MASTER THESIS Video Watermarking - Computer Graphics Group ...
MASTER THESIS Video Watermarking - Computer Graphics Group ...
MASTER THESIS Video Watermarking - Computer Graphics Group ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
auxiliary coded pictures),<br />
Supplemental Enhancement Information (necessary information for<br />
correct video playback and other data – timing information, buffer<br />
management hints, user data, scene information, pan-scan information,<br />
spare picture information, still frames etc.),<br />
Slice Data Partitions, i.e. partitions of too big slices.<br />
4.2 The <strong>Watermarking</strong> Framework<br />
The framework is designed for easiness when implementing any particular<br />
watermarking method in either spatial or frequency domain of H.264 video<br />
streams. Then, implementation of a method consists in writing only two<br />
functions, one for watermark embedding and the other for watermark detection.<br />
4.2.1 GStreamer Multimedia Framework<br />
In practice, a H.264 video stream is usually enveloped (multiplexed / muxed)<br />
together with an audio stream into a multimedia container format such as Audio<br />
<strong>Video</strong> Interleave (AVI) or Matroska (MKV). In order to avoid implementing of<br />
unpacking (demultiplexing / demuxing) various container formats and separating<br />
out the video stream, the watermarking framework is implemented as a plugin in<br />
the open source multimedia framework called GStreamer [12].<br />
GStreamer is a library that allows the construction of graphs of<br />
media-handling components, ranging from simple audio playback to complex<br />
audio and video processing.<br />
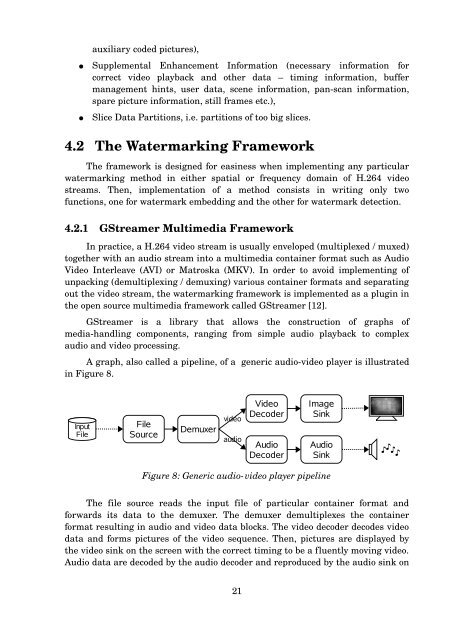
A graph, also called a pipeline, of a generic audio-video player is illustrated<br />
in Figure 8.<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Figure 8: Generic audio-video player pipeline<br />
The file source reads the input file of particular container format and<br />
forwards its data to the demuxer. The demuxer demultiplexes the container<br />
format resulting in audio and video data blocks. The video decoder decodes video<br />
data and forms pictures of the video sequence. Then, pictures are displayed by<br />
the video sink on the screen with the correct timing to be a fluently moving video.<br />
Audio data are decoded by the audio decoder and reproduced by the audio sink on<br />
21