The Röntgen Radiation and its application in studies of ... - Mansic
The Röntgen Radiation and its application in studies of ... - Mansic
The Röntgen Radiation and its application in studies of ... - Mansic
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
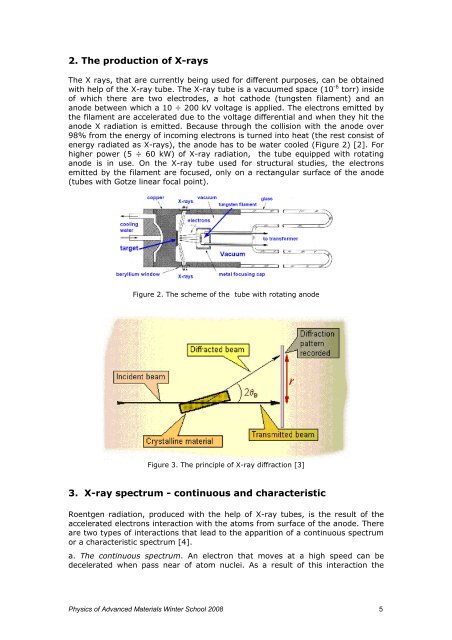
2. <strong>The</strong> production <strong>of</strong> X-rays<br />
<strong>The</strong> X rays, that are currently be<strong>in</strong>g used for different purposes, can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
with help <strong>of</strong> the X-ray tube. <strong>The</strong> X-ray tube is a vacuumed space (10 -6 torr) <strong>in</strong>side<br />
<strong>of</strong> which there are two electrodes, a hot cathode (tungsten filament) <strong>and</strong> an<br />
anode between which a 10 ÷ 200 kV voltage is applied. <strong>The</strong> electrons emitted by<br />
the filament are accelerated due to the voltage differential <strong>and</strong> when they hit the<br />
anode X radiation is emitted. Because through the collision with the anode over<br />
98% from the energy <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>com<strong>in</strong>g electrons is turned <strong>in</strong>to heat (the rest consist <strong>of</strong><br />
energy radiated as X-rays), the anode has to be water cooled (Figure 2) [2]. For<br />
higher power (5 ÷ 60 kW) <strong>of</strong> X-ray radiation, the tube equipped with rotat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
anode is <strong>in</strong> use. On the X-ray tube used for structural <strong>studies</strong>, the electrons<br />
emitted by the filament are focused, only on a rectangular surface <strong>of</strong> the anode<br />
(tubes with Gotze l<strong>in</strong>ear focal po<strong>in</strong>t).<br />
Figure 2. <strong>The</strong> scheme <strong>of</strong> the tube with rotat<strong>in</strong>g anode<br />
Figure 3. <strong>The</strong> pr<strong>in</strong>ciple <strong>of</strong> X-ray diffraction [3]<br />
3. X-ray spectrum - cont<strong>in</strong>uous <strong>and</strong> characteristic<br />
Roentgen radiation, produced with the help <strong>of</strong> X-ray tubes, is the result <strong>of</strong> the<br />
accelerated electrons <strong>in</strong>teraction with the atoms from surface <strong>of</strong> the anode. <strong>The</strong>re<br />
are two types <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>teractions that lead to the apparition <strong>of</strong> a cont<strong>in</strong>uous spectrum<br />
or a characteristic spectrum [4].<br />
a. <strong>The</strong> cont<strong>in</strong>uous spectrum. An electron that moves at a high speed can be<br />
decelerated when pass near <strong>of</strong> atom nuclei. As a result <strong>of</strong> this <strong>in</strong>teraction the<br />
Physics <strong>of</strong> Advanced Materials W<strong>in</strong>ter School 2008 5