Download File
Download File
Download File
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
252 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions<br />
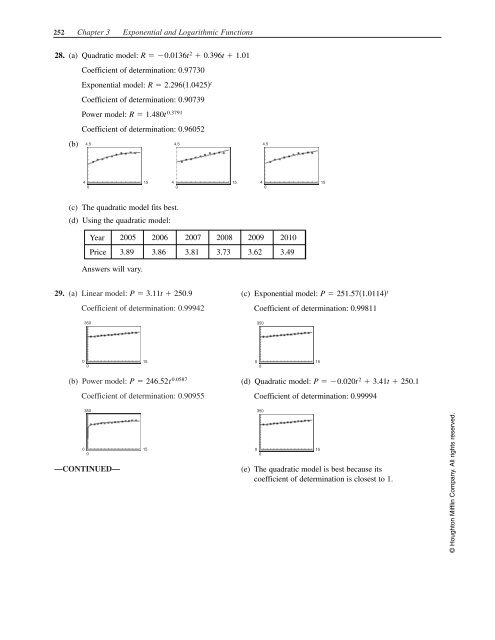
28. (a) Quadratic model: R 0.0136t 2 0.396t 1.01<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.97730<br />
Exponential model: R 2.2961.0425 t<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.90739<br />
Power model: R 1.480t 0.3791<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.96052<br />
(b)<br />
4.5<br />
4.5<br />
4.5<br />
4 15<br />
0<br />
4 15<br />
0<br />
4 15<br />
0<br />
(c) The quadratic model fits best.<br />
(d) Using the quadratic model:<br />
Year 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010<br />
Price 3.89 3.86 3.81 3.73 3.62 3.49<br />
Answers will vary.<br />
29. (a) Linear model: P 3.11t 250.9<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.99942<br />
(c) Exponential model: P 251.571.0114 t<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.99811<br />
350<br />
350<br />
0 15<br />
0<br />
(b) Power model: P 246.52t 0.0587<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.90955<br />
350<br />
0 15<br />
0<br />
—CONTINUED—<br />
0 15<br />
0<br />
(d) Quadratic model: P 0.020t 2 3.41t 250.1<br />
Coefficient of determination: 0.99994<br />
350<br />
0 15<br />
0<br />
(e) The quadratic model is best because its<br />
coefficient of determination is closest to 1.<br />
© Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.