Poly(2-oxazolines) in biological and biomedical application contexts
Poly(2-oxazolines) in biological and biomedical application contexts
Poly(2-oxazolines) in biological and biomedical application contexts
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
N. Adams, U.S. Schubert / Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 59 (2007) 1504–1520<br />
1515<br />
polymers, the organic solvent used <strong>in</strong> the dialysis experiment<br />
<strong>and</strong> the weight ratio of drug to polymer. In experiments, the<br />
toxicity of the polymer was found to be <strong>in</strong>significant when<br />
compared to other matrices such as Tween 80 <strong>and</strong> comparable to<br />
Cremophore EL (polyoxyethylated castor oil, CreEL). Paclitaxel<br />
conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g micelles were shown to <strong>in</strong>hibit the growth of<br />
KB cells (cell l<strong>in</strong>e derived from a human carc<strong>in</strong>oma of the<br />
nasopharynx) to the same extent as comparable CreEL<br />
formulations (but with reduced toxicity of the carrier).<br />
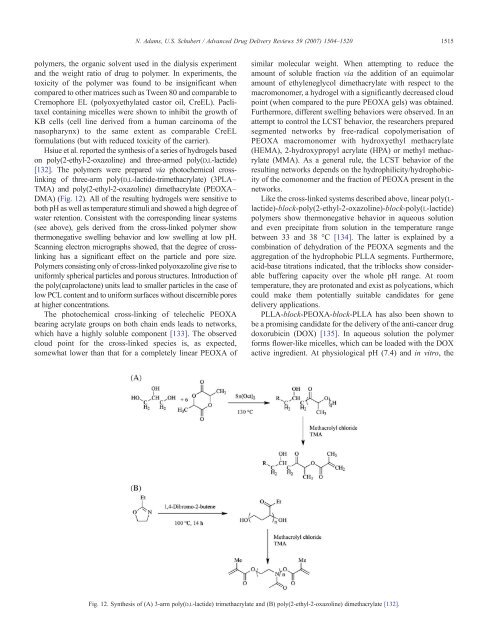
Hsiue et al. reported the synthesis of a series of hydrogels based<br />
on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazol<strong>in</strong>e) <strong>and</strong> three-armed poly(D,L-lactide)<br />
[132]. The polymers were prepared via photochemical crossl<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g<br />
of three-arm poly(D,L-lactide-trimethacrylate) (3PLA–<br />
TMA) <strong>and</strong> poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazol<strong>in</strong>e) dimethacrylate (PEOXA–<br />
DMA) (Fig. 12). All of the result<strong>in</strong>g hydrogels were sensitive to<br />
both pH as well as temperature stimuli <strong>and</strong> showed a high degree of<br />
water retention. Consistent with the correspond<strong>in</strong>g l<strong>in</strong>ear systems<br />
(see above), gels derived from the cross-l<strong>in</strong>ked polymer show<br />
thermonegative swell<strong>in</strong>g behavior <strong>and</strong> low swell<strong>in</strong>g at low pH.<br />
Scann<strong>in</strong>g electron micrographs showed, that the degree of crossl<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g<br />
has a significant effect on the particle <strong>and</strong> pore size.<br />
<strong>Poly</strong>mers consist<strong>in</strong>g only of cross-l<strong>in</strong>ked polyoxazol<strong>in</strong>e give rise to<br />
uniformly spherical particles <strong>and</strong> porous structures. Introduction of<br />
the poly(caprolactone) units lead to smaller particles <strong>in</strong> the case of<br />
low PCL content <strong>and</strong> to uniform surfaces without discernible pores<br />
at higher concentrations.<br />
The photochemical cross-l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g of telechelic PEOXA<br />
bear<strong>in</strong>g acrylate groups on both cha<strong>in</strong> ends leads to networks,<br />
which have a highly soluble component [133]. The observed<br />
cloud po<strong>in</strong>t for the cross-l<strong>in</strong>ked species is, as expected,<br />
somewhat lower than that for a completely l<strong>in</strong>ear PEOXA of<br />
similar molecular weight. When attempt<strong>in</strong>g to reduce the<br />
amount of soluble fraction via the addition of an equimolar<br />
amount of ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate with respect to the<br />
macromonomer, a hydrogel with a significantly decreased cloud<br />
po<strong>in</strong>t (when compared to the pure PEOXA gels) was obta<strong>in</strong>ed.<br />
Furthermore, different swell<strong>in</strong>g behaviors were observed. In an<br />
attempt to control the LCST behavior, the researchers prepared<br />
segmented networks by free-radical copolymerisation of<br />
PEOXA macromonomer with hydroxyethyl methacrylate<br />
(HEMA), 2-hydroxypropyl acrylate (HPA) or methyl methacrylate<br />
(MMA). As a general rule, the LCST behavior of the<br />
result<strong>in</strong>g networks depends on the hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity<br />
of the comonomer <strong>and</strong> the fraction of PEOXA present <strong>in</strong> the<br />
networks.<br />
Like the cross-l<strong>in</strong>ked systems described above, l<strong>in</strong>ear poly(Llactide)-block-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazol<strong>in</strong>e)-block-poly(L-lactide)<br />
polymers show thermonegative behavior <strong>in</strong> aqueous solution<br />
<strong>and</strong> even precipitate from solution <strong>in</strong> the temperature range<br />
between 33 <strong>and</strong> 38 °C [134]. The latter is expla<strong>in</strong>ed by a<br />
comb<strong>in</strong>ation of dehydration of the PEOXA segments <strong>and</strong> the<br />
aggregation of the hydrophobic PLLA segments. Furthermore,<br />
acid-base titrations <strong>in</strong>dicated, that the triblocks show considerable<br />
buffer<strong>in</strong>g capacity over the whole pH range. At room<br />
temperature, they are protonated <strong>and</strong> exist as polycations, which<br />
could make them potentially suitable c<strong>and</strong>idates for gene<br />
delivery <strong>application</strong>s.<br />
PLLA-block-PEOXA-block-PLLA has also been shown to<br />
be a promis<strong>in</strong>g c<strong>and</strong>idate for the delivery of the anti-cancer drug<br />
doxorubic<strong>in</strong> (DOX) [135]. In aqueous solution the polymer<br />
forms flower-like micelles, which can be loaded with the DOX<br />
active <strong>in</strong>gredient. At physiological pH (7.4) <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong> vitro, the<br />
Fig. 12. Synthesis of (A) 3-arm poly(D,L-lactide) trimethacrylate <strong>and</strong> (B) poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazol<strong>in</strong>e) dimethacrylate [132].