Siyavula: Life Sciences Grade 10 - Cd3wd.com
Siyavula: Life Sciences Grade 10 - Cd3wd.com
Siyavula: Life Sciences Grade 10 - Cd3wd.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
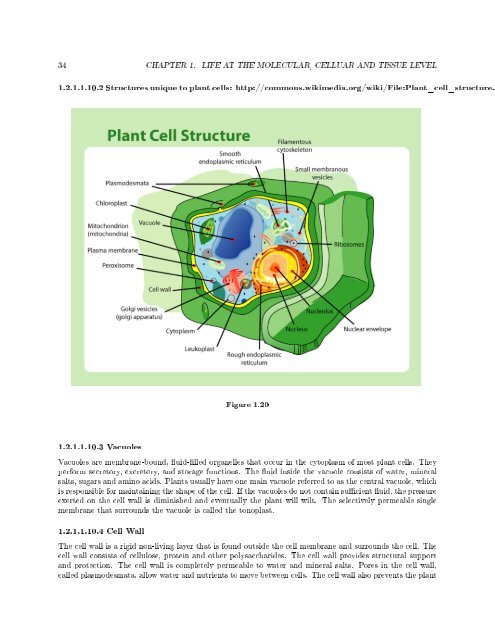
34 CHAPTER 1. LIFE AT THE MOLECULAR, CELLUAR AND TISSUE LEVEL1.2.1.1.<strong>10</strong>.2 Structures unique to plant cells: http://<strong>com</strong>mons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plant_cell_structure.pFigure 1.201.2.1.1.<strong>10</strong>.3 VacuolesVacuoles are membrane-bound, uid-lled organelles that occur in the cytoplasm of most plant cells. Theyperform secretory, excretory, and storage functions. The uid inside the vacuole consists of water, mineralsalts, sugars and amino acids. Plants usually have one main vacuole referred to as the central vacuole, whichis responsible for maintaining the shape of the cell. If the vacuoles do not contain sucient uid, the pressureexerted on the cell wall is diminished and eventually the plant will wilt. The selectively permeable singlemembrane that surrounds the vacuole is called the tonoplast.1.2.1.1.<strong>10</strong>.4 Cell WallThe cell wall is a rigid non-living layer that is found outside the cell membrane and surrounds the cell. Thecell wall consists of cellulose, protein and other polysaccharides. The cell wall provides structural supportand protection. The cell wall is <strong>com</strong>pletely permeable to water and mineral salts. Pores in the cell wall,called plasmodesmata, allow water and nutrients to move between cells. The cell wall also prevents the plant



![Mum, int. [man] - Cd3wd.com](https://img.yumpu.com/51564724/1/190x134/mum-int-man-cd3wdcom.jpg?quality=85)











