The Röntgen Radiation and its application in studies of ... - Mansic
The Röntgen Radiation and its application in studies of ... - Mansic
The Röntgen Radiation and its application in studies of ... - Mansic
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
k<strong>in</strong>etic energy <strong>of</strong> the electron is transformed totally or partially, <strong>in</strong>to a photon <strong>of</strong><br />
X-ray, with <strong>its</strong> frequency ν given by E<strong>in</strong>ste<strong>in</strong>’s equation:<br />
2 2 ( v − v ) = ⋅ϑ<br />
⎛ m ⎞<br />
∆E = ⎜ ⎟ ⋅ 1 2 h<br />
⎝ 2 ⎠<br />
b. <strong>The</strong> characteristic spectrum. Another type <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>teraction <strong>of</strong> the accelerated<br />
electron with an atom could result <strong>in</strong> the expulsion <strong>of</strong> an electron from the<br />
<strong>in</strong>terior electronic orb<strong>its</strong> <strong>of</strong> the target atom <strong>and</strong> then the atom rema<strong>in</strong>s <strong>in</strong> an<br />
excited, ionized state. In order to come back to the normal state the jump <strong>of</strong> one<br />
electron from higher orbital is needed. Excess <strong>of</strong> energy is emitted as a photon <strong>of</strong> X-ray<br />
whit constant value <strong>of</strong> the wavelength.<br />
X-ray diffraction is used for:<br />
• Measur<strong>in</strong>g the average spac<strong>in</strong>g between crystallographic pla<strong>in</strong>s<br />
• Determ<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>of</strong> the orientation <strong>of</strong> a s<strong>in</strong>gle crystal or gra<strong>in</strong><br />
• Quantitative <strong>and</strong> qualitative phase analysis<br />
• F<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g the crystal structure <strong>of</strong> an unknown material<br />
• Measur<strong>in</strong>g the size, shape <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>ternal stress <strong>of</strong> small crystall<strong>in</strong>e regions.<br />
Properties <strong>of</strong> X-rays<br />
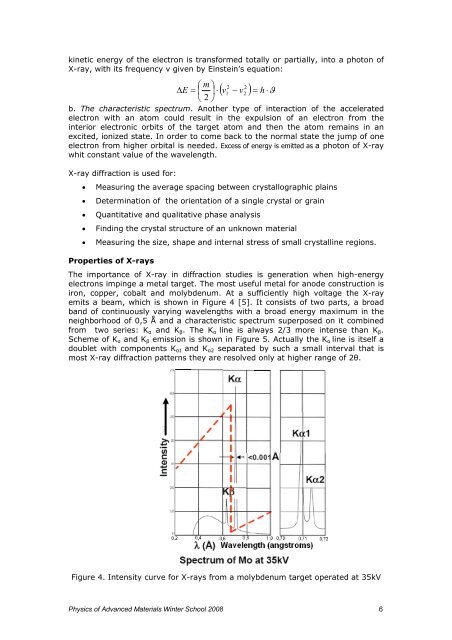
<strong>The</strong> importance <strong>of</strong> X-ray <strong>in</strong> diffraction <strong>studies</strong> is generation when high-energy<br />
electrons imp<strong>in</strong>ge a metal target. <strong>The</strong> most useful metal for anode construction is<br />
iron, copper, cobalt <strong>and</strong> molybdenum. At a sufficiently high voltage the X-ray<br />
em<strong>its</strong> a beam, which is shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 4 [5]. It consists <strong>of</strong> two parts, a broad<br />
b<strong>and</strong> <strong>of</strong> cont<strong>in</strong>uously vary<strong>in</strong>g wavelengths with a broad energy maximum <strong>in</strong> the<br />
neighborhood <strong>of</strong> 0,5 Å <strong>and</strong> a characteristic spectrum superposed on it comb<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
from two series: Kα <strong>and</strong> Kβ. <strong>The</strong> Kα l<strong>in</strong>e is always 2/3 more <strong>in</strong>tense than Kβ.<br />
Scheme <strong>of</strong> Kα <strong>and</strong> Kβ emission is shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 5. Actually the Kα l<strong>in</strong>e is <strong>its</strong>elf a<br />
doublet with components Kα1 <strong>and</strong> Kα2 separated by such a small <strong>in</strong>terval that is<br />
most X-ray diffraction patterns they are resolved only at higher range <strong>of</strong> 2θ.<br />
Figure 4. Intensity curve for X-rays from a molybdenum target operated at 35kV<br />
Physics <strong>of</strong> Advanced Materials W<strong>in</strong>ter School 2008 6