Dental Asia January/February 2023
For more than two decades, Dental Asia is the premium journal in linking dental innovators and manufacturers to its rightful audience. We devote ourselves in showcasing the latest dental technology and share evidence-based clinical philosophies to serve as an educational platform to dental professionals. Our combined portfolio of print and digital media also allows us to reach a wider market and secure our position as the leading dental media in the Asia Pacific region while facilitating global interactions among our readers.
For more than two decades, Dental Asia is the premium journal in linking dental innovators and manufacturers to its rightful audience. We devote ourselves in showcasing the latest dental technology and share evidence-based clinical philosophies to serve as an educational platform to dental professionals. Our combined portfolio of print and digital media also allows us to reach a wider market and secure our position as the leading dental media in the Asia Pacific region while facilitating global interactions among our readers.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CLINICAL FEATURE<br />
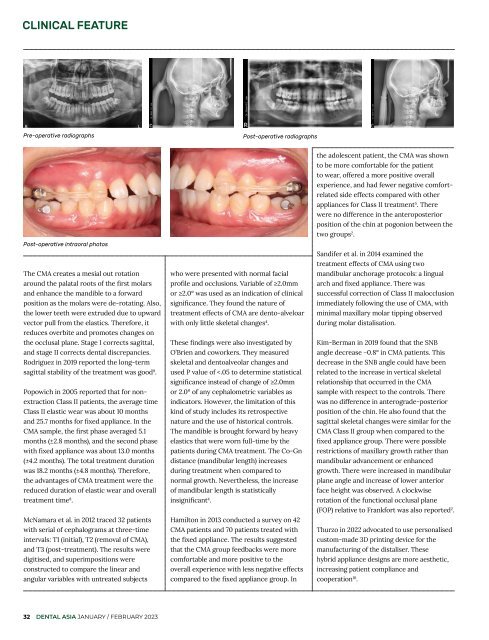
Pre-operative radiographs<br />
Post-operative radiographs<br />
Post-operative intraoral photos<br />
The CMA creates a mesial out rotation<br />
around the palatal roots of the first molars<br />
and enhance the mandible to a forward<br />
position as the molars were de-rotating. Also,<br />
the lower teeth were extruded due to upward<br />
vector pull from the elastics. Therefore, it<br />
reduces overbite and promotes changes on<br />
the occlusal plane. Stage I corrects sagittal,<br />
and stage II corrects dental discrepancies.<br />
Rodriguez in 2019 reported the long-term<br />
sagittal stability of the treatment was good 9 .<br />
Popowich in 2005 reported that for nonextraction<br />
Class II patients, the average time<br />
Class II elastic wear was about 10 months<br />
and 25.7 months for fixed appliance. In the<br />
CMA sample, the first phase averaged 5.1<br />
months (±2.8 months), and the second phase<br />
with fixed appliance was about 13.0 months<br />
(±4.2 months). The total treatment duration<br />
was 18.2 months (±4.8 months). Therefore,<br />
the advantages of CMA treatment were the<br />
reduced duration of elastic wear and overall<br />
treatment time 8 .<br />
McNamara et al. in 2012 traced 32 patients<br />
with serial of cephalograms at three-time<br />
intervals: T1 (initial), T2 (removal of CMA),<br />
and T3 (post-treatment). The results were<br />
digitised, and superimpositions were<br />
constructed to compare the linear and<br />
angular variables with untreated subjects<br />
who were presented with normal facial<br />
profile and occlusions. Variable of ≥2.0mm<br />
or ≥2.0° was used as an indication of clinical<br />
significance. They found the nature of<br />
treatment effects of CMA are dento-alveloar<br />
with only little skeletal changes 4 .<br />
These findings were also investigated by<br />
O’Brien and coworkers. They measured<br />
skeletal and dentoalveolar changes and<br />
used P value of