assessment of changes in the phosphorus status of forest ...
assessment of changes in the phosphorus status of forest ...
assessment of changes in the phosphorus status of forest ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
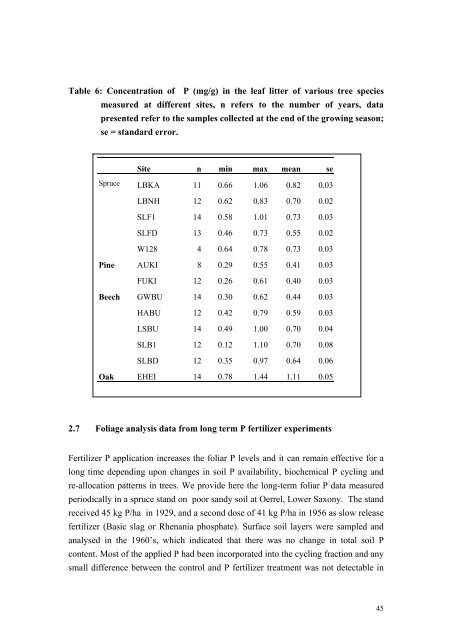
Table 6: Concentration <strong>of</strong> P (mg/g) <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> leaf litter <strong>of</strong> various tree species<br />
measured at different sites, n refers to <strong>the</strong> number <strong>of</strong> years, data<br />
presented refer to <strong>the</strong> samples collected at <strong>the</strong> end <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> grow<strong>in</strong>g season;<br />
se = standard error.<br />
Site n m<strong>in</strong> max mean se<br />
Spruce LBKA 11 0.66 1.06 0.82 0.03<br />
LBNH 12 0.62 0.83 0.70 0.02<br />
SLF1 14 0.58 1.01 0.73 0.03<br />
SLFD 13 0.46 0.73 0.55 0.02<br />
W128 4 0.64 0.78 0.73 0.03<br />
P<strong>in</strong>e AUKI 8 0.29 0.55 0.41 0.03<br />
FUKI 12 0.26 0.61 0.40 0.03<br />
Beech GWBU 14 0.30 0.62 0.44 0.03<br />
HABU 12 0.42 0.79 0.59 0.03<br />
LSBU 14 0.49 1.00 0.70 0.04<br />
SLB1 12 0.12 1.10 0.70 0.08<br />
SLBD 12 0.35 0.97 0.64 0.06<br />
Oak EHEI 14 0.78 1.44 1.11 0.05<br />
2.7 Foliage analysis data from long term P fertilizer experiments<br />
Fertilizer P application <strong>in</strong>creases <strong>the</strong> foliar P levels and it can rema<strong>in</strong> effective for a<br />
long time depend<strong>in</strong>g upon <strong>changes</strong> <strong>in</strong> soil P availability, biochemical P cycl<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
re-allocation patterns <strong>in</strong> trees. We provide here <strong>the</strong> long-term foliar P data measured<br />
periodically <strong>in</strong> a spruce stand on poor sandy soil at Oerrel, Lower Saxony. The stand<br />
received 45 kg P/ha <strong>in</strong> 1929, and a second dose <strong>of</strong> 41 kg P/ha <strong>in</strong> 1956 as slow release<br />
fertilizer (Basic slag or Rhenania phosphate). Surface soil layers were sampled and<br />
analysed <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> 1960’s, which <strong>in</strong>dicated that <strong>the</strong>re was no change <strong>in</strong> total soil P<br />
content. Most <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> applied P had been <strong>in</strong>corporated <strong>in</strong>to <strong>the</strong> cycl<strong>in</strong>g fraction and any<br />
small difference between <strong>the</strong> control and P fertilizer treatment was not detectable <strong>in</strong><br />
45