Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
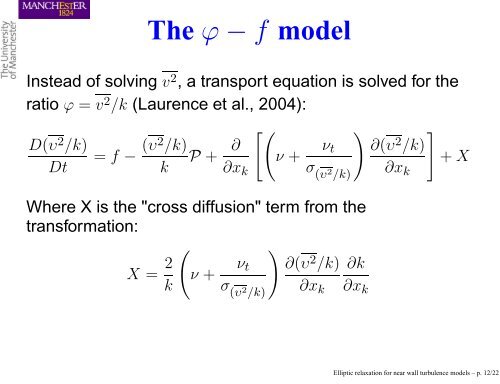
The ϕ − f model<br />
Instead of solving v 2 , a transport equation is solved <strong>for</strong> the<br />
ratio ϕ = v 2 /k (Laurence et al., 2004):<br />
D(υ 2 /k)<br />
Dt<br />
= f − (υ2 /k)<br />
k<br />
P + ∂<br />
∂xk<br />
<br />
ν + νt<br />
σ (υ 2 /k)<br />
ν + νt<br />
σ (υ 2 /k)<br />
Where X is the "cross diffusion" term from the<br />
trans<strong>for</strong>mation:<br />
X = 2<br />
<br />
∂(υ<br />
k<br />
2 /k) ∂k<br />
∂xk ∂xk<br />
<br />
∂(υ2 <br />
/k)<br />
+ X<br />
∂xk<br />
<strong>Elliptic</strong> <strong>relaxation</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>near</strong> <strong>wall</strong> <strong>turbulence</strong> <strong>models</strong> – p. 12/22