Basic concepts of population genetics - Bioversity International
Basic concepts of population genetics - Bioversity International
Basic concepts of population genetics - Bioversity International
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
… with a codominant marker<br />
Locus A<br />
Gel<br />
Indiv. 1 Indiv. 2 Indiv. 3<br />
A1 1 1 0<br />
A2 0 1 1<br />
M<br />
Genotypes<br />
A 1A 1<br />
Individuals<br />
1 2 3<br />
Scoring bands<br />
Copyright: IPGRI and Cornell University, 2003 Population <strong>genetics</strong> 22<br />
22<br />
A 1A 2<br />
Locus A<br />
A 2A 2<br />
M 1 2 3<br />
1,0 1,1 0,1<br />
(continued on next slide)<br />
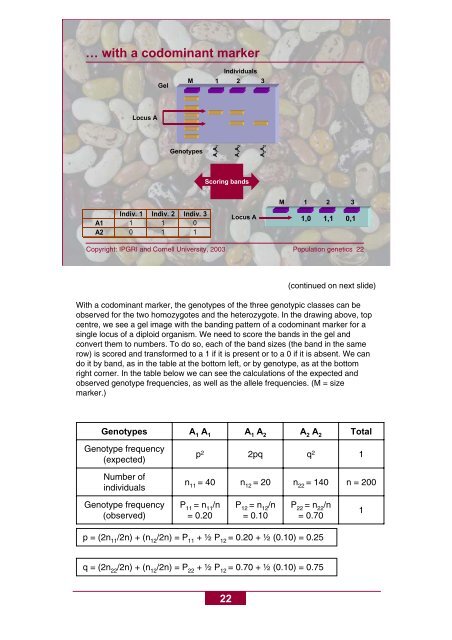
With a codominant marker, the genotypes <strong>of</strong> the three genotypic classes can be<br />
observed for the two homozygotes and the heterozygote. In the drawing above, top<br />
centre, we see a gel image with the banding pattern <strong>of</strong> a codominant marker for a<br />
single locus <strong>of</strong> a diploid organism. We need to score the bands in the gel and<br />
convert them to numbers. To do so, each <strong>of</strong> the band sizes (the band in the same<br />
row) is scored and transformed to a 1 if it is present or to a 0 if it is absent. We can<br />
do it by band, as in the table at the bottom left, or by genotype, as at the bottom<br />
right corner. In the table below we can see the calculations <strong>of</strong> the expected and<br />
observed genotype frequencies, as well as the allele frequencies. (M = size<br />
marker.)<br />
Genotypes<br />
Genotype frequency<br />
(expected)<br />
Number <strong>of</strong><br />
individuals<br />
Genotype frequency<br />
(observed)<br />
A 1 A 1<br />
p 2<br />
n 11 = 40<br />
P 11 = n 11 /n<br />
= 0.20<br />
A 1 A 2<br />
2pq<br />
n 12 = 20<br />
P 12 = n 12 /n<br />
= 0.10<br />
A 2 A 2<br />
q 2<br />
n 22 = 140<br />
P 22 = n 22 /n<br />
= 0.70<br />
p = (2n 11 /2n) + (n 12 /2n) = P 11 + ½ P 12 = 0.20 + ½ (0.10) = 0.25<br />
q = (2n 22 /2n) + (n 12 /2n) = P 22 + ½ P 12 = 0.70 + ½ (0.10) = 0.75<br />
Total<br />
1<br />
n = 200<br />
1