Chapter 6 TRADE AND LOCAL INCOME DISTRIBUTION: THE ...
Chapter 6 TRADE AND LOCAL INCOME DISTRIBUTION: THE ...
Chapter 6 TRADE AND LOCAL INCOME DISTRIBUTION: THE ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
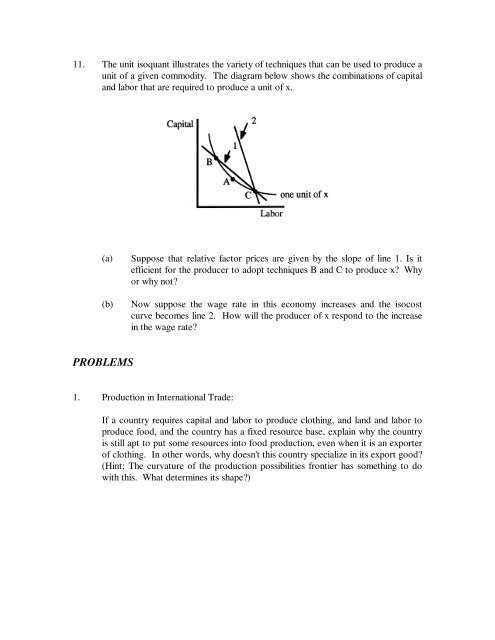
11. The unit isoquant illustrates the variety of techniques that can be used to produce a<br />
unit of a given commodity. The diagram below shows the combinations of capital<br />
and labor that are required to produce a unit of x.<br />
(a) Suppose that relative factor prices are given by the slope of line 1. Is it<br />
efficient for the producer to adopt techniques B and C to produce x? Why<br />
or why not?<br />
(b) Now suppose the wage rate in this economy increases and the isocost<br />
curve becomes line 2. How will the producer of x respond to the increase<br />
in the wage rate?<br />
PROBLEMS<br />
1. Production in International Trade:<br />
If a country requires capital and labor to produce clothing, and land and labor to<br />
produce food, and the country has a fixed resource base, explain why the country<br />
is still apt to put some resources into food production, even when it is an exporter<br />
of clothing. In other words, why doesn't this country specialize in its export good?<br />
(Hint: The curvature of the production possibilities frontier has something to do<br />
with this. What determines its shape?)