Warfarin interaction2
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
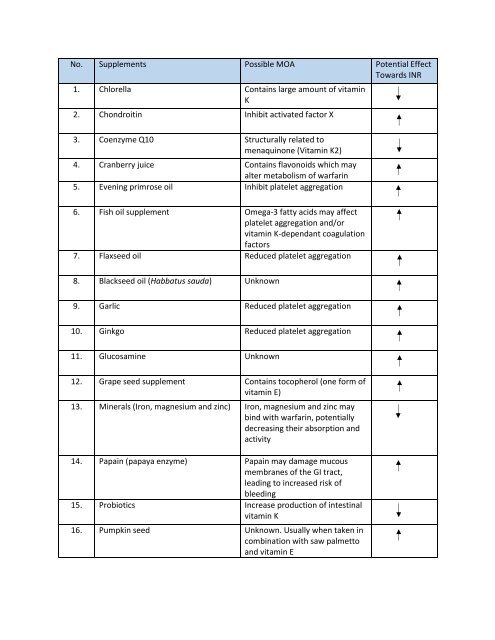
No. Supplements Possible MOA Potential Effect<br />
Towards INR<br />
1. Chlorella Contains large amount of vitamin<br />
K<br />
2. Chondroitin Inhibit activated factor X<br />
3. Coenzyme Q10 Structurally related to<br />
menaquinone (Vitamin K2)<br />
4. Cranberry juice Contains flavonoids which may<br />
alter metabolism of warfarin<br />
5. Evening primrose oil Inhibit platelet aggregation<br />
6. Fish oil supplement Omega-3 fatty acids may affect<br />
platelet aggregation and/or<br />
vitamin K-dependant coagulation<br />
factors<br />
7. Flaxseed oil Reduced platelet aggregation<br />
8. Blackseed oil (Habbatus sauda) Unknown<br />
9. Garlic Reduced platelet aggregation<br />
10. Ginkgo Reduced platelet aggregation<br />
11. Glucosamine Unknown<br />
12. Grape seed supplement Contains tocopherol (one form of<br />
vitamin E)<br />
13. Minerals (Iron, magnesium and zinc) Iron, magnesium and zinc may<br />
bind with warfarin, potentially<br />
decreasing their absorption and<br />
activity<br />
14. Papain (papaya enzyme) Papain may damage mucous<br />
membranes of the GI tract,<br />
leading to increased risk of<br />
bleeding<br />
15. Probiotics Increase production of intestinal<br />
vitamin K<br />
16. Pumpkin seed Unknown. Usually when taken in<br />
combination with saw palmetto<br />
and vitamin E