- Page 1 and 2:
ANATOMY • Anatomical Models • 3
- Page 3 and 4:
Utilizing the newest technology and
- Page 5 and 6:
Strap-on IV trainers P. 239 Animal
- Page 7 and 8:
1 IDEALIZED SKULL The three part sk
- Page 9 and 10:
1 Skeleton “Willi” The ideal mo
- Page 11 and 12:
1 1 Skeleton “Hugo” This therap
- Page 13 and 14:
Muscle Marking 1 Skeleton “Arnold
- Page 15 and 16:
Articular Ligaments Muscle Marking
- Page 17 and 18:
1 2 Movable Spine Movable Spine Mus
- Page 19 and 20:
1 2 1 Skeleton, unassembled (bone c
- Page 21 and 22:
3 1 1 Female pelvis with sacrum and
- Page 23 and 24:
1 1 Female pelvis with pelvic floor
- Page 25 and 26:
1 Professional Spine for intensive
- Page 27 and 28:
2 Professional Spine for intensive
- Page 29 and 30:
1 2 3 1 Vertebral column for demons
- Page 31 and 32:
1 Cervical vertebral column C1 to C
- Page 33 and 34:
1 3 4 1 Head articulations, schemat
- Page 35 and 36:
2 1 1 Osteoporosis vertebrae model,
- Page 37 and 38:
2 Lumbar vertebrae with prolapsed i
- Page 39 and 40:
1 Demonstration figure “correct a
- Page 41 and 42:
1 Skull model, 3-part, numbered Sku
- Page 43 and 44:
TOP MODEL 2 Neurovascular Skull Thi
- Page 45 and 46:
2 Didactical version This version i
- Page 47 and 48:
1 1 Functional and regional brain m
- Page 49 and 50:
1 Disarticulated Human Medical Stud
- Page 51 and 52:
1 2 3 4 5 1 Adolescent skull, femal
- Page 53 and 54:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Foetal s
- Page 55 and 56:
1 Skull stand, cervical spine This
- Page 57 and 58:
i Sliding joint in shoulder All nat
- Page 59 and 60:
1 1 Skeleton of arm with vessels Na
- Page 61 and 62:
1 Skeleton of leg with half pelvis
- Page 63 and 64:
1 2 3 Foot Model Series This life s
- Page 65 and 66:
3 1 2 1 Knee Joint, life size, with
- Page 67 and 68:
1 Knee-Implant-Model This impressiv
- Page 69 and 70:
1 4-stage Osteoarthritis (OA) Shoul
- Page 71 and 72:
Thoracic vertebrae Half of Brain Ey
- Page 73 and 74:
1 Muscles removable Soft, flexible
- Page 75 and 76:
1 Head model, 4 parts 1 Life size m
- Page 77 and 78:
1 1 Transparent model nose Using th
- Page 79 and 80:
1 2 NEW! NEW! 1 Regional brain half
- Page 81 and 82:
1 Human Brain Multiple Frontal Sect
- Page 83 and 84:
1 Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation E
- Page 85 and 86:
1 Vertebra with spinal cord section
- Page 87 and 88:
1 1 White Skin Cancer Trainer - Enl
- Page 89 and 90:
2 Ear model, 1.5 times life size 1
- Page 91 and 92:
1 Dental Morphology Series, 7-part,
- Page 93 and 94:
1 Larynx model, 2 times enlarged, 5
- Page 95 and 96:
1 2 3 1 Respiratory organs A life s
- Page 97 and 98:
1 Heart model, life size, 2 parts T
- Page 99 and 100:
1 1 Circulatory system, relief mode
- Page 101 and 102:
1 2 1 Heart model, flexible, didact
- Page 103 and 104:
1 Pediatric heart with ventricular
- Page 105 and 106:
1 Kidney Stone Model This model is
- Page 107 and 108:
1 1 Gallstone Model This half natur
- Page 109 and 110:
1 3 2 1 Stomach with Ulcers This re
- Page 111 and 112:
1 Urogenital Organs, Female 1 Life
- Page 113 and 114:
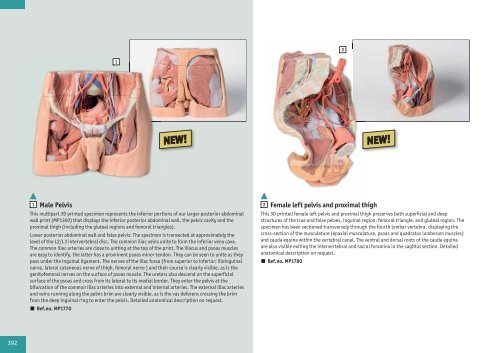
1 Male Pelvis, life size, 4-part Th
- Page 115 and 116:
2 3 1 1 Uterus model Life size mode
- Page 117 and 118:
4 Fetus doll Simulating an average
- Page 119 and 120:
1 1 Pregnancy examination model wit
- Page 121 and 122:
1 Vulva - Casts showing antomical d
- Page 123 and 124:
1 1 Cervical Dilatation and Effacem
- Page 125 and 126:
1 Obstetric Trainer This modular mo
- Page 127 and 128:
Options: 2 Postpartum hemorrhage ma
- Page 129 and 130:
1 Advanced birthing torso Versatile
- Page 131 and 132:
1 Obstetrical Manikin An anatomical
- Page 133 and 134:
C C Obstetrics Module This module c
- Page 135 and 136:
1 2 Noelle Maternal Birthing Simula
- Page 137 and 138:
Complete Lucy Maternal and Neonatal
- Page 139 and 140:
2 1 1 Female genital organs This re
- Page 141 and 142:
Intrauterine Device Placement Clear
- Page 143 and 144:
1 Gynaecological Training Manikin 1
- Page 145 and 146:
1 Advanced Pelvic Examination and G
- Page 147 and 148:
1 2 3 1 Single breast examination t
- Page 149 and 150:
1 2 1 Breast Palpation Simulator fo
- Page 151 and 152:
1 Transparent Hand-Eye Coordination
- Page 153 and 154:
1 Scrotal Ultrasound Phantom 1 Scro
- Page 155 and 156:
2 1 2 Clinical Prostate/Rectal Exam
- Page 157 and 158:
1 Micro-Preemie-Simulator According
- Page 159 and 160:
1 Baby C.H.A.R.L.I.E. Neonatal Resu
- Page 161 and 162:
Parent Education Baby This Newborn
- Page 163 and 164:
2 Neonatal Wound Kit 1 Newborn baby
- Page 165 and 166:
1 2 1 Infant Hip Sonography Trainin
- Page 167 and 168:
1 One Year Pediatric Care Simulator
- Page 169 and 170:
1 Nursing Kid training manikin Nurs
- Page 171 and 172:
1 Clinical Chloe Patient Care Simul
- Page 173 and 174:
1 Nursing Doll „Keiko“ This nur
- Page 175 and 176:
Assessment of chest and abdomen •
- Page 177 and 178:
1 GERi geriatric care doll With thi
- Page 179 and 180:
1 Nursing Anne Manikin Nursing Anne
- Page 181 and 182:
1 1 Ostomy Care Training Models Set
- Page 183 and 184:
1 1 Freddie Fistula Skills Trainer
- Page 185 and 186:
1 Pat Pressure Ulcer Staging Model
- Page 187 and 188:
Professional Nursing Wounds This se
- Page 189 and 190:
1 Tracheotomy care simulator 1 This
- Page 191 and 192:
1 Suction training model With this
- Page 193 and 194:
1 Tube feeding simulator NG, OG and
- Page 195 and 196:
1 2 1 Injection belly This soft sto
- Page 197 and 198:
1 Common foot problems An incredibl
- Page 199 and 200:
1 Pitting edema model 1 Five variat
- Page 201 and 202:
1 1 PAT Professional Adipositas Tra
- Page 203 and 204:
1 Age simulation Set This unique se
- Page 205 and 206:
2 3 2 3 3 2 203
- Page 207 and 208:
1 Male catheterization and enema si
- Page 209 and 210:
1 2 Supplementary ears 2 This set i
- Page 211 and 212:
1 Ear examination Simulator 1 This
- Page 213 and 214:
1 OtoSim Educators Toolkit, Softwar
- Page 215 and 216:
1 OpthoSim • Ref.no. R65200 2 Ext
- Page 217 and 218:
1 Advanced Oral Care Simulator The
- Page 219 and 220:
1 PAT 2 PAT, the Pediatric Ausculta
- Page 221 and 222:
SimScope - the hybrid simulator The
- Page 223 and 224:
1 1 SimulScope Auscultation - Syste
- Page 225 and 226:
1 1 Clinical E-Scope The E-Scope, E
- Page 227 and 228:
1 1 Baby stap Reproduction of a neo
- Page 229 and 230:
1 Ultrasound compatible lumbar punc
- Page 231 and 232:
1 Epidural-Spinal Injection Simulat
- Page 233 and 234:
1 2 1 Training arm for intravenous
- Page 235 and 236:
1 Geriatric IV training arm 1 Devel
- Page 237 and 238:
1 I.v. injection hand The dorsal su
- Page 239 and 240:
1 2 1 Intradermal injection simulat
- Page 241 and 242:
1 Advanced Four-Vein Venipuncture T
- Page 243 and 244:
1 Intramuscular Training Model This
- Page 245 and 246:
1 Model of shoulder and arm anatomy
- Page 247 and 248:
1 1 1 Central venous puncture train
- Page 249 and 250:
1 CVC Insertion Simulator III The C
- Page 251 and 252:
Chester Chest Chester Chest is a li
- Page 253 and 254:
1 Breast plate for implantable port
- Page 255 and 256:
1 1 Pneumothorax training manikin R
- Page 257 and 258:
1 1 1 Ultrasound-guided pericardioc
- Page 259 and 260:
1 1 Intraosseous infusion trainer T
- Page 261 and 262:
1 ECMO Trainer Professional Simulat
- Page 263 and 264:
1 1 Cricothyrotomy and tracheostomy
- Page 265 and 266:
1 Difficult Airway Management Simul
- Page 267 and 268:
1 Difficult Airway Management Simul
- Page 269 and 270:
1 Intubation- and reanimation neona
- Page 271 and 272:
4 1 AVAILABLE SUPPLIES: 2 Replaceme
- Page 273 and 274:
1 Little Anne QCPR The proven train
- Page 275 and 276:
1 Adam training manikin Rugged and
- Page 277 and 278:
Resusci Anne First Aid The Resusci
- Page 279 and 280:
The following product versions are
- Page 281 and 282:
AVAILABLE VERSIONS: 1 Resusci Anne
- Page 283 and 284:
3 Resusci Junior QCPR 1 1 CPR torso
- Page 285 and 286:
NEW VERSION 2 Resusci Baby QCPR 1 1
- Page 287 and 288:
1 Airway Larry adult airway managem
- Page 289 and 290:
1 IO Legs for CRISIS and CPRLENE ma
- Page 291 and 292:
1 3 3 Blood pressure simulator Desi
- Page 293 and 294:
1 Complete CRiSis manikin Complete
- Page 295 and 296:
1 1 Child CRiSis manikin A dramatic
- Page 297 and 298:
1 Infant CRiSis manikin Practice:
- Page 299 and 300:
1 1 15-lead ECG placement trainer T
- Page 301 and 302:
Rescue manikin This manikin allows
- Page 303 and 304:
1 Manikin casualty simulation kit C
- Page 305 and 306:
1 Casualty simulation-basic The mos
- Page 307 and 308:
1 Xtreme trauma moulage kit Represe
- Page 309 and 310:
1 EZ wounds - professional wound si
- Page 311 and 312:
1 First aid arm 1 Train students in
- Page 313 and 314:
2 3 1 Skin suture trainer 1 This su
- Page 315 and 316:
1 Abdominal open and closure traine
- Page 317 and 318:
1 Laparoscopic trainer The portable
- Page 319 and 320:
1 Hole for polyps 1 EGD (esophagoga
- Page 321 and 322:
1 Colonoscopy Simulator The Colonos
- Page 323 and 324:
2 Tripod for x-ray phantom head Ver
- Page 325 and 326:
5 X-ray phantom elbow Part of upper
- Page 327 and 328:
Right Elbow Movable. Normal flexion
- Page 329 and 330:
327 We maintain and repair your x-r
- Page 331 and 332:
1 Pediatric whole body phantom The
- Page 333 and 334:
1 Whole body CT phantom A unique, l
- Page 335 and 336:
1 CT torso phantom A one-piece anth
- Page 337 and 338:
NEW! 1 Extremity Phantoms for CT, X
- Page 339 and 340:
1 Lung cancer screening model 1 Thi
- Page 341 and 342:
1 CT prostate phantom Resourceful m
- Page 343 and 344: 1 Abdominal intraoperative & laparo
- Page 345 and 346: 1 NEW! 1 Ultrasound Neonatal Head P
- Page 347 and 348: ULTRASOUND-PHANTOMS FOR QUALITY ASS
- Page 349 and 350: 1 1 Chinese acupuncture set, 5 mode
- Page 351 and 352: 1 1 Canine jaw with healthy and dis
- Page 353 and 354: 1 CPR dog CasPeR CasPeR the CPR Dog
- Page 355 and 356: 2 1 1 Goldie - K9 Breath/Heart Soun
- Page 357 and 358: 1 Canine i.v. leg 1 We are proud to
- Page 359 and 360: 1 Canine Dental / Surgical Model Th
- Page 361 and 362: 1 Fluffy Feline CPR Manikin The fel
- Page 363 and 364: 1 Squeekums The Squeekums Rat manik
- Page 365 and 366: 1 Horse foot, flexible The foot con
- Page 367 and 368: 4 Real animal bones Our animal bone
- Page 369 and 370: 1 Chart „The human muscles“ 2 C
- Page 371 and 372: 1 Chart „Upper Limb“ 2 Chart
- Page 373 and 374: 1 Chart „Reflexzones hand and foo
- Page 375 and 376: 1 Chart „Internal organs“ 70 x
- Page 377 and 378: 3D Anatomy Series The ground-breaki
- Page 379 and 380: 2 Posterior Abdominal wall 1 This l
- Page 381 and 382: 1 Posterior Body Wall / Ventral Dee
- Page 383 and 384: 1 NEW! 1 Upper Limb This 3D-printed
- Page 385 and 386: 1 Right thoracic wall - axilla, and
- Page 387 and 388: 1 1 Circle of Willis NEW! This 3D p
- Page 389 and 390: 1 Head and visceral column of the n
- Page 391 and 392: 1 2 NEW! NEW! 1 Heart This 3D print
- Page 393: NEW! 1 3 1 Cubital Fossa This 3D pr
- Page 397 and 398: 1 Lower Limb - deep dissection This
- Page 399 and 400: 1 Lower limb - superficial dissecti
- Page 401 and 402: Patient education models Product re
- Page 403 and 404: No, we do not repair bears, but…