9 Contact Stresses
9 Contact Stresses
9 Contact Stresses
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
424<br />
The maximum compressive stress becomes<br />
σc = 0.579nc<br />
<br />
F/(K 2 γ 2 1/3 )<br />
<br />
40 000<br />
= 0.579 × 0.9964<br />
0.39382 × 9.1592 × 10−24 1/3 The rigid approach of the two bodies is given as<br />
d = 0.825nd(F 2 γ 2 /K ) 1/3<br />
<br />
40 000<br />
= 0.825(0.9964)<br />
2 × 9.1592 × 10−24 1/3 0.3938<br />
CONTACT STRESSES<br />
= 838.8 MPa (16)<br />
= 0.05742 mm (17)<br />
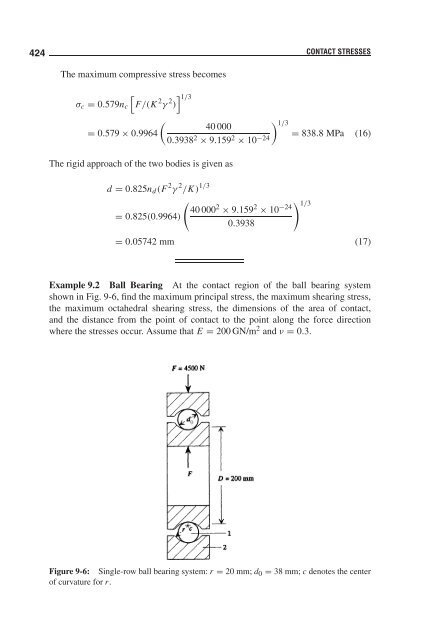
Example 9.2 Ball Bearing At the contact region of the ball bearing system<br />
shown in Fig. 9-6, find the maximum principal stress, the maximum shearing stress,<br />
the maximum octahedral shearing stress, the dimensions of the area of contact,<br />
and the distance from the point of contact to the point along the force direction<br />
where the stresses occur. Assume that E = 200 GN/m 2 and ν = 0.3.<br />
Figure 9-6: Single-row ball bearing system: r = 20 mm; d0 = 38 mm; c denotes the center<br />
of curvature for r.