels = 1 hogshead10 milliliters = 1 centiliter10 centiliters = 1 deciliter10 deciliters = 1 liter10 liters = 1 dekaliter10 dekaliters = 1 hectoliter10 hectoliters = 1 kiloliterMass Measure10 milligrams = 1 centigram10 centigrams = 1 decigram10 decigrams = 1 gram10 grams = 1 dekagrams10 dekagrams = 1 hectogram10 hectograms = 1 kilogram100 kilograms = 1 quintal10 quintals = 1 tonSquare Measure144 square inches = 1 square foot9 square feet = 1 square yard30 1 / 4 square yards = 1 sq. rod160 square rods = 1 acre640 acres = 1 square mile100 sq. millimeters = 1 sq. cm.100 sq. centimeters = 1 sq. dcm.100 sq. decimeters = 1 sq. meter100 sq. meters = 1 sq. dekameter100 sq. dekameters = 1 sq. hm.100 sq. hectometers = 1 sq. km.Troy Weight24 grains = 1 pennyweight20 pennyweights = 1 ounce12 ounces = 1 poundLiquid or Volume Measures (approximate)1 /4 teaspoon = 0.042 fluid ounce1 /2 teaspoon = 0.083 fluid ounce1 teaspoon = 0.167 fluid ounce1 tablespoon = 0.5 fluid ounce2 tablespoons = 1 fluid ounce1 /4 cup = 2 fluid ounces1 /3 cup = 2.67 fluid ounces1 /2 cup = 4 fluid ounces2 /3 cup = 5.33 fluid ounces3 /4 cup = 6 fluid ounces7 /8 cup = 7 fluid ounces1 cup = 8 fluid ounces1 pint = 16 fluid ounces1 quart = 32 fluid ounces1 gallon = 128 fluid ounces1 liter = 33.82 fluid ouncesThis section uses the Science Tools App for the <strong>TI</strong>-84 Plus Silver Editionto help convert any unit.Example: Convert 250km to fathoms1. Select LENGTH from the unit converter Menu.2. Enter 250, the numerical value to convert.3. Use the arrow keys to select km, the conversion unit to convertfrom, and then press Õ.4. Use the arrow key to select fath, the conversion unit to convert to,and then press Õ.© Texas Instruments, 2007education.ti.com