Meiosi I - Bgbunict.it
Meiosi I - Bgbunict.it
Meiosi I - Bgbunict.it
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
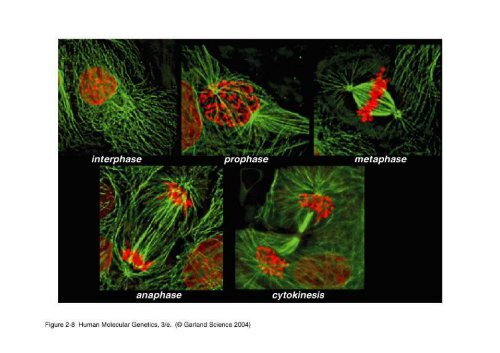
02_08.jpg
Nei Batteri – Scissione binaria
Evoluzione dei meccanismi di<br />
divisione cellulare
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
• Formazione del fuso<br />
• Condensazione della cromatina
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Riproduzione sessuale<br />
<strong>Meiosi</strong>
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
Variabil<strong>it</strong>à Genetica<br />
• Divers<strong>it</strong>à dei gameti prodotti da un individuo<br />
Crossing-over<br />
Assortimento indipendente<br />
• Fecondazione
MEIOSI<br />
2 successive divisioni cellulari<br />
1 duplicazione del DNA<br />
<strong>Meiosi</strong> I - si separano i cromosomi omologhi<br />
Riduzionale<br />
<strong>Meiosi</strong> II – si separano i cromatidi fratelli<br />
Equazionale
n - indica la ploidia<br />
c - indica il contenuto di DNA<br />
I <strong>Meiosi</strong><br />
II <strong>Meiosi</strong><br />
2n 2c 1n 2c 1n 1c<br />
1 cellula<br />
2 cellule 4 cellule
02_11.jpg<br />
Preparazione del<br />
complesso di assemblaggio<br />
I cromosomi omologhi iniziano<br />
ad appaiarsi si formano i<br />
bivalenti o tetradi<br />
Avviene il crossing-over<br />
Gli omologhi iniziano a separarsi<br />
ma restano un<strong>it</strong>i nei punti in cui è<br />
Avvenuto il crossing-over<br />
Si visualizzano i chiasmi<br />
I bivalenti diventano più contratti
Dal Volume: La Cellula, un approccio molecolare<br />
Piccin Nuova Libraria S.p.A.
ASSORTIMENTO INDIPENDENTE
02_10.jpg
<strong>Meiosi</strong>s is a unique form of cellular division by which a<br />
diploid cell produces genetically distinct haploid gametes.<br />
In<strong>it</strong>iation and regulation of mammalian meiosis differs<br />
between the sexes.<br />
In females, meiosis is in<strong>it</strong>iated during embryo development<br />
and arrested shortly after birth during prophase I.<br />
In males, spermatogonial stem cells in<strong>it</strong>iate meiosis at puberty<br />
and proceed through gametogenesis w<strong>it</strong>h no cell cycle arrest.
Spermatogenesis
Oogenesis
Genetic loci and alleles<br />
• defin<strong>it</strong>ions<br />
• genetic locus: a specific pos<strong>it</strong>ion or location on a chromosome<br />
• allele: one of the alternative versions of a DNA nucleotide<br />
sequence that may be at a given chromosomal locus<br />
A<br />
a<br />
b<br />
b<br />
maternal chr. 1<br />
paternal chr. 1<br />
locus A<br />
locus B<br />
• diploid: having maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes<br />
• haploid: having only one of the two homologous chromosomes<br />
• homozygous: having the same alleles at a genetic locus<br />
• heterozygous: having different alleles at a genetic locus<br />
• dominant: tra<strong>it</strong>s that are expressed in heterozygotes<br />
(i.e., one mutant allele and one normal allele)<br />
• recessive: tra<strong>it</strong>s that are expressed only in homozygotes<br />
(or compound heterozygotes w<strong>it</strong>h two mutant alleles)







![Glucidi-Lipidi-010210 [modalità compatibilità] - Bgbunict.it](https://img.yumpu.com/41100335/1/190x134/glucidi-lipidi-010210-modalita-compatibilita-bgbunictit.jpg?quality=85)






