Effect of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties and Morphology ...
Effect of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties and Morphology ...
Effect of Coupling Agents on Mechanical Properties and Morphology ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
134<br />
PHUEAKBUAKHAO, N. et al.<br />
chemical b<strong>on</strong>ding can be improved the interacti<strong>on</strong><br />
at interface areas between the polymer matrix <strong>and</strong><br />
CaCO 3 particles more than physical b<strong>on</strong>ding or van<br />
der waals forces.<br />
Using other coupling agents at c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> 2, 3, 4 <strong>and</strong> 5 wt.% to study the possibility <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
increasing the polymer-CaCO 3 interacti<strong>on</strong>. It was<br />
found that the mechanical properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> composite<br />
can be improved, especially impact resistance when<br />
increase the c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> coupling agents.<br />
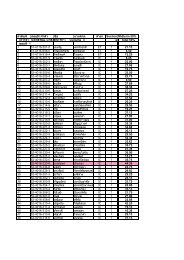
Table 4 summarizes the mechanical properties<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the r-HDPE filled CaCO 3 treated with the<br />
optimum c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> each coupling agent.<br />
The results show that each coupling agent gives<br />
rise to increase in a particular mechanical properties<br />
due to its characteristics. The r-HDPE/treated-<br />
CaCO 3 composites show the best mechanical<br />
properties when CaCO 3 were treated with SA,<br />
AMPTES, GPTMS <strong>and</strong> MA-g-HDPE at 1, 2, 3 <strong>and</strong><br />
4 wt.%, respectively. This behavior can be<br />
explained based <strong>on</strong> the fact that increasing the<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> coupling agents can improve the<br />
interacti<strong>on</strong> between the polymer matrix <strong>and</strong> CaCO 3<br />
particle, which are physical forces or van der waals<br />
forces as well as chemical forces but have to use<br />
more c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s. This indicates that selecti<strong>on</strong><br />
the type <strong>and</strong> quantity <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> coupling agents for the<br />
composites is important to gets the optimum<br />
property <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> final products.<br />
<strong>and</strong> the surface was rather smooth. This shows that<br />
the polymer matrix <strong>and</strong> CaCO 3 particles didn’t<br />
restrain together. On the other h<strong>and</strong>, the rough<br />
surfaces are observed for the r-HDPE/treated<br />
CaCO 3 composites, as presented in Figure 4(b) -<br />
Figure 4(e). This indicates the ductile fracture. The<br />
morphologies <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the fractured surfaces were<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sistent with the impact strength listed in Table 2<br />
<strong>and</strong> Table 3. High magnified SEM micrographs<br />
(x3500) <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the r-HDPE/CaCO 3 composites are<br />
illustrated in Figure 5. Phase separati<strong>on</strong> can be<br />
seen when the untreated CaCO 3 was incorporated<br />
in the r-HDPE matrix (Figure 5(a)). This<br />
phenomen<strong>on</strong> is not visible when the treated CaCO 3<br />
was used (Figure 5(b) - Figure 5(e)). The interfacial<br />
interacti<strong>on</strong> between the r-HDPE matrix <strong>and</strong> CaCO 3<br />
particles was str<strong>on</strong>ger, resulted from the<br />
pretreatment <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> CaCO 3 particles. This would be<br />
another reas<strong>on</strong> for the improvement in the<br />
mechanical properties, particularly impact strength,<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the r-HDPE/CaCO 3 composites. (9)<br />
(a) untreated<br />
Table 4. <strong>Mechanical</strong> properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> r-HDPE/CaCO 3<br />
composites (CaCO 3 treated with optimum<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tent <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> coupling agents)<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Coupling</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
Agent<br />
Tensile<br />
strength<br />
(MPa)<br />
Flexural<br />
strength<br />
(MPa)<br />
Impact<br />
strength<br />
(kJ/m 2 )<br />
El<strong>on</strong>gati<strong>on</strong><br />
at Break<br />
(%)<br />
Untreated 14.01 19.87 10.28 18.77<br />
1. wt%<br />
Stearic acid<br />
2. wt%<br />
AMPTES<br />
3. wt%<br />
GPTMS<br />
4. wt%<br />
MA-g-HDPE<br />
15.68 24.93 13.23 21.65<br />
16.17 25.54 15.00 22.32<br />
15.87 25.28 14.67 21.95<br />
16.03 25.84 14.89 23.24<br />
(b) 1 wt.% SA<br />
(c) 2 wt.% AMPTES<br />
<strong>Morphology</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> r-HDPE/CaCO 3 Composites<br />
The fractured surfaces <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the r-HDPE/CaCO 3<br />
composites after the impact test were examined by<br />
SEM. Figure 4(a) shows that the r-HDPE filled<br />
with the untreated CaCO 3 exhibits brittle fracture<br />
(d) 3 wt.% GPTMS<br />
(e) 4 wt.% MA-g-HDPE<br />
Figure 4. SEM micrographs (x500) <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> r-HDPE/CaCO 3<br />
composites when CaCO 3 treated with different<br />
coupling agents