9 Contact Stresses
9 Contact Stresses
9 Contact Stresses
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
420<br />
Values of Coefficients<br />
1.000<br />
0.800<br />
0.600<br />
0.400<br />
0.300<br />
0.200<br />
0.100<br />
0.080<br />
0.060<br />
0.040<br />
0.030<br />
0.020<br />
0.010<br />
0.008<br />
0.006<br />
0.004<br />
C Cz C <br />
C oct<br />
CONTACT STRESSES<br />
0.003<br />
200 300 400 600 800 1000 2000 3000 6000 10,000<br />
B/A<br />
C d<br />
k = b/a<br />
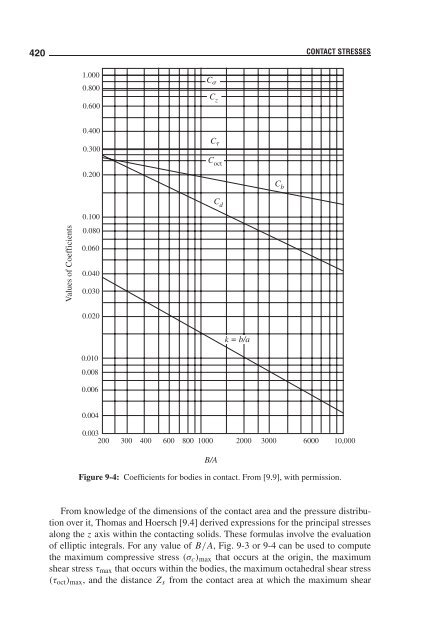
Figure 9-4: Coefficients for bodies in contact. From [9.9], with permission.<br />
From knowledge of the dimensions of the contact area and the pressure distribution<br />
over it, Thomas and Hoersch [9.4] derived expressions for the principal stresses<br />
along the z axis within the contacting solids. These formulas involve the evaluation<br />
of elliptic integrals. For any value of B/A, Fig. 9-3 or 9-4 can be used to compute<br />
the maximum compressive stress (σc)max that occurs at the origin, the maximum<br />
shear stress τmax that occurs within the bodies, the maximum octahedral shear stress<br />
(τoct)max, and the distance Zs from the contact area at which the maximum shear<br />
C b