WindPRO / PARK - EMD International AS.
WindPRO / PARK - EMD International AS.
WindPRO / PARK - EMD International AS.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Introduction to the Ainslie Wake Model (Eddy Viscosity Model)<br />
100<br />
Near wake length [m]<br />
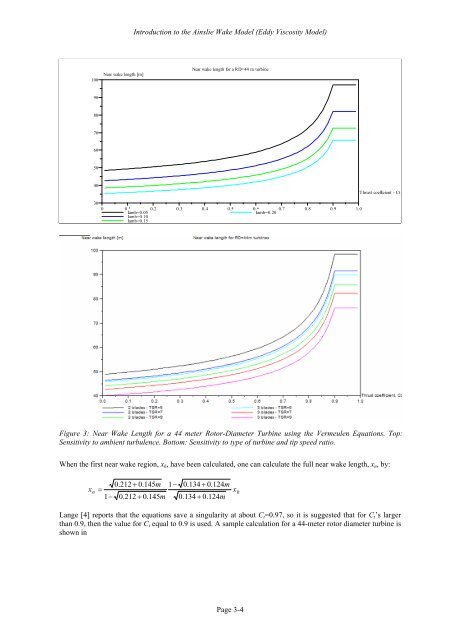
Near wake length for a RD=44 m turbine<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
Thrust coefficient - Ct<br />
30<br />
0 0.1 0.2<br />
Iamb=0.05<br />
0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7<br />
Iamb=0.20<br />
0.8 0.9 1.0<br />
Iamb=0.10<br />
Iamb=0.15<br />
Figure 3: Near Wake Length for a 44 meter Rotor-Diameter Turbine using the Vermeulen Equations. Top:<br />
Sensitivity to ambient turbulence. Bottom: Sensitivity to type of turbine and tip speed ratio.<br />
When the first near wake region, x h , have been calculated, one can calculate the full near wake length, x n , by:<br />
x<br />
=<br />
1−<br />
0.212 + 0.145m<br />
0.134 + 0.124m<br />
n x h<br />
0.212 + 0.145m<br />
1−<br />
0.134 + 0.124m<br />
Lange [4] reports that the equations save a singularity at about C t =0.97, so it is suggested that for C t ’s larger<br />
than 0.9, then the value for C t equal to 0.9 is used. A sample calculation for a 44-meter rotor diameter turbine is<br />
shown in<br />
Page 3-4