- Page 2:
Applied Statistics Using SPSS, STAT
- Page 6:
E d itors Prof. Dr. Joaquim P. Marq
- Page 10:
Contents Preface to the Second Edit
- Page 14:
Contents ix 5.2.3 The Chi-Square Te
- Page 18:
Contents xi Appendix A - Short Surv
- Page 22:
Contents xiii E.26 Soil Pollution .
- Page 26:
Preface to the First Edition This b
- Page 30:
Symbols and Abbreviations Sample Se
- Page 34:
|A| determinant of matrix A tr(A) t
- Page 38:
Σ covariance matrix x arithmetic m
- Page 42:
1 Introduction 1.1 Deterministic Da
- Page 46:
18 h 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1.1 Dete
- Page 50:
1.2 Population, Sample and Statisti
- Page 54:
Table 1.3 1.2 Population, Sample an
- Page 58:
Table 1.4 1.3 Random Variables 9 Da
- Page 62:
1.4 Probabilities and Distributions
- Page 66:
1.5 Beyond a Reasonable Doubt... 13
- Page 70:
1.5 Beyond a Reasonable Doubt... 15
- Page 74:
1.6 Statistical Significance and Ot
- Page 78:
1.8 Software Tools 19 book we will
- Page 82:
1.8 Software Tools 21 In the follow
- Page 86:
1.8 Software Tools 23 illustrates t
- Page 90:
1.8 Software Tools 25 On-line help
- Page 94:
1.8 Software Tools 27 Figure 1.12.
- Page 98:
2 Presenting and Summarising the Da
- Page 102:
2.1 Preliminaries 31 The data can t
- Page 106:
» meteo=[ 181 143 36 39 37 % Pasti
- Page 110:
2.1 Preliminaries 35 are interested
- Page 114:
2.1 Preliminaries 37 Besides the in
- Page 118:
2.2 Presenting the Data 39 Sorting
- Page 122:
2.2 Presenting the Data 41 In Table
- Page 126:
2.2 Presenting the Data 43 With SPS
- Page 130:
2.2 Presenting the Data 45 Figure 2
- Page 134:
2.2 Presenting the Data 47 Figure 2
- Page 138:
2.2 Presenting the Data 49 Let X de
- Page 142:
2.2 Presenting the Data 51 Commands
- Page 146:
2.2 Presenting the Data 53 A: The c
- Page 150:
2.2 Presenting the Data 55 The s, c
- Page 154:
2.2 Presenting the Data 57 histogra
- Page 158:
2.3 Summarising the Data 59 type da
- Page 162:
2.3 Summarising the Data 61 delimit
- Page 166:
2.3 Summarising the Data 63 The sam
- Page 170:
Note that: 2.3 Summarising the Data
- Page 174:
where sXY, the sample covariance of
- Page 178:
2.3 Summarising the Data 69 STATIST
- Page 182:
2.3 Summarising the Data 71 A: The
- Page 186:
2.3.6 Measures of Association for N
- Page 190:
2.3 Summarising the Data 75 with th
- Page 194:
Exercises 77 A: We use the N, S and
- Page 198:
Exercises 79 2.13 Determine the box
- Page 202:
3 Estimating Data Parameters Making
- Page 206:
3.1 Point Estimation and Interval E
- Page 210:
3.2 Estimating a Mean 85 In Chapter
- Page 214:
3.2 Estimating a Mean 87 There are
- Page 218:
3.2 Estimating a Mean 89 A: Using M
- Page 222:
3.2 Estimating a Mean 91 Figure 3.5
- Page 226:
3.3 Estimating a Proportion 93 esti
- Page 230:
3.4 Estimating a Variance 95 is to
- Page 234:
3.5 Estimating a Variance Ratio 97
- Page 238:
3.6 Bootstrap Estimation 99 i. F df
- Page 242:
3.6 Bootstrap Estimation 101 about
- Page 246:
3.6 Bootstrap Estimation 103 The bi
- Page 250:
3.6 Bootstrap Estimation 105 In the
- Page 254:
Exercises 107 In order to obtain bo
- Page 258:
Exercises 109 3.14 Consider the CTG
- Page 262:
112 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 266:
114 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 270:
116 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 274:
118 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 278:
120 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 282:
122 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 286:
124 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 290:
126 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 294:
128 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 298:
130 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 302:
132 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 306:
134 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 310:
136 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 314:
138 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 318:
140 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 322:
142 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 326:
144 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 330:
146 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 334:
148 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 338:
150 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 342:
152 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 346:
154 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 350:
156 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 354:
158 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 358:
160 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 362:
162 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 366:
164 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 370:
166 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 374:
168 4 Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 378:
5 Non-Parametric Tests of Hypothese
- Page 382:
5.1 Inference on One Population 173
- Page 386:
5.1 Inference on One Population 175
- Page 390:
s = npq = 224× 0. 75× 0. 25 = 6.4
- Page 394:
5.1.3 The Chi-Square Goodness of Fi
- Page 398:
5.1 Inference on One Population 181
- Page 402:
5.1 Inference on One Population 183
- Page 406:
1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 F
- Page 410:
5.1.5 The Lilliefors Test for Norma
- Page 414:
5.2 Contingency Tables 189 fewer mi
- Page 418:
2 1 5.2 Contingency Tables 191 degr
- Page 422:
5.2 Contingency Tables 193 An alter
- Page 426:
5.2 Contingency Tables 195 male and
- Page 430:
5.2 Contingency Tables 197 first ca
- Page 434:
5.2 Contingency Tables 199 very low
- Page 438:
5.3.1 Tests for Two Independent Sam
- Page 442:
5.3 Inference on Two Populations 20
- Page 446:
5.3 Inference on Two Populations 20
- Page 450:
5.3 Inference on Two Populations 20
- Page 454:
5.3 Inference on Two Populations 20
- Page 458:
Example 5.19 5.3 Inference on Two P
- Page 462:
3 ( N − N ) 5.4 Inference on More
- Page 466:
5.4 Inference on More Than Two Popu
- Page 470:
5.4 Inference on More Than Two Popu
- Page 474:
Exercises 219 5.7 Several previous
- Page 478:
Exercises 221 5.23 Run the non-para
- Page 482:
6 Statistical Classification Statis
- Page 486:
x 2 o o o o o o o o oo o o o o o o
- Page 490:
6.2 Linear Discriminants 227 Figure
- Page 494:
6.2 Linear Discriminants 229 Figure
- Page 498:
6.2 Linear Discriminants 231 Let us
- Page 502:
Table 6.5. Summary of minimum dista
- Page 506:
6.3 Bayesian Classification 235 Not
- Page 510:
6.3 Bayesian Classification 237 Fig
- Page 514:
6.3 Bayesian Classification 239 Let
- Page 518:
6.3 Bayesian Classification 241 Not
- Page 522:
0.5 0.45 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 0.15
- Page 526:
6.3 Bayesian Classification 245 For
- Page 530:
Reality A N Decision A N a b c d 6.
- Page 534:
6.4 The ROC Curve 249 Figure 6.17.
- Page 538:
6.4 The ROC Curve 251 In order to o
- Page 542:
6.5 Feature Selection 253 A: The RO
- Page 546:
6.5 Feature Selection 255 comfortab
- Page 550:
6.6 Classifier Evaluation 257 Resub
- Page 554:
259 A: Table 6.12 shows the leave-o
- Page 558:
6.7 Tree Classifiers 261 Figure 6.2
- Page 562:
6.7 Tree Classifiers 263 or not a g
- Page 566:
6.7 Tree Classifiers 265 The classi
- Page 570:
6.7 Tree Classifiers 267 The classi
- Page 574:
Exercises 269 6.2 Repeat the previo
- Page 578:
7 Data Regression An important obje
- Page 582:
7.1.2 Estimating the Regression Fun
- Page 586:
7.1 Simple Linear Regression 275 Fi
- Page 590:
2 2 2 7.1 Simple Linear Regression
- Page 594:
7.1 Simple Linear Regression 279 Co
- Page 598:
Example 7.3 7.1 Simple Linear Regre
- Page 602:
7.1 Simple Linear Regression 283 Th
- Page 606:
7.1 Simple Linear Regression 285 Fi
- Page 610:
7.1 Simple Linear Regression 287 Le
- Page 614:
7.2 Multiple Regression 7.2.1 Gener
- Page 618:
7.2 Multiple Regression 291 For the
- Page 622:
YYˆ = ∑ ∑ ( y ( y − y)( yˆ
- Page 626:
7.2 Multiple Regression 295 Figure
- Page 630:
7.2 Multiple Regression 297 Table 7
- Page 634:
7.2.5.1 Tests for Regression Coeffi
- Page 638:
The Yi can also be linearly modelle
- Page 642:
3000 2000 1000 0 -1000 -2000 Raw Re
- Page 646:
7.3 Building and Evaluating the Reg
- Page 650:
There are other ways to detect outl
- Page 654:
a 4 3 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 Expected Norma
- Page 658:
7.3 Building and Evaluating the Reg
- Page 662:
7.3 Building and Evaluating the Reg
- Page 666:
Example 7.19 7.4 Regression Through
- Page 670:
6 y 4 2 0 -2 -4 -6 -8 -10 x 7.5 Rid
- Page 674:
7.5 Ridge Regression 319 The b vect
- Page 678:
Example 7.20 7.5 Ridge Regression 3
- Page 682:
7.5 Logit and Probit Models 323 Let
- Page 686:
7.5 Logit and Probit Models 325 sec
- Page 690:
Exercises 327 Commands 7.7. SPSS an
- Page 694:
8 Data Structure Analysis In the pr
- Page 698:
8.1 Principal Components 331 where
- Page 702:
8.1 Principal Components 333 » % E
- Page 706:
8.1 Principal Components 335 A: The
- Page 710:
8.2 Dimensional Reduction 8.2 Dimen
- Page 714:
12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 eig
- Page 718:
0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 -0.1 -0.2 U2 8.
- Page 722:
8.3 Principal Components of Correla
- Page 726:
8.3 Principal Components of Correla
- Page 730:
8.4 Factor Analysis 8.4 Factor Anal
- Page 734:
8.4 Factor Analysis 349 The main be
- Page 738:
Exercises 351 c) The scatter plot o
- Page 742:
9 Survival Analysis In medical stud
- Page 746:
9.2 Non-Parametric Analysis of Surv
- Page 750:
9.2 Non-Parametric Analysis of Surv
- Page 754:
9.2 Non-Parametric Analysis of Surv
- Page 758:
9.2 Non-Parametric Analysis of Surv
- Page 762:
9.2 Non-Parametric Analysis of Surv
- Page 766:
1. The Log-Rank Test. 9.3 Comparing
- Page 770:
9.4 Models for Survival Data 367 Th
- Page 774:
9.4 Models for Survival Data 369 ST
- Page 778:
9.4 Models for Survival Data 371 Ex
- Page 782:
1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 Cumulat
- Page 786:
10 Directional Data The analysis an
- Page 790:
10.1 Representing Directional Data
- Page 794:
10.1 Representing Directional Data
- Page 798:
10.2 Descriptive Statistics 381 com
- Page 802:
10.3 The von Mises Distributions 38
- Page 806:
10.3 The von Mises Distributions 38
- Page 810:
10.4 Assessing the Distribution of
- Page 814:
Example 10.10 10.4 Assessing the Di
- Page 818:
10.4 Assessing the Distribution of
- Page 822:
10.4 Assessing the Distribution of
- Page 826:
10.5 Tests on von Mises Distributio
- Page 830:
10.6 Non-Parametric Tests 10.6 Non-
- Page 834:
10.6 Non-Parametric Tests 399 Examp
- Page 838:
Exercises 401 10.8 Compare the two
- Page 842:
404 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 846: 406 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 850: 408 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 854: 410 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 858: 412 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 862: 414 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 866: 416 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 870: 418 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 874: 420 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 878: 422 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 882: 424 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 886: 426 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 890: 428 Appendix A - Short Survey on Pr
- Page 894: Appendix B - Distributions B.1 Disc
- Page 900: 434 Appendix B - Distributions A: T
- Page 904: 436 Appendix B - Distributions For
- Page 908: 438 Appendix B - Distributions A: T
- Page 912: 440 Appendix B - Distributions Dist
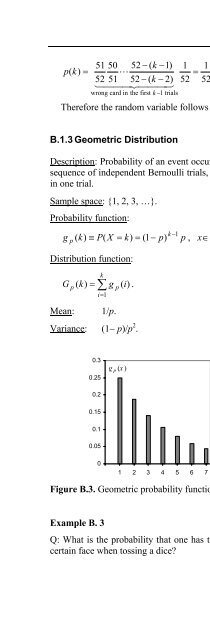
- Page 916: 442 Appendix B - Distributions 0.45
- Page 920: 444 Appendix B - Distributions B.2.
- Page 924: 446 Appendix B - Distributions 1.2
- Page 928: 448 Appendix B - Distributions B.2.
- Page 932: 450 Appendix B - Distributions Dist
- Page 936: 452 Appendix B - Distributions 1 0.
- Page 940: 454 Appendix B - Distributions 0.6
- Page 944: 456 Appendix C - Point Estimation T
- Page 948:
458 Appendix C - Point Estimation
- Page 952:
460 Appendix D - Tables p n k 0.05
- Page 956:
462 Appendix D - Tables p n k 0.05
- Page 960:
464 Appendix D - Tables p n k 0.05
- Page 964:
466 Appendix D - Tables D.3 Student
- Page 968:
468 Appendix D - Tables D.5 Critica
- Page 972:
470 Appendix E - Datasets The varia
- Page 976:
472 Appendix E - Datasets E.6 CTG T
- Page 980:
474 Appendix E - Datasets E.9 FHR T
- Page 984:
476 Appendix E - Datasets E.14 Fore
- Page 988:
478 Appendix E - Datasets DATE_REOP
- Page 992:
480 Appendix E - Datasets CG: Conic
- Page 996:
482 Appendix E - Datasets E.26 Soil
- Page 1000:
484 Appendix E - Datasets E.29 VCG
- Page 1004:
Appendix F - Tools F.1 MATLAB Funct
- Page 1008:
Appendix F - Tools 489 r
- Page 1012:
References Chapters 1 and 2 Anderso
- Page 1016:
References 493 Gardner MJ, Altman D
- Page 1020:
References 495 Raudys S, Pikelis V
- Page 1024:
References 497 Mardia KV, Jupp PE (
- Page 1028:
500 Index 5.9 (two paired samples t
- Page 1032:
502 Index H hazard function, 353 ha
- Page 1036:
504 Index S sample, 5 mean, 416 siz