Bax and APPL1 are involved in DCC-ADD induced colorectal ...
Bax and APPL1 are involved in DCC-ADD induced colorectal ...
Bax and APPL1 are involved in DCC-ADD induced colorectal ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
III. Discussion<br />
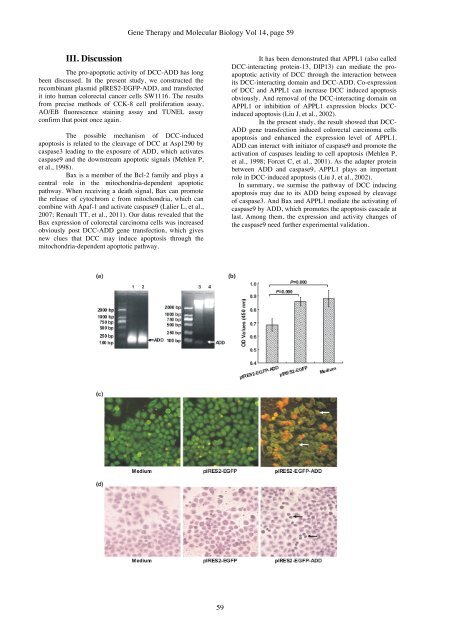
The pro-apoptotic activity of <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>ADD</strong> has long<br />
been discussed. In the present study, we constructed the<br />
recomb<strong>in</strong>ant plasmid pIRES2-EGFP-<strong>ADD</strong>, <strong>and</strong> transfected<br />
it <strong>in</strong>to human <strong>colorectal</strong> cancer cells SW1116. The results<br />
from precise methods of CCK-8 cell proliferation assay,<br />
AO/EB fluorescence sta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g assay <strong>and</strong> TUNEL assay<br />
confirm that po<strong>in</strong>t once aga<strong>in</strong>.<br />
The possible mechanism of <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>in</strong>duced<br />
apoptosis is related to the cleavage of <strong>DCC</strong> at Asp1290 by<br />
caspase3 lead<strong>in</strong>g to the exposure of <strong>ADD</strong>, which activates<br />
caspase9 <strong>and</strong> the downstream apoptotic signals (Mehlen P,<br />
et al., 1998).<br />
<strong>Bax</strong> is a member of the Bcl-2 family <strong>and</strong> plays a<br />
central role <strong>in</strong> the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic<br />
pathway. When receiv<strong>in</strong>g a death signal, <strong>Bax</strong> can promote<br />
the release of cytochrom c from mitochondria, which can<br />
comb<strong>in</strong>e with Apaf-1 <strong>and</strong> activate caspase9 (Lalier L, et al.,<br />
2007; Renault TT, et al., 2011). Our datas revealed that the<br />
<strong>Bax</strong> expression of <strong>colorectal</strong> carc<strong>in</strong>oma cells was <strong>in</strong>creased<br />
obviously post <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>ADD</strong> gene transfection, which gives<br />
new clues that <strong>DCC</strong> may <strong>in</strong>duce apoptosis through the<br />
mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.<br />
Gene Therapy <strong>and</strong> Molecular Biology Vol 14, page 59<br />
59<br />
It has been demonstrated that <strong>APPL1</strong> (also called<br />
<strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>in</strong>teract<strong>in</strong>g prote<strong>in</strong>-13, DIP13) can mediate the proapoptotic<br />
activity of <strong>DCC</strong> through the <strong>in</strong>teraction between<br />
its <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>in</strong>teract<strong>in</strong>g doma<strong>in</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>ADD</strong>. Co-expression<br />
of <strong>DCC</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>APPL1</strong> can <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>DCC</strong> <strong>in</strong>duced apoptosis<br />
obviously. And removal of the <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>in</strong>teract<strong>in</strong>g doma<strong>in</strong> on<br />
<strong>APPL1</strong> or <strong>in</strong>hibition of <strong>APPL1</strong> expression blocks <strong>DCC</strong><strong>in</strong>duced<br />
apoptosis (Liu J, et al., 2002).<br />
In the present study, the result showed that <strong>DCC</strong>-<br />
<strong>ADD</strong> gene transfection <strong>in</strong>duced <strong>colorectal</strong> carc<strong>in</strong>oma cells<br />
apoptosis <strong>and</strong> enhanced the expression level of <strong>APPL1</strong>.<br />
<strong>ADD</strong> can <strong>in</strong>teract with <strong>in</strong>itiator of caspase9 <strong>and</strong> promote the<br />
activation of caspases lead<strong>in</strong>g to cell apoptosis (Mehlen P,<br />
et al., 1998; Forcet C, et al., 2001). As the adapter prote<strong>in</strong><br />
between <strong>ADD</strong> <strong>and</strong> caspase9, <strong>APPL1</strong> plays an important<br />
role <strong>in</strong> <strong>DCC</strong>-<strong>in</strong>duced apoptosis (Liu J, et al., 2002).<br />
In summary, we surmise the pathway of <strong>DCC</strong> <strong>in</strong>duc<strong>in</strong>g<br />
apoptosis may due to its <strong>ADD</strong> be<strong>in</strong>g exposed by cleavage<br />
of caspase3. And <strong>Bax</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>APPL1</strong> mediate the activat<strong>in</strong>g of<br />
caspase9 by <strong>ADD</strong>, which promotes the apoptosis cascade at<br />
last. Among them, the expression <strong>and</strong> activity changes of<br />
the caspase9 need further experimental validation.