Perio_III
Perio_III
Perio_III
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Perio</strong>dontics <strong>III</strong> Summary Notes Enoch Ng<br />
Occlusion and Orthodontics<br />
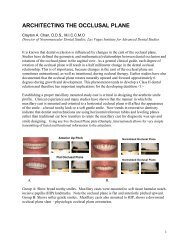
Occlusion<br />
o<br />
o<br />
o<br />
Physiologic – no signs of dysfunction or disease<br />
Traumatic – occlusion associated with dysfunction or disease<br />
• More rapid progression of periodontally involved teeth<br />
• Primary – excessive occlusal force on normal dentition<br />
• Secondary – normal force on a periodontally compromised tooth<br />
Therapeutic – specific interventions designed to treat dysfunction<br />
• Stable endpoint of Mn closure<br />
• Bilateral distribution of occlusal forces<br />
• Axial loading of teeth<br />
- Therapeutic priority – control inflammation<br />
o After inflammation, THEN address residual mobility<br />
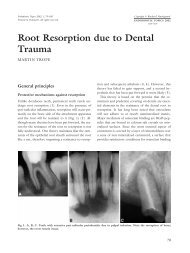
- Clinical Features of Occlusal Trauma<br />
o Tooth mobility, increased displacement, stable pattern adaptation<br />
o Tooth migration, pain on percussion, radiographic changes (widened PDL, apical resorption, etc)<br />
o TMJ dysfunction<br />
o Excessive wave facets, fractures<br />
o Fremitus – vibration of palpation<br />
- Treatment<br />
o Evaluate vitality and parafunctional habits<br />
o Occlusal adjustments – prophylactic equilibration is contraindicated<br />
o Splitting<br />
o Orthodontic tooth movement<br />
o Occlusal reconstruction<br />
o Extraction<br />
- Outcome Assessment<br />
o Decreased mobility or stable pattern<br />
o Decreased migration of teeth<br />
o Stable of decreased radiographic changes<br />
o Relief of pain, fremitus, occlusal interferences<br />
o Stable, functional, physiologic and esthetically acceptable occlusion