- Page 1 and 2: 2 0 1 0 P R O C E E D I N G S W A S
- Page 3 and 4: TABLE OF CONTENTS Research Papers _
- Page 5 and 6: Public Relations Leadership through
- Page 7 and 8: Millennial Students Relationship wi
- Page 9 and 10: elationship approach to PR provides
- Page 11 and 12: social media marketing is effective
- Page 13 and 14: students who noted they were 17 or
- Page 15 and 16: discussed previously, Millennial st
- Page 17 and 18: strongly committed to maintaining a
- Page 19 and 20: gender (male/female) and each of th
- Page 21 and 22: social media. One focus of the arti
- Page 23 and 24: Shah, A. (2007, June 18). Social me
- Page 25 and 26: Appendix B Table 2 Differences Betw
- Page 27 and 28: Appendix D Table 4 Differences Betw
- Page 29 and 30: Appendix F Table 6 Pearson Correlat
- Page 31 and 32: Mentoring 2.0: How PR Educators Use
- Page 33 and 34: Despite this, however, studies have
- Page 35 and 36: Sometimes using Facebook to IM is a
- Page 37 and 38: Investing time. As with any relatio
- Page 39 and 40: pursuing chosen fields. For public
- Page 41 and 42: Tam, S. Y., Dozier, D. M., Lauzen,
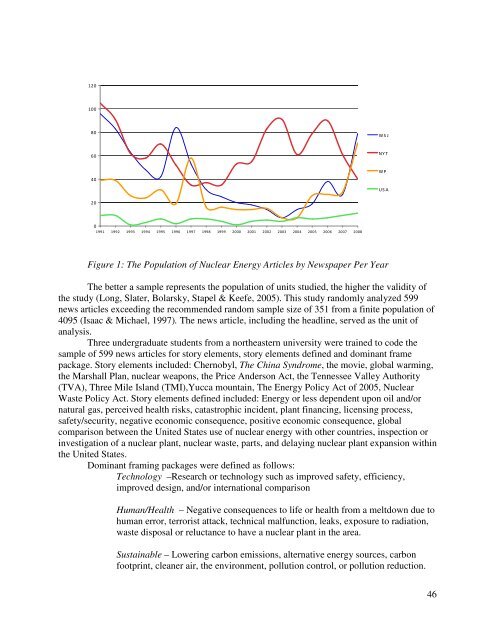
- Page 43 and 44: While favor towards nuclear energy
- Page 45: frames present new considerations w
- Page 49 and 50: “Shoreham Board Begins a Hunt for
- Page 51 and 52: While the story element “positive
- Page 53 and 54: Gamson, W. & Lasch, K. (1983). The
- Page 55 and 56: Reputation Matters: Impact of Organ
- Page 57 and 58: leadership had at hand a number of
- Page 59 and 60: and 65+ (15.4%). More than half wer
- Page 61 and 62: evealed significant differences for
- Page 63 and 64: will be rewarded in the marketplace
- Page 65 and 66: Investigating Multiplier Effects of
- Page 67 and 68: RQ1: Do PR practitioners and busine
- Page 69 and 70: accepting information they receive
- Page 71 and 72: still smacks of news. News coverage
- Page 73 and 74: Even when testimonials do not withs
- Page 75 and 76: viewed to some degree as a valuable
- Page 77 and 78: Perceptions of Product Blogs in Tai
- Page 79 and 80: Uses and gratifications theory has
- Page 81 and 82: Thus the degree to which blog reade
- Page 83 and 84: hours). Blog reading was dwarfed by
- Page 85 and 86: Effects of Language on Responses Ba
- Page 87 and 88: esponse (M = 4.13). For online acti
- Page 89 and 90: 5-item Index 4.41(1.030) 3.80(1.033
- Page 91 and 92: ecommendations were more objective
- Page 93 and 94: Choney, B. (2009, September 29). Mi
- Page 95 and 96: Lenhart, A., Purecell, K., Smith, A
- Page 97 and 98:
elational trust. Journal of Public
- Page 99 and 100:
challenge will be to persuade survi
- Page 101 and 102:
of Avian Flu. It is important to no
- Page 103 and 104:
with an arousing stimulus or messag
- Page 105 and 106:
Chen, N. (2009). Institutionalizing
- Page 107 and 108:
Excellence in an Activist Organizat
- Page 109 and 110:
public relations functions or tacti
- Page 111 and 112:
Data Collection Documents. In an ef
- Page 113 and 114:
Research. A key area of CTFK’s we
- Page 115 and 116:
Engaging individuals. Many times ac
- Page 117 and 118:
Washington, DC, and Puerto Rico; ge
- Page 119 and 120:
Murphy, P. & Dee, J. (1996) Reconci
- Page 121 and 122:
of Educational Progress (NAEP), 80%
- Page 123 and 124:
school assessment, and that the pro
- Page 125 and 126:
Both the paper and Web-based survey
- Page 127 and 128:
student was admitted to their acade
- Page 129 and 130:
Problems with the measures: Here, s
- Page 131 and 132:
Patterns in the open-ended response
- Page 133 and 134:
Trends evident in K-12 education, t
- Page 135 and 136:
Another 15% of respondents (n = 8)
- Page 137 and 138:
Table 1 Respondents’ Perceptions
- Page 139 and 140:
Table 4 Frequencies of Listed Writi
- Page 141 and 142:
Hansen, R.S. (1993). Clear, concise
- Page 143 and 144:
so, this study follows up on recent
- Page 145 and 146:
2009). In BMCC context, in addition
- Page 147 and 148:
--------------------------------- I
- Page 149 and 150:
social media is not crisis communic
- Page 151 and 152:
and uses and gratifications theorie
- Page 153 and 154:
Hennig-Thurau, T., Gwinner, K. P.,
- Page 155 and 156:
Table 1 BMCC Model Propositions (__
- Page 157 and 158:
FIGURE 1 BMM Model (_____ & _____,
- Page 159 and 160:
practitioners and scholars argue fo
- Page 161 and 162:
Several studies, however, suggest t
- Page 163 and 164:
factors that impact the development
- Page 165 and 166:
perceptions of administrative suppo
- Page 167 and 168:
(2009) reminds us that the limitati
- Page 169 and 170:
412-414. Gonzalez-Herrero, A., & Ru
- Page 171 and 172:
Intersections and Overlaps: Buildin
- Page 173 and 174:
elations excellence, relationship-b
- Page 175 and 176:
2002), all of which encourage emplo
- Page 177 and 178:
Conley and Wagner-Marsh (1998) prop
- Page 179 and 180:
passion, caring for people.” Note
- Page 181 and 182:
done.” Accommodations such as fle
- Page 183 and 184:
organizational commitment and loyal
- Page 185 and 186:
Founder/Leader Faith & Vision Authe
- Page 187 and 188:
Practical implications This study a
- Page 189 and 190:
public relations (pp. 3-22). Mahwah
- Page 191 and 192:
Grunig, L. A. (1992). Power in the
- Page 193 and 194:
presented to the annual conference
- Page 195 and 196:
Prioritizing Stakeholders for Publi
- Page 197 and 198:
developed by Grunig and Hunt (1984)
- Page 199 and 200:
expectant stakeholders possess two
- Page 201 and 202:
each other” (p. 125). Examples of
- Page 203 and 204:
Priority publics are those whose pa
- Page 205 and 206:
Collection of data triangulated (Yi
- Page 207 and 208:
Diffused Linkage. A diffused stakeh
- Page 209 and 210:
Envirocare take it. They are also m
- Page 211 and 212:
Dunham, L., Freeman, R. E., & Liedt
- Page 213 and 214:
PEDAGOGICAL POSTERS 213
- Page 215 and 216:
seem to be context-dependent (Lauri
- Page 217 and 218:
Shapiro, A. (2003). Case Studies in
- Page 219 and 220:
Argument #2: stories are for childr
- Page 221 and 222:
Physiology “…your mind was evol
- Page 223 and 224:
Conclusion In the movie, Indiana Jo
- Page 225 and 226:
Pitching on your Feet: Using a Mock
- Page 227 and 228:
speaker(s) are available after the
- Page 229 and 230:
college’s connection to the commu
- Page 231 and 232:
“I felt the class built upon our
- Page 233 and 234:
community. Many participants have c
- Page 235 and 236:
posting content to the Internet, bu
- Page 237 and 238:
What’s All The Hype About Skype?
- Page 239 and 240:
In between the times the class meet
- Page 241 and 242:
Best Practices in Public Relations:
- Page 243 and 244:
Assignment Structure Client Selecti
- Page 245 and 246:
Conclusion Integrating real-world c
- Page 247 and 248:
equires true fluency in the host co
- Page 249 and 250:
living in London. Because visa and
- Page 251 and 252:
Using the Case Study approach to an
- Page 253 and 254:
tier responders hadn’t participat
- Page 255 and 256:
Harnessing the Web for Teaching Wri
- Page 257 and 258:
these tools and platforms. With wri
- Page 259 and 260:
article 2. 259
- Page 261 and 262:
Experimental methods may be better
- Page 263 and 264:
The third hypothesis asked whether
- Page 265 and 266:
Crisis in the Classroom: A cross-de
- Page 267 and 268:
prepare and do the research. I prov
- Page 269 and 270:
• September 2009 - More students
- Page 271 and 272:
Public Relations Leadership Through
- Page 273 and 274:
from using it multiple times a day
- Page 275 and 276:
Kent, M. (2010). Directions in soci
- Page 277 and 278:
Professor Clare Morgan at Oxford no
- Page 279 and 280:
evenings at home working on his poe
- Page 281 and 282:
Another strategy for the students w
- Page 283 and 284:
Media list and crisis media list So
- Page 285 and 286:
understand that knowledge of the cl
- Page 287 and 288:
If creating separate teams for one
- Page 289 and 290:
Integrating ethics into the undergr
- Page 291 and 292:
Three-step approach The present aut
- Page 293:
Putting Theory, Research and Strate