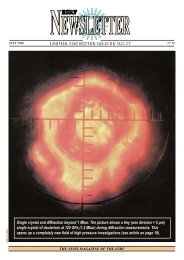
New Scientific Opportunities at the European Synchrotron Radiation ...
New Scientific Opportunities at the European Synchrotron Radiation ...
New Scientific Opportunities at the European Synchrotron Radiation ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>European</strong> <strong>Synchrotron</strong> Radi<strong>at</strong>ion Facility Long-Term Str<strong>at</strong>egy 7 July 2006<br />
basic research effort towards <strong>the</strong> development of a future quantum computer.<br />
Studies in magnetic fields of unprecedented strength will lead to <strong>the</strong> discovery of<br />
novel effects and will have a decisive influence on <strong>the</strong> better understanding of<br />
semiconductors, superconductors and magnetic m<strong>at</strong>erials. The use of hard X-rays<br />
as a probe of m<strong>at</strong>erials subjected to intense magnetic fields will offer unique<br />
possibilities, as is <strong>the</strong> case for infrared spectroscopy, where <strong>the</strong> (soft radi<strong>at</strong>ion) free<br />
electron laser ELBE <strong>at</strong> <strong>the</strong> high magnetic field labor<strong>at</strong>ory in Dresden will allow<br />
experiments up to 100T.<br />
Although an increasing number of different experimental methods have been<br />
employed over <strong>the</strong> last decade, X-ray diffraction is expected to remain <strong>the</strong> most<br />
widely used technique in <strong>the</strong> context of extreme conditions research because it<br />
provides fundamental structural inform<strong>at</strong>ion th<strong>at</strong> is <strong>the</strong> basis for o<strong>the</strong>r synchrotron<br />
techniques. This area requires a major effort in <strong>the</strong> development of new beamlines,<br />
new instrument<strong>at</strong>ion (particularly in sample environment and X-ray detectors), and in<br />
<strong>the</strong> rel<strong>at</strong>ed scientific infrastructure.<br />
<strong>New</strong> Science: illustr<strong>at</strong>ive examples<br />
The construction and install<strong>at</strong>ion of a multi-analyser spectrometer capable of<br />
retrieving <strong>the</strong> sample's complete phonon dispersion curve <strong>at</strong> only one setting<br />
of <strong>the</strong> spectrometer (and sample) would enable, for example, <strong>the</strong> study of<br />
single crystal minerals under pressure and temper<strong>at</strong>ure conditions of <strong>the</strong><br />
Earth's mantle which can only be reached by combining diamond anvil cell<br />
techniques and laser he<strong>at</strong>ing. This is currently impossible due to low countr<strong>at</strong>es<br />
and <strong>the</strong> difficulties of orienting <strong>the</strong> sample crystal (in its complic<strong>at</strong>ed<br />
sample environment) <strong>at</strong> many different angles.<br />
Quantum effects in magnetic systems are enhanced by low dimensionality,<br />
low spin and frustr<strong>at</strong>ed interactions. Two-dimensional “spin dimer” systems,<br />
where <strong>the</strong> magnetic interactions are strongly anisotropic and <strong>the</strong> spin dimers<br />
form spin singlet ground st<strong>at</strong>es, are especially interesting. By applying an<br />
external magnetic field above 20 Tesla, we may close <strong>the</strong> spin gap and form<br />
a gas of spin triplets. At certain characteristic field strengths pl<strong>at</strong>eaus are<br />
observed in <strong>the</strong> magnetis<strong>at</strong>ion curves. These arise from <strong>the</strong> crystallis<strong>at</strong>ion of<br />
<strong>the</strong> triplets into superl<strong>at</strong>tices. Their precise n<strong>at</strong>ure is still controversial as no<br />
direct microscopic probes are currently available. Through studies of <strong>the</strong><br />
corresponding superl<strong>at</strong>tice reflections under extremely high applied magnetic<br />
fields (above 20T), X-ray resonant magnetic sc<strong>at</strong>tering will provide direct<br />
insight into <strong>the</strong> long range interactions of <strong>the</strong> triplets. In addition, X-ray<br />
spectroscopy, in particular resonant inelastic x-ray sc<strong>at</strong>tering, will<br />
complement <strong>the</strong>se d<strong>at</strong>a with inform<strong>at</strong>ion on <strong>the</strong> relevant energy scales and<br />
local symmetries.<br />
12