Baobab Monograph.pdf - Crops for the Future
Baobab Monograph.pdf - Crops for the Future
Baobab Monograph.pdf - Crops for the Future
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4.3 Seeds<br />
Seed kernels are widely used, despite <strong>the</strong> need to remove <strong>the</strong> relatively thick<br />
shell. They are eaten fresh, dry or ground and used in cooking. Kernels have<br />
an energy value of 1803 kJ/100g (Arnold et al., 1985) approximately 50%<br />
higher than leaves. Arnold et al. (1985) also provided data on chemical<br />
composition: moisture 8.1%, protein 33.7%, fat 30.6%, carbohydrates 4.8%,<br />
fibre 16.9% and ash 5.9%. However, higher levels of carbohydrates have<br />
been recorded (Palmer and Pitman, 1972).<br />
Glew et al., (1997) reported that lipid content was 155 mg/g of dry weight<br />
with 1-2 mg/g linoleic acid. Amino acids and mineral contents are shown in<br />
tables 4.7 and 4.8.<br />
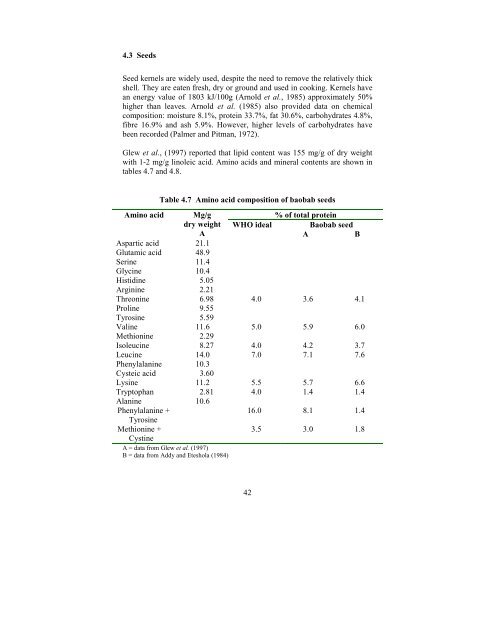
Table 4.7 Amino acid composition of baobab seeds<br />
Amino acid Mg/g<br />
% of total protein<br />
dry weight WHO ideal <strong>Baobab</strong> seed<br />
A<br />
A<br />
B<br />
Aspartic acid 21.1<br />
Glutamic acid 48.9<br />
Serine 11.4<br />
Glycine 10.4<br />
Histidine 5.05<br />
Arginine 2.21<br />
Threonine 6.98 4.0 3.6 4.1<br />
Proline 9.55<br />
Tyrosine 5.59<br />
Valine 11.6 5.0 5.9 6.0<br />
Methionine 2.29<br />
Isoleucine 8.27 4.0 4.2 3.7<br />
Leucine 14.0 7.0 7.1 7.6<br />
Phenylalanine 10.3<br />
Cysteic acid 3.60<br />
Lysine 11.2 5.5 5.7 6.6<br />
Tryptophan 2.81 4.0 1.4 1.4<br />
Alanine 10.6<br />
Phenylalanine +<br />
16.0 8.1 1.4<br />
Tyrosine<br />
Methionine +<br />
3.5 3.0 1.8<br />
Cystine<br />
A = data from Glew et al. (1997)<br />
B = data from Addy and Eteshola (1984)<br />
42