WindPRO / PARK - EMD International AS.
WindPRO / PARK - EMD International AS.
WindPRO / PARK - EMD International AS.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Introduction to the Ainslie Wake Model (Eddy Viscosity Model)<br />
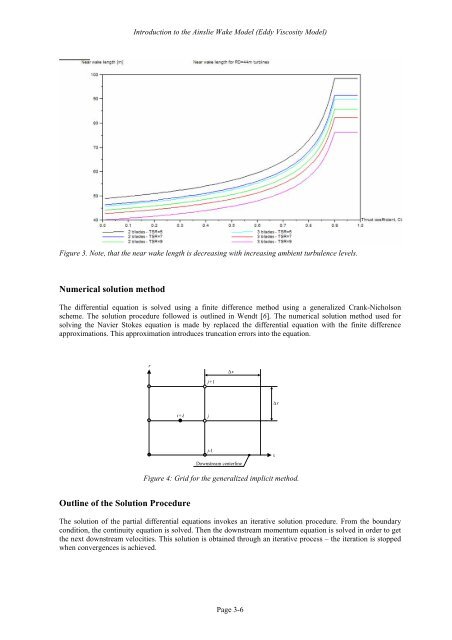
Figure 3. Note, that the near wake length is decreasing with increasing ambient turbulence levels.<br />
Numerical solution method<br />
The differential equation is solved using a finite difference method using a generalized Crank-Nicholson<br />
scheme. The solution procedure followed is outlined in Wendt [6]. The numerical solution method used for<br />
solving the Navier Stokes equation is made by replaced the differential equation with the finite difference<br />
approximations. This approximation introduces truncation errors into the equation.<br />
r<br />
∆ x<br />
j+1<br />
∆ r<br />
i+λ<br />
j<br />
j-1<br />
Downstream centerline<br />
x<br />
Figure 4: Grid for the generalized implicit method.<br />
Outline of the Solution Procedure<br />
The solution of the partial differential equations invokes an iterative solution procedure. From the boundary<br />
condition, the continuity equation is solved. Then the downstream momentum equation is solved in order to get<br />
the next downstream velocities. This solution is obtained through an iterative process – the iteration is stopped<br />
when convergences is achieved.<br />
Page 3-6