Effect of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties and Morphology ...
Effect of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties and Morphology ...
Effect of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties and Morphology ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Effect</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Coupling</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Agents</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong><br />
<strong>Mechanical</strong> <strong>Properties</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Morphology</strong><br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO<br />
3 -filled Recycled High Density Polyethylene<br />
133<br />
untreated<br />
1 wt.%<br />
2 wt.%<br />
3 wt.%<br />
4 wt.%<br />
5 wt.%<br />
treatment <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 improves the mechanical<br />
properties, including tensile strength, flexurall<br />
strength, impact strength <strong>and</strong> el<strong>on</strong>gati<strong>on</strong> at break,<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the r-HDPE/CaCO 3 composites, compared to<br />
untreatment. By treatment with 1 wt.%<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> different<br />
coupling agents, SA-treated CaCO3 appears to<br />
exhibit the greatest improvement in the<br />
mechanical<br />
properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the r-HDPE/CaCO 3 composites,<br />
particularly impact strength<br />
are shown in Figure 3.<br />
Table 3 <strong>Mechanical</strong> properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> r-HDPE/10<br />
wt.% CaCO 3<br />
composi ites. (CaCO 3 treated with 1 wt.% coupling<br />
agents)<br />
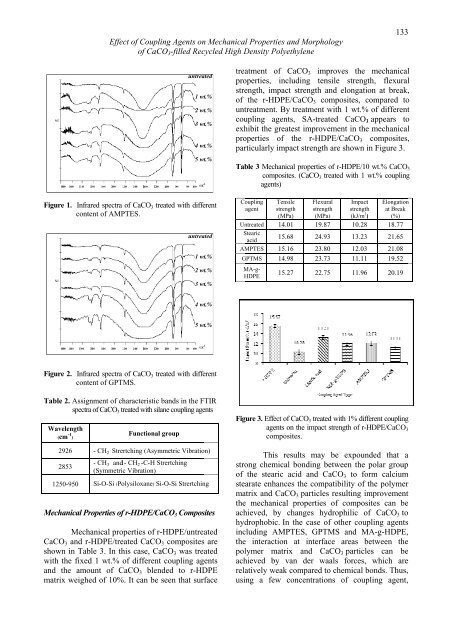
Figure 1. Infrared spectra <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 treated with different<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tent <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> AMPTES.<br />
untreated<br />
1 wt.%<br />
2 wt.%<br />
3 wt.%<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Coupling</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
agent<br />
Tensile<br />
strength<br />
Flexural<br />
strength<br />
Impact<br />
strength<br />
(MPa)<br />
(MPa)<br />
(kJ/m 2 )<br />
Untreated Stearic<br />
acid<br />
AMPTES GPTMS MA-g-<br />
HDPE<br />
14. .01<br />
15. .68<br />
15. .16<br />
14. .98<br />
15. .27<br />
19.87 24.93 23.80 23.73 22.75 10.28<br />
13.23<br />
12.03<br />
11.11<br />
11.96<br />
El<strong>on</strong>gati<strong>on</strong>n<br />
at Break<br />
(%)<br />
18.77<br />
21.65<br />
21.08<br />
19.52<br />
20.19<br />
4 wt.%<br />
5 wt.%<br />
Figure 2. Infrared spectra <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 treated with different<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tent <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> GPTMS.<br />
Table 2. Assignment <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> characteristic b<strong>and</strong>s in the FTIR<br />
spec ctra <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 treated with silane coupling agents<br />
Wavelength<br />
(cm -1 )<br />
Functi<strong>on</strong>al group<br />
2926 - CH 2 Strertching (Asymmetric Vibrati<strong>on</strong>)<br />
- CH<br />
2853<br />
3 <strong>and</strong><br />
- CH 2 -C-H Strertching<br />
(Symmetric Vibrati<strong>on</strong>)<br />
1250-950 Si-O-Si (Polysiloxane) Si-O-Si Strertching<br />
<strong>Mechanical</strong><br />
<strong>Properties</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
r-HDPE/CaCO 3 Composites<br />
<strong>Mechanical</strong> properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> r-HDPE/untreated<br />
CaCO 3 <strong>and</strong><br />
r-HDPE/treated CaCO 3 compositess are<br />
shown in Table 3. In this case, CaCO 3 was treated<br />
with the fixed 1 wt.% <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> different coupling agents<br />
<strong>and</strong> the amount <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 blended to r-HDPE<br />
matrix weighed <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> 10% %. It can be seen that surface<br />
Figure 3. <str<strong>on</strong>g>Effect</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 treated with 1% different coupling<br />
agents <strong>on</strong> the impact strength <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> r-HDPE/CaCO 3<br />
composites.<br />
This results may be expounded that a<br />
str<strong>on</strong>g chemical b<strong>on</strong>ding between the polar group<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the stearic acid <strong>and</strong> CaCO 3 to form calcium<br />
stearate enhances the compatibility <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the polymer<br />
matrix <strong>and</strong> CaCO 3 particles<br />
resulting improvement<br />
the<br />
mechanical properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> composites can be<br />
achieved, by changes hydrophilic <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 to<br />
hydrophobic. In<br />
the case <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> other coupling agents<br />
including AMPTES, GPTMS <strong>and</strong> MA-g-HDPE,<br />
the<br />
interacti<strong>on</strong>n at interface areas between the<br />
polymer matrix <strong>and</strong> CaCO 3 particles can be<br />
achieved by van der waals forces, which are<br />
relatively weak<br />
compared to chemical b<strong>on</strong>ds. Thus,<br />
using a few c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> coupling agent,