Predictors of Bullying and Victimization in Childhood and Adolescence
Predictors of Bullying and Victimization in Childhood and Adolescence
Predictors of Bullying and Victimization in Childhood and Adolescence
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
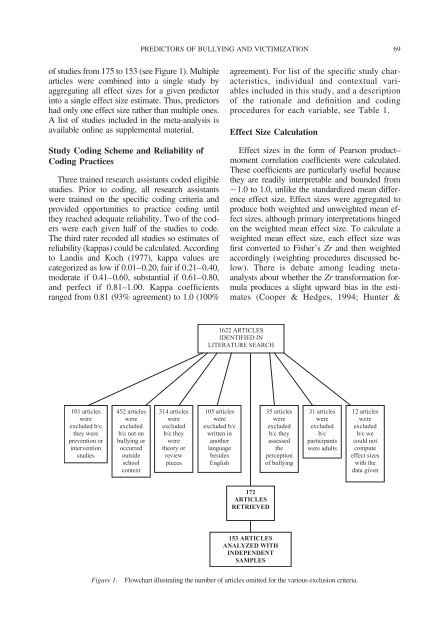
<strong>of</strong> studies from 175 to 153 (see Figure 1). Multiple<br />
articles were comb<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong>to a s<strong>in</strong>gle study by<br />
aggregat<strong>in</strong>g all effect sizes for a given predictor<br />
<strong>in</strong>to a s<strong>in</strong>gle effect size estimate. Thus, predictors<br />
had only one effect size rather than multiple ones.<br />
A list <strong>of</strong> studies <strong>in</strong>cluded <strong>in</strong> the meta-analysis is<br />
available onl<strong>in</strong>e as supplemental material.<br />
Study Cod<strong>in</strong>g Scheme <strong>and</strong> Reliability <strong>of</strong><br />
Cod<strong>in</strong>g Practices<br />
Three tra<strong>in</strong>ed research assistants coded eligible<br />
studies. Prior to cod<strong>in</strong>g, all research assistants<br />
were tra<strong>in</strong>ed on the specific cod<strong>in</strong>g criteria <strong>and</strong><br />
provided opportunities to practice cod<strong>in</strong>g until<br />
they reached adequate reliability. Two <strong>of</strong> the coders<br />
were each given half <strong>of</strong> the studies to code.<br />
The third rater recoded all studies so estimates <strong>of</strong><br />
reliability (kappas) could be calculated. Accord<strong>in</strong>g<br />
to L<strong>and</strong>is <strong>and</strong> Koch (1977), kappa values are<br />
categorized as low if 0.01–0.20, fair if 0.21–0.40,<br />
moderate if 0.41–0.60, substantial if 0.61–0.80,<br />
<strong>and</strong> perfect if 0.81–1.00. Kappa coefficients<br />
ranged from 0.81 (93% agreement) to 1.0 (100%<br />
101 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded b/c<br />
they were<br />
prevention or<br />
<strong>in</strong>tervention<br />
studies<br />
452 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded<br />
b/c not on<br />
bully<strong>in</strong>g or<br />
occurred<br />
outside<br />
school<br />
context<br />
PREDICTORS OF BULLYING AND VICTIMIZATION<br />
314 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded<br />
b/c they<br />
were<br />
theory or<br />
review<br />
pieces<br />
agreement). For list <strong>of</strong> the specific study characteristics,<br />
<strong>in</strong>dividual <strong>and</strong> contextual variables<br />
<strong>in</strong>cluded <strong>in</strong> this study, <strong>and</strong> a description<br />
<strong>of</strong> the rationale <strong>and</strong> def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>and</strong> cod<strong>in</strong>g<br />
procedures for each variable, see Table 1.<br />
Effect Size Calculation<br />
Effect sizes <strong>in</strong> the form <strong>of</strong> Pearson product–<br />
moment correlation coefficients were calculated.<br />
These coefficients are particularly useful because<br />
they are readily <strong>in</strong>terpretable <strong>and</strong> bounded from<br />
1.0 to 1.0, unlike the st<strong>and</strong>ardized mean difference<br />
effect size. Effect sizes were aggregated to<br />
produce both weighted <strong>and</strong> unweighted mean effect<br />
sizes, although primary <strong>in</strong>terpretations h<strong>in</strong>ged<br />
on the weighted mean effect size. To calculate a<br />
weighted mean effect size, each effect size was<br />
first converted to Fisher’s Zr <strong>and</strong> then weighted<br />
accord<strong>in</strong>gly (weight<strong>in</strong>g procedures discussed below).<br />
There is debate among lead<strong>in</strong>g metaanalysts<br />
about whether the Zr transformation formula<br />
produces a slight upward bias <strong>in</strong> the estimates<br />
(Cooper & Hedges, 1994; Hunter &<br />
1622 ARTICLES<br />
IDENTIFIED IN<br />
LITERATURE SEARCH<br />
105 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded b/c<br />
written <strong>in</strong><br />
another<br />
language<br />
besides<br />
English<br />
172<br />
ARTICLES<br />
RETRIEVED<br />
35 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded<br />
b/c they<br />
assessed<br />
the<br />
perception<br />
<strong>of</strong> bully<strong>in</strong>g<br />
153 ARTICLES<br />
ANALYZED WITH<br />
INDEPENDENT<br />
SAMPLES<br />
31 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded<br />
b/c<br />
participants<br />
were adults<br />
Figure 1. Flowchart illustrat<strong>in</strong>g the number <strong>of</strong> articles omitted for the various exclusion criteria.<br />
12 articles<br />
were<br />
excluded<br />
b/c we<br />
could not<br />
compute<br />
effect sizes<br />
with the<br />
data given<br />
69