High Availability Theoretical Basics - Schneider Electric
High Availability Theoretical Basics - Schneider Electric
High Availability Theoretical Basics - Schneider Electric
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>High</strong> <strong>Availability</strong> with Collaborative Control System<br />
<strong>High</strong> <strong>Availability</strong> with Collaborative Control System<br />
In an automation system, how can you reach the level of availability required to keep<br />
the plant in operation? By what means should you enforce the system architecture,<br />
providing and maintaining access to the information required to monitor and control<br />
the process?<br />
This chapter provides answers to these questions, and reviews the system<br />
architecture from top to bottom, that is, from operator stations and data servers<br />
(Information Management) to Controllers and Devices (Control System Level), via<br />
communication networks (Communication Infrastructure Level).<br />
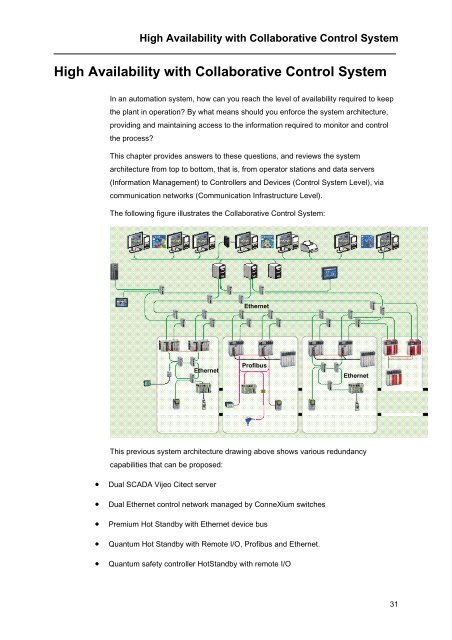
The following figure illustrates the Collaborative Control System:<br />
Ethernet<br />
This previous system architecture drawing above shows various redundancy<br />
capabilities that can be proposed:<br />
• Dual SCADA Vijeo Citect server<br />
Ethernet<br />
Profibus<br />
• Dual Ethernet control network managed by ConneXium switches<br />
• Premium Hot Standby with Ethernet device bus<br />
• Quantum Hot Standby with Remote I/O, Profibus and Ethernet.<br />
• Quantum safety controller HotStandby with remote I/O<br />
Ethernet<br />
31