Subsurface Iron and Arsenic Removal
qj78kp8
qj78kp8
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Subsurface</strong> iron <strong>and</strong> arsenic removal for drinking water treatment in Bangladesh<br />
3<br />
this a mass balance can be calculated <strong>and</strong>, for this cycle,<br />
was calaculted to be an approximate removal of 0.66<br />
mmol <strong>and</strong> 0.77 µmol for iron <strong>and</strong> arsenic, respectively.<br />
One isolated cycle does however not describe the<br />
potential of subsurface iron <strong>and</strong> arsenic removal, since<br />
this technology is known for its increasing efficacy with<br />
every successive cycle.<br />
Influence of Fe:As ratio in the groundwater<br />
<strong>Subsurface</strong> iron <strong>and</strong> arsenic removal is applied directly<br />
at the shallow tube well <strong>and</strong> therefore depends greatly<br />
on the occurring groundwater geochemistry. One<br />
of the parameters that may enhance the effective coremoval<br />
of arsenic with the iron is the presence of<br />
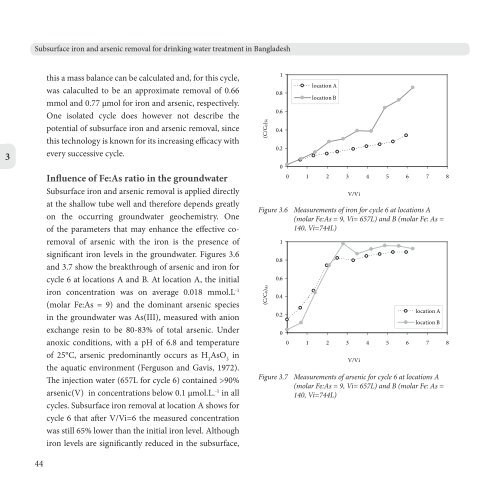
significant iron levels in the groundwater. Figures 3.6<br />
<strong>and</strong> 3.7 show the breakthrough of arsenic <strong>and</strong> iron for<br />
cycle 6 at locations A <strong>and</strong> B. At location A, the initial<br />
iron concentration was on average 0.018 mmol.L -1<br />
(molar Fe:As = 9) <strong>and</strong> the dominant arsenic species<br />
in the groundwater was As(III), measured with anion<br />
exchange resin to be 80-83% of total arsenic. Under<br />
anoxic conditions, with a pH of 6.8 <strong>and</strong> temperature<br />
of 25°C, arsenic predominantly occurs as H 3<br />
AsO 3<br />
in<br />
the aquatic environment (Ferguson <strong>and</strong> Gavis, 1972).<br />
The injection water (657L for cycle 6) contained >90%<br />
arsenic(V) in concentrations below 0.1 μmol.L. -1 in all<br />
cycles. <strong>Subsurface</strong> iron removal at location A shows for<br />
cycle 6 that after V/Vi=6 the measured concentration<br />
was still 65% lower than the initial iron level. Although<br />
iron levels are significantly reduced in the subsurface,<br />
(C/C0)Fe<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
location A<br />
location B<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8<br />
V/Vi<br />
Figure 3.6 Measurements of iron for cycle 6 at locations A<br />
(molar Fe:As = 9, Vi= 657L) <strong>and</strong> B (molar Fe: As =<br />
140, Vi=744L)<br />
(C/C0)As<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8<br />
V/Vi<br />
location A<br />
location B<br />
Figure 3.7 Measurements of arsenic for cycle 6 at locations A<br />
(molar Fe:As = 9, Vi= 657L) <strong>and</strong> B (molar Fe: As =<br />
140, Vi=744L)<br />
44