Residents' Evacuation Capability in Buildings
Residents' Evacuation Capability in Buildings
Residents' Evacuation Capability in Buildings
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
establishment as a whole, was the most applicable method <strong>in</strong> blocks of service flats and<br />
old people«s homes. In group-residential units every resident <strong>in</strong> the randomized units<br />
were rated. The estimation was based on daily observation of the residents and made by<br />
the staff members who know each resident best. The residents themselves were not<br />
<strong>in</strong>terviewed because of psychological problems. The method conforms with the rat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
systems established for estimat<strong>in</strong>g peoples« ability to cope with different tasks of<br />
everyday life (ADL-Index) and with the SFES for rat<strong>in</strong>g evacuation difficulties<br />
mentioned above.<br />
Results<br />
The results of the rat<strong>in</strong>g, residents« evacuation capability, is presented <strong>in</strong> three ways;<br />
- the percentage distribution of risk factors <strong>in</strong> service flats, homes for old people and<br />
group-residential units,<br />
- the percentage distribution of the need for assistance from staff dur<strong>in</strong>g an evacuation<br />
and the reason for necessary assistance,<br />
- the average staff needed per resident <strong>in</strong> an emergency situation <strong>in</strong> each type of care<br />
hous<strong>in</strong>g studied.<br />
Risk factors<br />
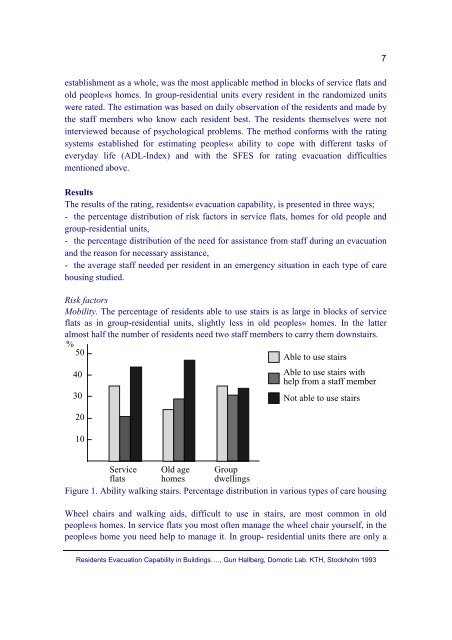
Mobility. The percentage of residents able to use stairs is as large <strong>in</strong> blocks of service<br />
flats as <strong>in</strong> group-residential units, slightly less <strong>in</strong> old peoples« homes. In the latter<br />
almost half the number of residents need two staff members to carry them downstairs.<br />
%<br />
50<br />
Able to use stairs<br />
40<br />
Able to use stairs with<br />
help from a staff member<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
Not able to use stairs<br />
7<br />
Service Old age Group<br />
flats homes dwell<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
Figure 1. Ability walk<strong>in</strong>g stairs. Percentage distribution <strong>in</strong> various types of care hous<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Wheel chairs and walk<strong>in</strong>g aids, difficult to use <strong>in</strong> stairs, are most common <strong>in</strong> old<br />
people«s homes. In service flats you most often manage the wheel chair yourself, <strong>in</strong> the<br />
people«s home you need help to manage it. In group- residential units there are only a<br />
Residents <strong>Evacuation</strong> <strong>Capability</strong> <strong>in</strong> Build<strong>in</strong>gs…., Gun Hallberg, Domotic Lab. KTH, Stockholm 1993