Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
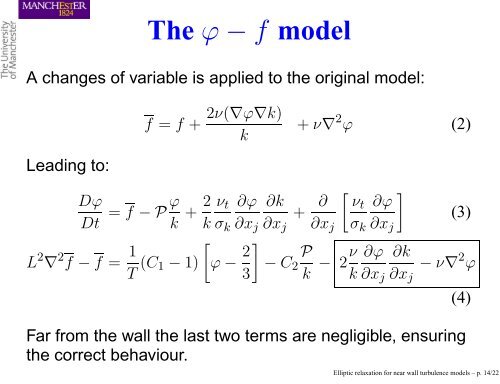
The ϕ − f model<br />
A changes of variable is applied to the original model:<br />
Leading to:<br />
Dϕ<br />
Dt<br />
= f − P ϕ<br />
k<br />
L 2 ∇ 2 f − f = 1<br />
T (C1 − 1)<br />
f = f + 2ν(∇ϕ∇k)<br />
k<br />
2 νt ∂ϕ ∂k<br />
+<br />
k σk ∂xj ∂xj<br />
<br />
ϕ − 2<br />
<br />
3<br />
− C2<br />
+ ν∇ 2 ϕ (2)<br />
+ ∂<br />
∂xj<br />
P<br />
k<br />
νt<br />
σk<br />
− 2ν<br />
k<br />
∂ϕ<br />
∂xj<br />
∂ϕ<br />
∂xj<br />
<br />
∂k<br />
∂xj<br />
(3)<br />
− ν∇ 2 ϕ<br />
Far from the <strong>wall</strong> the last two terms are negligible, ensuring<br />
the correct behaviour.<br />
(4)<br />
<strong>Elliptic</strong> <strong>relaxation</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>near</strong> <strong>wall</strong> <strong>turbulence</strong> <strong>models</strong> – p. 14/22