Broadband Applications & Construction Manual - Public - CommScope
Broadband Applications & Construction Manual - Public - CommScope
Broadband Applications & Construction Manual - Public - CommScope
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Wiring Schemes<br />
Commercial Installations 11.2<br />
Wiring Schemes<br />
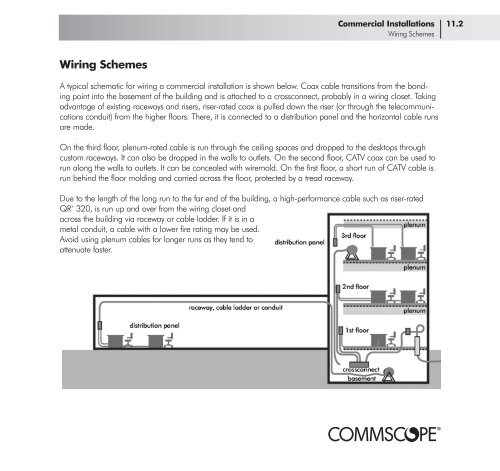
A typical schematic for wiring a commercial installation is shown below. Coax cable transitions from the bonding<br />
point into the basement of the building and is attached to a crossconnect, probably in a wiring closet. Taking<br />
advantage of existing raceways and risers, riser-rated coax is pulled down the riser (or through the telecommunications<br />
conduit) from the higher floors. There, it is connected to a distribution panel and the horizontal cable runs<br />
are made.<br />
On the third floor, plenum-rated cable is run through the ceiling spaces and dropped to the desktops through<br />
custom raceways. It can also be dropped in the walls to outlets. On the second floor, CATV coax can be used to<br />
run along the walls to outlets. It can be concealed with wiremold. On the first floor, a short run of CATV cable is<br />
run behind the floor molding and carried across the floor, protected by a tread raceway.<br />
Due to the length of the long run to the far end of the building, a high-performance cable such as riser-rated<br />
QR ®<br />
320, is run up and over from the wiring closet and<br />
across the building via raceway or cable ladder. If it is in a<br />
metal conduit, a cable with a lower fire rating may be used.<br />
Avoid using plenum cables for longer runs as they tend to<br />
attenuate faster.