worksheet and assessment card masters - National STEM Centre
worksheet and assessment card masters - National STEM Centre
worksheet and assessment card masters - National STEM Centre
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
fabric cling <strong>and</strong><br />
anti-stat<br />
Garments that cling feel uncomfortable, particularly<br />
when they ride up the body. They look unsightly <strong>and</strong><br />
may spoil the drape of other clothing worn over them.<br />
They also attract dust from the air <strong>and</strong> become quickly<br />
soiled.<br />
The clinging of charged garments to the body arises<br />
with certain types of fibres (especially nylon),<br />
particularly when worn next to each other in warm,<br />
dry conditions. This clinging effect is due mainly to<br />
the electro-static forces between the charge on the<br />
clothing <strong>and</strong> the opposite charge built up on the<br />
body. The charge on the body may be caused by<br />
layers of clothing next to each other (such as a dress<br />
<strong>and</strong> a petticoat) rubbing together when the wearer is<br />
walking about, causing the petticoat to be drawn to<br />
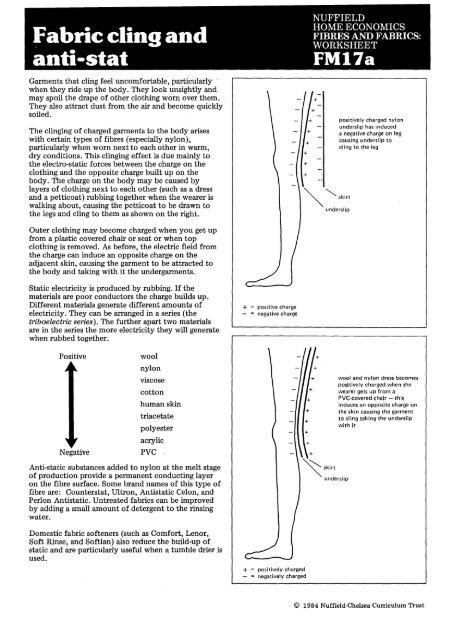
the legs <strong>and</strong> cling to them as shown on the right.<br />
Outer clothing may become charged when you get up<br />
from a plastic covered chair or seat or when top<br />
clothing is removed. As before, the electric field from<br />
the charge can induce an opposite charge on the<br />
adjacent skin, causing the garment to be attracted to<br />
the body <strong>and</strong> taking with it the undergarments.<br />
Static electricity is produced by rubbing. If the<br />
materials are poor conductors the charge builds up.<br />
Different materials generate different amounts of<br />
electricity. They can be arranged in a series (the<br />
triboelectric series). The further apart two materials<br />
are in the series the more electricity they will generate<br />
when rub bed together.<br />
Positive<br />
Negative<br />
wool<br />
nylon<br />
viscose<br />
cotton<br />
human skin<br />
triacetate<br />
polyester<br />
acrylic<br />
PVC 'C<br />
Anti-static substances added to nylon at the melt stage<br />
of production provide a permanent conducting layer<br />
on the fibre surface. Some br<strong>and</strong> names of this type of<br />
fibre are: Counterstat, Ultron, Antistatic Celon, <strong>and</strong><br />
Perlon Antistatic. Untreated fabrics can be improved<br />
by adding a small amount of detergent to the rinsing<br />
water.<br />
Domestic fabric softeners (such as Comfort, Lenor,<br />
Soft Rinse, <strong>and</strong> Softlan) also reduce the build-up of<br />
static <strong>and</strong> are particularly useful when a tumble drier is<br />
used.<br />
+ = positive charge<br />
- = negative charge<br />
+ = positively charged<br />
- = negatively charged<br />
+<br />
+<br />
NUFFIELD<br />
HOME ECONOMICS<br />
FIBRES AND FABRICS:<br />
WORKSHEET<br />
FM17a<br />
"'" '-..... skin<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
underslip<br />
positively charged nylon<br />
underslip has induced<br />
a negative charge on leg<br />
causing underslip to<br />
cling to the leg<br />
wool <strong>and</strong> nylon dress becomes<br />
positively charged when the<br />
wearer gets up from a<br />
PVC-covered chair - this<br />
induces an opposite charge on<br />
the skin causing the garment<br />
to cling taking the underslip<br />
with it<br />
© 1984 Nuffield-Chelsea Curriculum Trust