Key Concept Chart - Pearson
Key Concept Chart - Pearson
Key Concept Chart - Pearson
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Mathematics<br />
<strong>Key</strong> <strong>Concept</strong> <strong>Chart</strong><br />
Form 2<br />
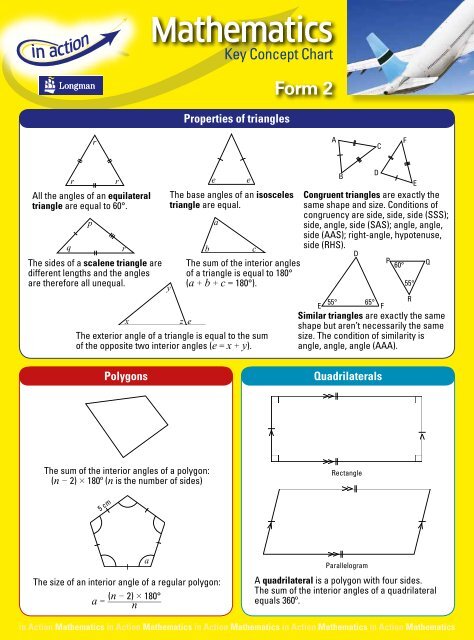
Properties of triangles<br />
r<br />
A<br />
C<br />
F<br />
r r<br />
All the angles of an equilateral<br />
triangle are equal to 60°.<br />
p<br />
q<br />
r<br />
The sides of a scalene triangle are<br />
different lengths and the angles<br />
are therefore all unequal.<br />
x<br />
e e<br />
The base angles of an isosceles<br />
triangle are equal.<br />
y<br />
b<br />
a<br />
The sum of the interior angles<br />
of a triangle is equal to 180°<br />
(a b c = 180°).<br />
z e<br />
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum<br />
of the opposite two interior angles (e = x y).<br />
c<br />
B<br />
D<br />
P<br />
60° Q<br />
55°<br />
E 55° 65° R<br />
F<br />
D<br />
Congruent triangles are exactly the<br />
same shape and size. Conditions of<br />
congruency are side, side, side (SSS);<br />
side, angle, side (SAS); angle, angle,<br />
side (AAS); right-angle, hypotenuse,<br />
side (RHS).<br />
Similar triangles are exactly the same<br />
shape but aren’t necessarily the same<br />
size. The condition of similarity is<br />
angle, angle, angle (AAA).<br />
E<br />
Polygons<br />
Quadrilaterals<br />
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon:<br />
(n 2) 180º (n is the number of sides)<br />
Rectangle<br />
5 cm<br />
a<br />
Parallelogram<br />
The size of an interior angle of a regular polygon: A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides.<br />
a ____________<br />
(n 2) 180°<br />
n The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral<br />
equals 360º.<br />
in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics
Algebra and numbers<br />
Definitions<br />
Factor: a number that divides exactly into another number without leaving a remainder (1, 2, 3 and 6 are<br />
factors of 6).<br />
Prime factor: a factor of a number that is also a prime number (2 and 3 are prime factors of 6).<br />
Prime number: a number that only has two factors: itself and one (2, 3, 5, 7…).<br />
Square number: the product of a number multiplied by itself (4 is the square number of 2: 2 2 = 4).<br />
Square root: a number that when multiplied by itself gives a square number (4 is the square root of 16).<br />
Cube number: the product of a number multiplied by itself twice (8 is the cube number of 2: 2 2 2 = 8).<br />
Cube root: a number that when multiplied by itself twice gives a cubed number (2 is the cube root of 8).<br />
A monomial expression has only one term, for example 5 x.<br />
A polynomial expression has more than one term, for example 3 x 5 6a.<br />
A binomial expression has two terms, for example 3 x 5.<br />
A trinomial expression has three terms, for example 5 x 2y 7.<br />
In a quadratic equation, the highest power of the variable is 2, for example 5 x 2 x 2 5.<br />
Equations<br />
Linear equation: 5 x 7 = 3<br />
5 x = 3 7 [Group like terms]<br />
5 x = 10 [Simplify]<br />
x = 2 [Solve for x]<br />
Simultaneous linear equation:<br />
Solve for p and q if 3p 5q = 29 and 4p q = 8.<br />
3p 5q = 29 (1)<br />
4p q = 8 (2)<br />
(2) 5: 20p 5q = 40 (3) [Multiply each term of (2) by 5]<br />
(1) (3): 23p 0 = 69 [Add equations (1) and (3)]<br />
\ p = 3 [Divide both sides by 23]<br />
Substitute p = 3 into (1): 3(3) 5q = 29<br />
\ 5q = 20 [Subtract 9 from both sides]<br />
\ q = 4 [Solve for q]<br />
\ p = 3 and q = 4<br />
Square of binomial: (a b) 2 = (first term) 2 2(product of two terms) (last term) 2 = a 2 2ab b 2 .<br />
Indices<br />
Useful infomation<br />
Order of Operations<br />
B: Brackets<br />
O: Of<br />
D: Division<br />
M: Multiplication<br />
A: Addition<br />
S: Subtraction<br />
a 2 index<br />
base<br />
Multiplying a 3 a 2 = (a a a) (a a) = a 3 2 = a 5<br />
Add the indices<br />
Dividing a 3 a 2 = _______ a a a a<br />
a = a 3 2 2 = a 1<br />
Subtract the indices<br />
Raising to (a 3 ) 2 = (a a a) (a a a) = a 3 2 = a 6<br />
a power Multiply the indices<br />
Zero as<br />
index<br />
A negative<br />
index<br />
3 0 = 1<br />
All numbers with the index zero = 1, so a 0 = 1<br />
2 1 = 1_<br />
2 <br />
A negative index becomes positive when written below the fraction line a n = __ <br />
a 1 n <br />
in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics
Graphs<br />
–5<br />
–4<br />
–3<br />
–2<br />
y<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
–1 0<br />
–1<br />
1 2 3 4 5<br />
–2<br />
–3<br />
–4<br />
–5<br />
x<br />
Graphs are visual representations of figures.<br />
A Cartesian plane is a plane with coordinate grids that is used to<br />
plot coordinates.<br />
Every point on the Cartesian plane represents an ordered pair<br />
and an ordered pair represents the coordinates of the point.<br />
The first number the x-coordinate is the horizontal position<br />
of the point with respect to the origin. The second number the<br />
y-coordinate is the vertical position of the point with respect to<br />
the origin. Always write the x-coordinate first and the y-coordinate<br />
second, e.g. (3; 2) represents the point x = 3 and y = 2.<br />
y = 2x – 3<br />
y<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
Straight-line graphs are also known as linear graphs.<br />
Straight-line graph equations: y = mx c where m is the gradient<br />
and c is the y-intercept.<br />
Alternative equations: y = mx, y = c and x = c.<br />
–5<br />
–4<br />
–3<br />
–2 –1 0<br />
–2<br />
1 2 3 4 5 6<br />
–4<br />
–6<br />
–8<br />
–10<br />
–12<br />
x<br />
The gradient (m) is the slope of the straight-line graph. If m is<br />
positive, the straight line slopes upwards from the bottom left to<br />
the top right of the Cartesian plane. If m is negative, the straight<br />
line slopes downwards from the top left to the bottom right of the<br />
Cartesian plane.<br />
m = ________<br />
change in y<br />
<br />
change in x (represented as a fraction).<br />
Another way to write this equation is m = __ Δy<br />
Δx .<br />
–6<br />
–5<br />
y = x 2 + 4x – 4<br />
y<br />
2<br />
1<br />
–4 –3 –2 –1 0<br />
–1<br />
–2<br />
–3<br />
–4<br />
–5<br />
–6<br />
–7<br />
–8<br />
–9<br />
1<br />
2<br />
x<br />
Parabola graphs are curved graphs.<br />
Parabola graph equations:<br />
y = ax 2 bx c; y = ax 2 bx; y = ax 2 c; y = ax 2 .<br />
Remember: The sign of the coefficient of x 2 indicates whether<br />
the arms of the parabola point upwards or downwards. If the<br />
coefficient is positive the arms of the graph point upward. If it<br />
is negative the arms of the graph point downward.<br />
in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics in Action Mathematics
Perimeter (P)<br />
Perimeter (P) is the total distance around a<br />
2D shape.<br />
Perimeter formulae<br />
Triangle = a b c<br />
Square = 4s<br />
Rectangle = 2l 2b or 2(l b)<br />
Circle = C = π d = 2 π r<br />
Volume (V ) and total surface area (TSA)<br />
Volume (V ) is the amount of space that a 3D object<br />
occupies in cubic metres (m 3 ), cubic centimetres<br />
(cm 3 ), or cubic millimetres (mm 3 ).<br />
TSA cylinder<br />
= 2 area of base area of curved side<br />
= 2pr 2 2prh<br />
V prism<br />
= area of base perpendicular height<br />
Example:<br />
TSA = 2 area of the circular base area of the<br />
rectangle<br />
= 2 π r 2 2π r h<br />
= 2 π (5 cm) 2 2 π 5 cm × 8 cm<br />
= 157.08 cm 2 251.33 cm 2<br />
Measurements<br />
Area (A)<br />
5 cm<br />
Solution:<br />
= 408.41 cm 2<br />
5 cm<br />
8 cm<br />
Data<br />
Area (A) is the number of square units that a 2D<br />
shape covers.<br />
Area formulae<br />
Triangle = 1_<br />
2 bh<br />
Square = s 2<br />
Rectangle = lb<br />
Parallelogram = bh<br />
Trapezium = 1_<br />
2 (s 1 s 2 ) h<br />
Kite = 1_<br />
2 (d 1 d 2 )<br />
Circle = π r 2 or π ( d__<br />
2 ) 2 = 1_<br />
4 π d 2<br />
Speed (v)<br />
Speed (v) is the measure of how fast an object is<br />
moving given by the ratio of distance versus time.<br />
distance (s)<br />
time (t)<br />
Speed (v) = ________ <br />
Example: A lion starts from 0 m/s to chase a buck<br />
for 4 min over 1.5 km. The buck outruns the lion and<br />
the lion gives up and stops. Calculate the average<br />
speed of the lion in km/h.<br />
Speed = ______ distance<br />
time<br />
<br />
= _______ <br />
1.5 km<br />
(4 60) h [4 min = __ <br />
60 4 h]<br />
= 22.5 km/h<br />
Central tendency: the middle values<br />
of a data set i.e. the mean, median<br />
and mode.<br />
Frequency polygon: a graph based<br />
on a histogram that you create by<br />
joining the midpoints of the top of<br />
each bar of the histogram.<br />
Frequency table: a table in which<br />
you record data as tallies.<br />
Scatter graph: a graph on which you<br />
plot two variables, usually x and y,<br />
that form a set of points on a set<br />
of axes.<br />
Scatter graph of Language marks<br />
versus Mathematics marks<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
20 40 60 80 100<br />
Mathematics mark<br />
Language mark<br />
Probability: the likelihood of an event<br />
occurring expressed as a number between<br />
0 and 1 in the form of a normal fraction,<br />
decimal or percentage.<br />
Mean = _______________<br />
<br />
total of all values<br />
total number of values <br />
Theoretical probability<br />
__________________________________<br />
the number of ways in which the outcome can occur<br />
= <br />
the total number of possible equally likely outcomes <br />
Experimental probability<br />
= _______________________________<br />
<br />
the number of times that the outcome occurred<br />
the total number of trials<br />
Contact details<br />
<strong>Pearson</strong> Botswana: Tel: +267 3922969 Fax: +267 3922682<br />
Plot 14386, New Lobatse Road, G-West Industrial Site,<br />
Gaborone, Botswana. Website: www.longmanafrica.co.za