The EMIS Audit
The EMIS Audit
The EMIS Audit
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
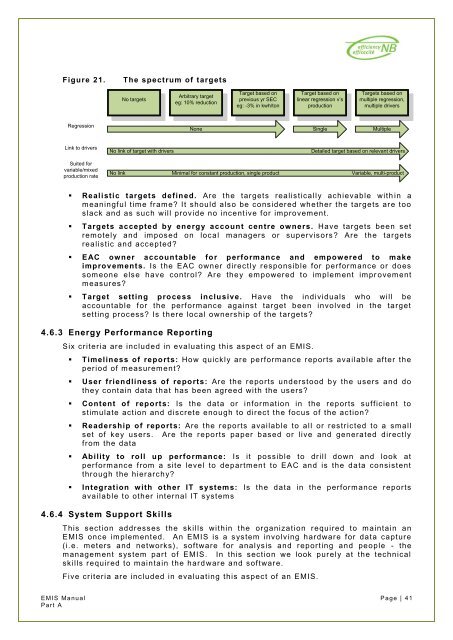
Figure 21. <strong>The</strong> spectrum of targets<br />
Regression<br />
Link to drivers<br />
Suited for<br />
variable/mixed<br />
production rate<br />
No targets<br />
Arbitrary target<br />
eg: 10% reduction<br />
None<br />
Target based on<br />
previous yr SEC<br />
eg: -3% in kwh/ton<br />
Target based on<br />
linear regression v‟s<br />
production<br />
Targets based on<br />
multiple regression,<br />
multiple drivers<br />
Single Multiple<br />
No link of target with drivers Detailed target based on relevant drivers<br />
No link Minimal for constant production, single product Variable, multi-product<br />
� Realistic targets defined. Are the targets realistically achievable with in a<br />
meaningful time frame? It should also be considered whether the targets are too<br />
slack and as such will provide no incentive for improvement.<br />
� Targets accepted by energy account centre owners. Have targets been set<br />
remotely and imposed on local managers or supervisors ? Are the targets<br />
realistic and accepted?<br />
� EAC owner accountable for performance and empowered to make<br />
improvements. Is the EAC owner directly responsible for performance or does<br />
someone else have control? Are they empowered to implement impr ovement<br />
measures?<br />
� Target setting process inclusive. Have the individuals who will be<br />
accountable for the performance against target been involved in the target<br />
setting process? Is there local ownership of the targets?<br />
4.6.3 Energy Performance Reporting<br />
Six criteria are included in evaluating this aspect of an <strong>EMIS</strong>.<br />
� Timeliness of reports: How quickly are performance reports available after the<br />
period of measurement?<br />
� User friendliness of reports: Are the reports understood by the users and do<br />
they contain data that has been agreed with the users?<br />
� Content of reports: Is the data or information in the reports sufficient to<br />
stimulate action and discrete enough to direct the focus of the action?<br />
� Readership of reports: Are the reports available to all or restricted to a small<br />
set of key users. Are the reports paper based or live and generated directly<br />
from the data<br />
� Ability to roll up performance: Is it possible to drill down and look at<br />
performance from a site level to department to EAC and is the data consistent<br />
through the hierarchy?<br />
� Integration with other IT systems: Is the data in the performance reports<br />
available to other internal IT s ystems<br />
4.6.4 System Support Skills<br />
This section addresses the skills within the organization required to maintain an<br />
<strong>EMIS</strong> once implemented. An <strong>EMIS</strong> is a s ystem involving hardware for data capture<br />
(i.e. meters and networks), software for analysis and reporting and people - the<br />
management system part of <strong>EMIS</strong>. In this section we look purely at the technical<br />
skills required to maintain the hard ware and software.<br />
Five criteria are included in evaluating this aspect of an <strong>EMIS</strong>.<br />
<strong>EMIS</strong> Ma nu al Page | 41<br />
Part A