The Engineer's Guide to Standards Conversion - Snell
The Engineer's Guide to Standards Conversion - Snell
The Engineer's Guide to Standards Conversion - Snell
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
SECTION 2 - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES<br />
2.1 Sampling theory<br />
Sampling is simply the process of representing something continuous by periodic<br />
measurement. Whilst sampling is often considered <strong>to</strong> be synonymous with digital<br />
systems, in fact this is not the case. Sampling is in fact an analogue process and<br />
occurs extensively in analogue video. Sampling can take place on a time varying<br />
signal, in which case it will have a temporal sampling rate measured in Hertz(Hz).<br />
Alternatively sampling may take place on a parameter which varies with distance, in<br />
which case it will have a sample spacing or spatial sampling rate measured in cycles<br />
per picture height (c/p.h) or width. Where a two dimensional image is sampled,<br />
samples will be taken on a sampling grid or lattice. Film cameras sample a<br />
continuous world at the frame rate. Television cameras do so at field rate. In<br />
addition, TV fields are vertically sampled in<strong>to</strong> lines. If video is <strong>to</strong> be converted <strong>to</strong><br />
the digital domain the lines will be sampled a third time horizontally before<br />
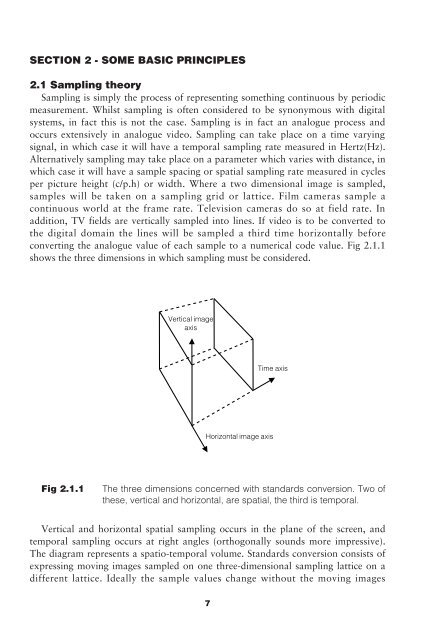
converting the analogue value of each sample <strong>to</strong> a numerical code value. Fig 2.1.1<br />
shows the three dimensions in which sampling must be considered.<br />
Vertical image<br />
axis<br />
Time axis<br />
Horizontal image axis<br />
Fig 2.1.1<br />
<strong>The</strong> three dimensions concerned with standards conversion. Two of<br />
these, vertical and horizontal, are spatial, the third is temporal.<br />
Vertical and horizontal spatial sampling occurs in the plane of the screen, and<br />
temporal sampling occurs at right angles (orthogonally sounds more impressive).<br />
<strong>The</strong> diagram represents a spatio-temporal volume. <strong>Standards</strong> conversion consists of<br />
expressing moving images sampled on one three-dimensional sampling lattice on a<br />
different lattice. Ideally the sample values change without the moving images<br />
7