C H A P T E R 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
C H A P T E R 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
C H A P T E R 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
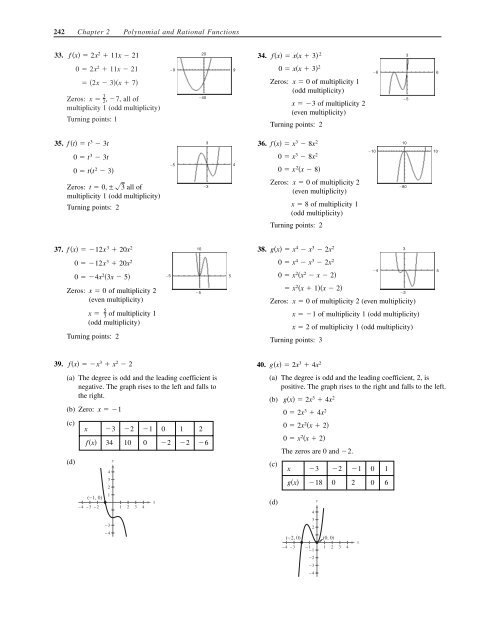
242 Chapter 2 <strong>Polynomial</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Rational</strong> <strong>Functions</strong><br />
33.<br />
35.<br />
37.<br />
39.<br />
20<br />
f x 2x2 11x 21 34.<br />
0 2x 2 11x 21 −9<br />
2x 3x 7<br />
Zeros: x all of<br />
multiplicity 1 (odd multiplicity)<br />
Turning points: 1<br />
3<br />
2 , 7,<br />
f t t 3<br />
3 3t 36.<br />
0 t 3 3t<br />
0 tt 2 3<br />
Zeros: t 0, ±3 all of<br />
multiplicity 1 (odd multiplicity)<br />
Turning points: 2<br />
f x 12x 10<br />
3 20x2 38.<br />
0 12x 3 20x 2<br />
0 4x 2 3x 5<br />
Zeros: of multiplicity 2<br />
(even multiplicity)<br />
x of multiplicity 1<br />
(odd multiplicity)<br />
5<br />
x 0<br />
3<br />
Turning points: 2<br />
−5<br />
fx x<br />
(a) The degree is odd <strong>and</strong> the leading coefficient is<br />
negative. The graph rises to the left <strong>and</strong> falls to<br />
the right.<br />
3 x2 2 40.<br />
(b) Zero: x 1<br />
(c)<br />
(d)<br />
x 3 2 1 0 1 2<br />
fx<br />
(−1, 0)<br />
−4 −3 −2<br />
−5<br />
−5<br />
−40<br />
34 10 0 2 2 6<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
−3<br />
−4<br />
y<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
x<br />
−3<br />
5<br />
9<br />
4<br />
fx xx 3 2<br />
0 xx 3 2<br />
Zeros: x 0 of multiplicity 1<br />
(odd multiplicity)<br />
x 3 of multiplicity 2<br />
(even multiplicity)<br />
Turning points: 2<br />
f x x 3 8x 2<br />
0 x 3 8x 2<br />
0 x 2 x 8<br />
Zeros: x 0 of multiplicity 2<br />
(even multiplicity)<br />
x 8 of multiplicity 1<br />
(odd multiplicity)<br />
Turning points: 2<br />
gx x 4 x 3 2x 2<br />
0 x 4 x 3 2x 2<br />
0 x 2 x 2 x 2<br />
x 2 x 1x 2<br />
Zeros: x 0 of multiplicity 2 (even multiplicity)<br />
x 1 of multiplicity 1 (odd multiplicity)<br />
x 2 of multiplicity 1 (odd multiplicity)<br />
Turning points: 3<br />
(a) The degree is odd <strong>and</strong> the leading coefficient, 2, is<br />
positive. The graph rises to the right <strong>and</strong> falls to the left.<br />
(b)<br />
0 x<br />
The zeros are 0 <strong>and</strong> 2.<br />
(c)<br />
2 0 2x<br />
x 2<br />
2 0 2x<br />
x 2<br />
3 4x2 gx 2x3 4x2 gx 2x3 4x2 x 3<br />
2 1 0 1<br />
(d)<br />
gx<br />
18<br />
(−2, 0) (0, 0)<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
−4 −3 −1<br />
−1<br />
−2<br />
−3<br />
−4<br />
y<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
x<br />
−10<br />
−6<br />
−4<br />
0 2 0 6<br />
3<br />
−5<br />
10<br />
−80<br />
3<br />
−3<br />
6<br />
10<br />
5