Addressing Language Access Issues in Your Practice: A Toolkit for ...
Addressing Language Access Issues in Your Practice: A Toolkit for ...
Addressing Language Access Issues in Your Practice: A Toolkit for ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CALIFORNIA ACADEMY OF FAMILY PHYSICIANS 6<br />
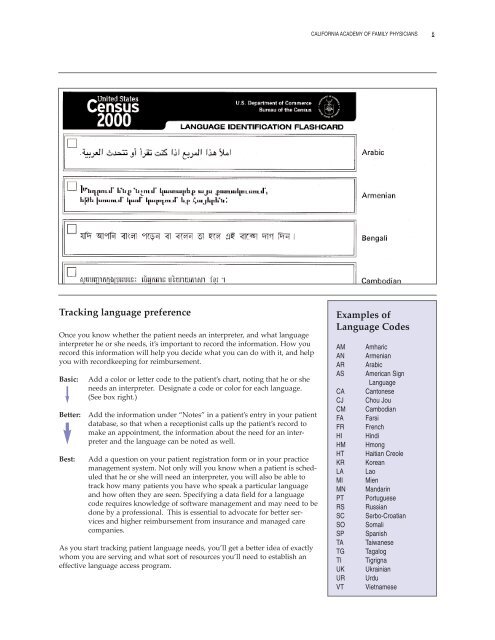
Track<strong>in</strong>g language preference<br />
Once you know whether the patient needs an <strong>in</strong>terpreter, and what language<br />
<strong>in</strong>terpreter he or she needs, it’s important to record the <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation. How you<br />
record this <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation will help you decide what you can do with it, and help<br />
you with recordkeep<strong>in</strong>g <strong>for</strong> reimbursement.<br />
Basic:<br />
Better:<br />
Best:<br />
Add a color or letter code to the patient’s chart, not<strong>in</strong>g that he or she<br />
needs an <strong>in</strong>terpreter. Designate a code or color <strong>for</strong> each language.<br />
(See box right.)<br />
Add the <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation under “Notes” <strong>in</strong> a patient’s entry <strong>in</strong> your patient<br />
database, so that when a receptionist calls up the patient’s record to<br />
make an appo<strong>in</strong>tment, the <strong>in</strong><strong>for</strong>mation about the need <strong>for</strong> an <strong>in</strong>terpreter<br />
and the language can be noted as well.<br />
Add a question on your patient registration <strong>for</strong>m or <strong>in</strong> your practice<br />
management system. Not only will you know when a patient is scheduled<br />
that he or she will need an <strong>in</strong>terpreter, you will also be able to<br />
track how many patients you have who speak a particular language<br />
and how often they are seen. Specify<strong>in</strong>g a data field <strong>for</strong> a language<br />
code requires knowledge of software management and may need to be<br />
done by a professional. This is essential to advocate <strong>for</strong> better services<br />
and higher reimbursement from <strong>in</strong>surance and managed care<br />
companies.<br />
As you start track<strong>in</strong>g patient language needs, you’ll get a better idea of exactly<br />
whom you are serv<strong>in</strong>g and what sort of resources you’ll need to establish an<br />
effective language access program.<br />
Examples of<br />
<strong>Language</strong> Codes<br />
AM<br />
AN<br />
AR<br />
AS<br />
CA<br />
CJ<br />
CM<br />
FA<br />
FR<br />
HI<br />
HM<br />
HT<br />
KR<br />
LA<br />
MI<br />
MN<br />
PT<br />
RS<br />
SC<br />
SO<br />
SP<br />
TA<br />
TG<br />
TI<br />
UK<br />
UR<br />
VT<br />
Amharic<br />
Armenian<br />
Arabic<br />
American Sign<br />
<strong>Language</strong><br />
Cantonese<br />
Chou Jou<br />
Cambodian<br />
Farsi<br />
French<br />
H<strong>in</strong>di<br />
Hmong<br />
Haitian Creole<br />
Korean<br />
Lao<br />
Mien<br />
Mandar<strong>in</strong><br />
Portuguese<br />
Russian<br />
Serbo-Croatian<br />
Somali<br />
Spanish<br />
Taiwanese<br />
Tagalog<br />
Tigrigna<br />
Ukra<strong>in</strong>ian<br />
Urdu<br />
Vietnamese