Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Elliptic relaxation for near wall turbulence models
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
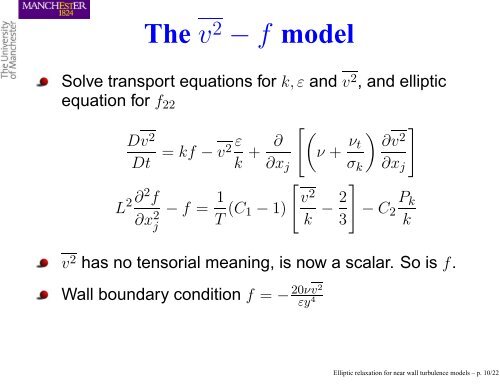
L 2 ∂2 f<br />
∂x 2 j<br />
The v 2 − f model<br />
Solve transport equations <strong>for</strong> k, ε and v2 , and elliptic<br />
equation <strong>for</strong> f22<br />
Dv2 ε ∂<br />
= kf − v2 + ν +<br />
Dt k ∂xj<br />
νt<br />
<br />
∂v2 σk ∂xj<br />
− f = 1<br />
T (C1<br />
<br />
v<br />
− 1)<br />
2<br />
<br />
2 Pk<br />
− − C2<br />
k 3 k<br />
v 2 has no tensorial meaning, is now a scalar. So is f.<br />
Wall boundary condition f = − 20νv2<br />
εy 4<br />
<strong>Elliptic</strong> <strong>relaxation</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>near</strong> <strong>wall</strong> <strong>turbulence</strong> <strong>models</strong> – p. 10/22