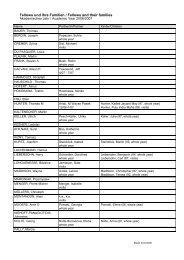
- Page 1 and 2:
Wissenschaftskolleg zu Berlin INSTI
- Page 3 and 4:
INHALTSVERZEICHNIS 11 . . . . . VOR
- Page 5 and 6:
105 . . . . . THERE IS NO SUCH STRE
- Page 7 and 8:
201 . . . . . IN THE FULLNESS OF TI
- Page 9 and 10:
VORWORT DER HERAUSGEBER Das Fellowj
- Page 11:
of science I achieved“, in einer
- Page 14 and 15:
16 Wissenschaftskolleg zu Berlin VE
- Page 16 and 17:
Dem Herzen gibt es nichts, dem lech
- Page 18 and 19:
Schlagwort unserer heutigen Wissens
- Page 20 and 21:
sondern auch ein neuer, gelassenere
- Page 22 and 23:
spring was redundant. Could this po
- Page 24 and 25:
their history impoverishes our unde
- Page 26 and 27:
with more pleasure than I ever have
- Page 28 and 29:
first weeks of Wiko life, infectiou
- Page 30 and 31:
seminate the idea that not only con
- Page 32 and 33:
One can, as always, find a nice quo
- Page 34 and 35:
continued to circle and approach fr
- Page 36 and 37:
„WELTHAUPTSTADT DES ATHEISMUS“
- Page 38 and 39:
Klugen Gelehrten und faszinierenden
- Page 40 and 41:
weiter aus in allen möglichen Inst
- Page 42 and 43:
Marxismus abgeschworen und beschlos
- Page 44 and 45:
VERGLEICHEN, VERÄNDERN, VERSTEHEN
- Page 46 and 47:
den ägyptischen Fatimidenkalifen d
- Page 48 and 49:
thodisch wichtigen Tagungen: am Eur
- Page 50 and 51:
EUROPAS TIEFGRÜNDIGKEIT TOSHIO HOS
- Page 52 and 53:
„Lied“ für Flöte und Klavier
- Page 54 and 55:
aufzupassen! Jedoch ist diese Rastz
- Page 56 and 57:
Working on a day-to-day basis with
- Page 58 and 59:
derstand the need to account for te
- Page 60 and 61:
van Arnim for her efforts in suppor
- Page 62 and 63:
„LEIHFRIST“ (TAGEBUCH) MARTIN K
- Page 64 and 65:
Die schwer atmende und sich auf der
- Page 66 and 67:
noch zur Musik. Ein Junge stürzt a
- Page 68 and 69:
BERLIN FOREVER ULRICH KELLER It wil
- Page 70 and 71:
ven”. Everything I have thus far
- Page 72 and 73:
For my wife and myself the “Gespr
- Page 74 and 75:
close-knit community that has lived
- Page 76 and 77:
of the lesson that developments in
- Page 78 and 79:
METAMORPHOSIS: HOW DID I BECOME AN
- Page 80 and 81:
The luxury of time offered by Wiko
- Page 82 and 83:
the University of Münster, Germany
- Page 84 and 85:
KOMPONIEREN HEISST NACHDENKEN HELMU
- Page 86 and 87:
Die knapp sechs Monate meines Aufen
- Page 88 and 89:
Der Versuchung, über wertvolle Beg
- Page 90 and 91:
My own time was taken up above all
- Page 92 and 93:
A COMMUNITY OF (NATURALIZED?) MINDS
- Page 94 and 95:
own conscious decision-making. He i
- Page 96 and 97:
year. Still, it is a nice surprise
- Page 98 and 99:
unique combination of rigor and fre
- Page 100 and 101:
Focus was achieved; solitude was no
- Page 102 and 103:
a new language, and Leticia (Fellow
- Page 104 and 105:
I described the use of Social Darwi
- Page 106 and 107:
Le travail dans l’œuvre Comment
- Page 108 and 109:
sition de personnel (travail tempor
- Page 110 and 111:
de l’expérience doit réenclench
- Page 112 and 113:
egagne mon pays avec l’espoir qu
- Page 114 and 115:
Abschiedsfest Neben vielem anderen,
- Page 116 and 117:
Gesprächskonzert Typisches Genre d
- Page 118 and 119:
Projekt Die Idee des „Projekts“
- Page 120 and 121:
franca, contre laquelle j’ai vain
- Page 122 and 123:
toujours quelques fellows (souvent
- Page 124 and 125:
DO SPECIES DIFFER IN VALUE? ARNE Ø
- Page 126 and 127:
distinctiveness, and this paper app
- Page 128 and 129:
Mooers, A. Ø., L. R. Prugh, M. Fes
- Page 130 and 131:
schwein“ leben durfte) ist wunder
- Page 132 and 133:
sein. Dass sich Herr Nettelbeck und
- Page 134 and 135:
EINSAMKEIT UND FREIHEIT GEORG NOLTE
- Page 136 and 137:
wir als Gruppe, stellvertretend auc
- Page 138 and 139:
and intellectual enrichment, and te
- Page 140 and 141:
Beyond these rather direct contribu
- Page 142 and 143:
The Limerick is an Anglo-Saxon form
- Page 144 and 145:
BERLIN FOOTPRINTS LISA PARKS Dr. Li
- Page 146 and 147:
Theater. While a Fellow, I was invi
- Page 148 and 149:
My essay about him, “Alexandru Dr
- Page 150 and 151:
FRIENDSHIPS MARTA PETRUSEWICZ Marta
- Page 152 and 153:
conscious of the age of the people
- Page 154 and 155:
A NEW OPTION SET FOR LIFE ANDREW F.
- Page 156 and 157:
not yet be over. But I resisted the
- Page 158 and 159:
frequency will rise for the rest of
- Page 160 and 161:
„SCHWER VERLÄSST, WAS NAHE DEM U
- Page 162 and 163:
So leben wir und nehmen immer Absch
- Page 164 and 165:
Kaum angekommen fragten mich Kathar
- Page 166 and 167:
F. R.: Also, z. B. die Frage, „Wi
- Page 168 and 169:
über die anderen. Und dann natürl
- Page 170 and 171:
ment von Musik nie gehört hätte.
- Page 172 and 173:
Wie klug durchdacht und institution
- Page 174 and 175:
BÜRGER UND GÄNSEKRAUT ODER DER AR
- Page 176 and 177:
Lange geschah nichts, doch die Duft
- Page 178 and 179:
gewalzt worden und die Muße, die n
- Page 180 and 181:
C’est à Berlin dans les premièr
- Page 182 and 183:
FAREWELL SPEECH HINRICH VON DER SCH
- Page 184 and 185:
INCLUSIONS, EXCLUSIONS AND ANGELIC
- Page 186 and 187:
its way to the Berlin museums (allo
- Page 188 and 189:
Is it because − as one probably m
- Page 190 and 191:
focused on the situation in South A
- Page 192 and 193:
visiting sites, reading notices, se
- Page 194 and 195:
„ISIS FÄHRT SCHLITTSCHUH“ MART
- Page 196 and 197:
der Demeter auf, einer anderen Ersc
- Page 198 and 199:
terstützung fand. Es widerstrebte
- Page 200 and 201:
y the gracious welcome of staff and
- Page 202 and 203:
versations). The meandering and eve
- Page 204 and 205:
Berlin and witnessed a hilarious su
- Page 206 and 207:
self that the statistical descripti
- Page 208 and 209:
In general, genotype-phenotype conn
- Page 210 and 211:
ecome morally and politically charg
- Page 212 and 213:
DAS TÄGLICHE GESCHENK ODER: WAS VO
- Page 214 and 215:
mermusiksaal entworfen hat, setzte
- Page 216 and 217:
STREICHQUARTETTE: URBILDER (1980);
- Page 218 and 219:
oshima ihr Leben verloren haben, al
- Page 220 and 221:
ter mit der traditionellen japanisc
- Page 222 and 223:
Das dritte Werk, das ich Ihnen vors
- Page 224 and 225:
ARGUING DEMOCRACY: INTELLECTUALS AN
- Page 226 and 227:
predicaments in which they found th
- Page 228 and 229:
Colonial subjection rested on a ref
- Page 230 and 231:
acy was not an invention of the Enl
- Page 232 and 233:
self-transformation, and therefore
- Page 234 and 235:
er the more benign view of the stat
- Page 236 and 237:
(who even after Partition formed so
- Page 238 and 239:
In a second paradox, it is precisel
- Page 240 and 241:
ner Zirbeldrüsentheorie ironisiert
- Page 242 and 243:
Zum Ersten: Wenn wir eine solche Ü
- Page 244 and 245:
erkannt, dass für die Untersuchung
- Page 246 and 247:
zu Recht herrscht, wahrscheinlich u
- Page 248 and 249:
natürlich auch in Bezug auf das Ge
- Page 250 and 251:
fekt, den ich gar nicht intendiere,
- Page 252 and 253:
prozesse (im Verhältnis zu der nat
- Page 254 and 255:
ganz elementaren Ebene an, beim Beu
- Page 256 and 257:
Kant, Immanuel. 1785, 1968. Grundle
- Page 258 and 259: nicht selten mit einer Art freundli
- Page 260 and 261: tionsvorsprung vielleicht auch ein
- Page 262 and 263: is Niklas Luhmann scheint begriffli
- Page 264 and 265: Auch wissenschaftstheoretisch hatte
- Page 266 and 267: Staatsrechtswissenschaft eine norma
- Page 268 and 269: Während die Freirechtsschule in De
- Page 270 and 271: Diese Situation einer Wissenschaft,
- Page 272 and 273: stand ausgerufen, und dies ist eine
- Page 274 and 275: wissenschaftlich und immer unreflek
- Page 276 and 277: EX-CENTRIC EUROPE: VISIONS AND PRAC
- Page 278 and 279: But it was simply not so. In the fi
- Page 280 and 281: and more than doubled in the next f
- Page 282 and 283: - they were peripheral in the topog
- Page 284 and 285: ment, and marked the culture of the
- Page 286 and 287: la terre, qui les fait exister et p
- Page 288 and 289: land in the 1830s, when a great num
- Page 290 and 291: ponent of the various experiments i
- Page 292 and 293: WIESO SIND EIGENTLICH PARASITEN SCH
- Page 294 and 295: nen Wirt nicht umbringen soll, da e
- Page 296 and 297: Stimmt die Theorie? Jede Theorie is
- Page 298 and 299: Zwei wichtige Faktoren spielen für
- Page 300 and 301: kann man hier nur staunen und stell
- Page 302 and 303: Abbildung 1. 304 Wissenschaftskolle
- Page 304 and 305: Abbildung 2. Insekten haben ein Imm
- Page 306 and 307: A central preoccupation in the disc
- Page 310 and 311: long observed scientifically and co
- Page 312 and 313: cists in Western countries does not
- Page 314 and 315: and in favor of adopting peaceful m
- Page 316 and 317: express strong reservations about S
- Page 318 and 319: Similarly caught unawares is the Is
- Page 320 and 321: mostly regarding capital and physic
- Page 322 and 323: search Council. Significant variati
- Page 324 and 325: lar or religious showing that, whil
- Page 326 and 327: Scriptural Studies Appendix on the