Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 report
Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 report
Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 report
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
DRUG-RESISTANT<br />
NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE<br />
FIGHTING THE SPREAD OF RESISTANCE<br />
Cephalospor<strong>in</strong>-resistant N. gonorrhoeae is often resistant to multiple classes of o<strong>the</strong>r antibiotics<br />
and as a result, <strong>in</strong>fections caused by <strong>the</strong>se bacteria will likely fail empiric treatment regimens. If<br />
cephalospor<strong>in</strong>-resistant N. gonorrhoeae becomes widespread, <strong>the</strong> public health impact dur<strong>in</strong>g a<br />
10-year period is estimated to be 75,000 additional cases of pelvic <strong>in</strong>flammatory disease (a major<br />
cause of <strong>in</strong>fertility), 15,000 cases of epididymitis, and 222 additional HIV <strong>in</strong>fections because HIV is<br />
transmitted more readily when someone is co-<strong>in</strong>fected with gonorrhea. In addition, <strong>the</strong> estimated<br />
direct medical costs would total $235 million. Additional costs are anticipated to be <strong>in</strong>curred as a<br />
result of <strong>in</strong>creased susceptibility monitor<strong>in</strong>g, provider education, case management, and <strong>the</strong> need<br />
for additional courses of antibiotics and follow-up.<br />
Gonorrhea is a global problem, requir<strong>in</strong>g a global approach. Action <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>United</strong> <strong>States</strong> alone<br />
is unlikely to prevent resistance from develop<strong>in</strong>g, but rapid detection and effective treatment<br />
of patients and <strong>the</strong>ir partners might slow <strong>the</strong> spread of resistance. Prevent<strong>in</strong>g gonorrhea is<br />
critical. Screen<strong>in</strong>g, rapid detection, prompt treatment, and partner services are <strong>the</strong> foundations of<br />
gonorrhea control <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>United</strong> <strong>States</strong>. Effectively address<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> heavy burden of gonorrhea and<br />
anticipated arrival of cephalospor<strong>in</strong> resistance requires cont<strong>in</strong>ued use of <strong>the</strong>se strategies as well<br />
as <strong>the</strong> use of expedited partner <strong>the</strong>rapy, promotion of safer sexual behaviors such as abst<strong>in</strong>ence,<br />
mutual monogamy, and correct and consistent condom use, and activities designed to rapidly<br />
detect and respond to antibiotic-resistant <strong>in</strong>fections<br />
WHAT CDC IS DOING<br />
CDC is closely monitor<strong>in</strong>g resistance <strong>in</strong> N. gonorrhoeae <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>United</strong> <strong>States</strong> and actively<br />
collaborat<strong>in</strong>g with <strong>the</strong> World Health Organization to enhance global surveillance. In <strong>the</strong><br />
<strong>United</strong> <strong>States</strong>, CDC recently released a national response plan and is work<strong>in</strong>g closely with<br />
local and state STD programs to enhance preparedness. CDC recently updated its gonorrhea<br />
treatment recommendations to stay a step ahead of this rapidly evolv<strong>in</strong>g bacterium, and is<br />
collaborat<strong>in</strong>g with <strong>the</strong> NIH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to f<strong>in</strong>d new<br />
treatment options.<br />
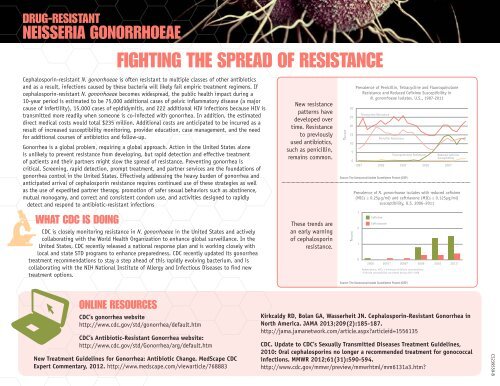
New resistance<br />
patterns have<br />
developed over<br />
time. <strong>Resistance</strong><br />
to previously<br />
used antibiotics,<br />
such as penicill<strong>in</strong>,<br />
rema<strong>in</strong>s common.<br />
These trends are<br />
an early warn<strong>in</strong>g<br />
of cephalospor<strong>in</strong><br />
resistance.<br />
Prevalence of Penicill<strong>in</strong>, Tetracycl<strong>in</strong>e and Fluoroqu<strong>in</strong>olone<br />
<strong>Resistance</strong> and Reduced Cefixime Susceptibility <strong>in</strong><br />
N. gonorrhoeae isolates, U.S., 1987-2011<br />
Source: The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP).<br />
Prevalence of N. gonorrhoeae isolates with reduced cefixime<br />
(MICs ≥ 0.25μg/ml) and ceftriaxone (MICs ≥ 0.125μg/ml)<br />
susceptibility, U.S. 2006–2011<br />
Source: The Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (GISP).<br />
ONLINE RESOURCES<br />
CDC’s gonorrhea website<br />
http://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/default.htm<br />
CDC’s <strong>Antibiotic</strong>-Resistant Gonorrhea website:<br />
http://www.cdc.gov/std/Gonorrhea/arg/default.htm<br />
New Treatment Guidel<strong>in</strong>es for Gonorrhea: <strong>Antibiotic</strong> Change. MedScape CDC<br />
Expert Commentary, 2012. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/768883<br />
Kirkcaldy RD, Bolan GA, Wasserheit JN. Cephalospor<strong>in</strong>-Resistant Gonorrhea <strong>in</strong><br />
North America. JAMA <strong>2013</strong>;209(2):185-187.<br />
http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=1556135<br />
CDC. Update to CDC’s Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidel<strong>in</strong>es,<br />
2010: Oral cephalospor<strong>in</strong>s no longer a recommended treatment for gonococcal<br />
<strong>in</strong>fections. MMWR 2012;61(31):590-594.<br />
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6131a3.htm?<br />
CS239559-B