Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
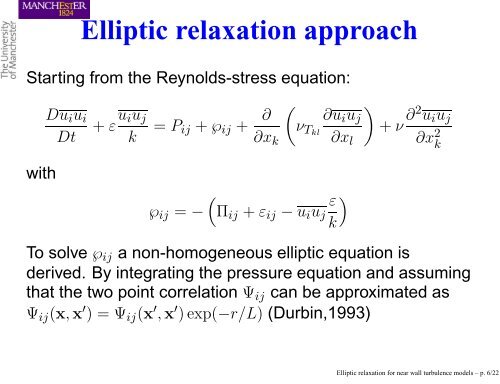
<strong>Elliptic</strong> <strong>relaxation</strong> approach<br />
Starting from the Reynolds-stress equation:<br />
with<br />
Duiui<br />
Dt<br />
+ εuiuj<br />
k = Pij + ℘ij + ∂<br />
∂xk<br />
℘ij = −<br />
<br />
νTkl<br />
<br />
Πij + εij − uiuj<br />
∂uiuj<br />
∂xl<br />
ε<br />
<br />
k<br />
<br />
+ ν ∂2 uiuj<br />
∂x 2 k<br />
To solve ℘ij a non-homogeneous elliptic equation is<br />
derived. By integrating the pressure equation and assuming<br />
that the two point correlation Ψij can be approximated as<br />
Ψij(x, x ′ ) = Ψij(x ′ , x ′ ) exp(−r/L) (Durbin,1993)<br />
<strong>Elliptic</strong> <strong>relaxation</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>near</strong> <strong>wall</strong> <strong>turbulence</strong> <strong>models</strong> – p. 6/22