UNDP Capacity Assessment Users Guide.pdf - Africa Adaptation ...
UNDP Capacity Assessment Users Guide.pdf - Africa Adaptation ...
UNDP Capacity Assessment Users Guide.pdf - Africa Adaptation ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
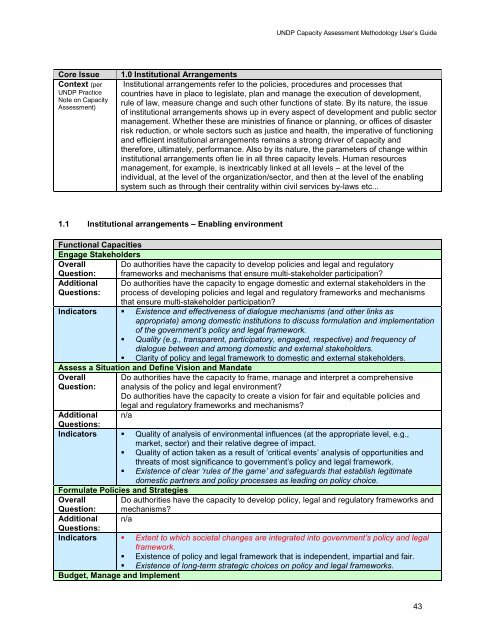
<strong>UNDP</strong> <strong>Capacity</strong> <strong>Assessment</strong> Methodology User‘s <strong>Guide</strong>Core IssueContext (per<strong>UNDP</strong> PracticeNote on <strong>Capacity</strong><strong>Assessment</strong>)1.0 Institutional ArrangementsInstitutional arrangements refer to the policies, procedures and processes thatcountries have in place to legislate, plan and manage the execution of development,rule of law, measure change and such other functions of state. By its nature, the issueof institutional arrangements shows up in every aspect of development and public sectormanagement. Whether these are ministries of finance or planning, or offices of disasterrisk reduction, or whole sectors such as justice and health, the imperative of functioningand efficient institutional arrangements remains a strong driver of capacity andtherefore, ultimately, performance. Also by its nature, the parameters of change withininstitutional arrangements often lie in all three capacity levels. Human resourcesmanagement, for example, is inextricably linked at all levels – at the level of theindividual, at the level of the organization/sector, and then at the level of the enablingsystem such as through their centrality within civil services by-laws etc...1.1 Institutional arrangements – Enabling environmentFunctional CapacitiesEngage StakeholdersOverall Do authorities have the capacity to develop policies and legal and regulatoryQuestion: frameworks and mechanisms that ensure multi-stakeholder participation?AdditionalQuestions:Do authorities have the capacity to engage domestic and external stakeholders in theprocess of developing policies and legal and regulatory frameworks and mechanismsthat ensure multi-stakeholder participation?Indicators • Existence and effectiveness of dialogue mechanisms (and other links asappropriate) among domestic institutions to discuss formulation and implementationof the government‟s policy and legal framework.• Quality (e.g., transparent, participatory, engaged, respective) and frequency ofdialogue between and among domestic and external stakeholders.• Clarity of policy and legal framework to domestic and external stakeholders.Assess a Situation and Define Vision and MandateOverallQuestion:Do authorities have the capacity to frame, manage and interpret a comprehensiveanalysis of the policy and legal environment?Do authorities have the capacity to create a vision for fair and equitable policies andlegal and regulatory frameworks and mechanisms?Additional n/aQuestions:Indicators • Quality of analysis of environmental influences (at the appropriate level, e.g.,market, sector) and their relative degree of impact.• Quality of action taken as a result of ‗critical events‘ analysis of opportunities andthreats of most significance to government‘s policy and legal framework.• Existence of clear „rules of the game‟ and safeguards that establish legitimatedomestic partners and policy processes as leading on policy choice.Formulate Policies and StrategiesOverallQuestion:Do authorities have the capacity to develop policy, legal and regulatory frameworks andmechanisms?Additional n/aQuestions:Indicators • Extent to which societal changes are integrated into government‟s policy and legalframework.• Existence of policy and legal framework that is independent, impartial and fair.• Existence of long-term strategic choices on policy and legal frameworks.Budget, Manage and Implement43