A Clinical Comparison of Technegas and Xenon-133 in 50 Patients ...
A Clinical Comparison of Technegas and Xenon-133 in 50 Patients ...
A Clinical Comparison of Technegas and Xenon-133 in 50 Patients ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
second (equivalent to about 37 MBq [1 mCi] <strong>in</strong> the lung). Adequate<br />
counts were normally obta<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> one or two <strong>in</strong>halations. Sicker<br />
patients <strong>of</strong>ten required several more breaths. Six planar views (100k)<br />
were performed: posterior; posterior obliques; anterior; <strong>and</strong> anterior<br />
obliques.<br />
<strong>Xenon</strong> imag<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the posterior view was performed immediately<br />
prior to the <strong>Technegas</strong> study A s<strong>in</strong>gle-use disposable breath<strong>in</strong>g<br />
system (Atomic Products) was used. After <strong>in</strong>halations <strong>of</strong> approximately<br />
400 MBq <strong>of</strong> xenon-<strong>133</strong> (11 mCi), a st<strong>and</strong>ard protocol <strong>of</strong><br />
breath-hold<strong>in</strong>g, equilibration, <strong>and</strong> washout was performed. Perfusion<br />
imag<strong>in</strong>g (macroaggregated album<strong>in</strong>) was performed immediately<br />
after the <strong>Technegas</strong> study An adm<strong>in</strong>istered activity <strong>of</strong> 180<br />
MBq (5 mCi) to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> a pixel count ratio <strong>of</strong> about five times the<br />
<strong>Technegas</strong> activity was used. Multiple planar images identical with<br />
the <strong>Technegas</strong> sequence were collected.<br />
<strong>Technegas</strong> <strong>and</strong> xenon images were compared for technical quality<br />
<strong>and</strong> diagnostic value. The images were viewed <strong>and</strong> graded without<br />
digital process<strong>in</strong>g by two experienced nuclear medic<strong>in</strong>e physicians<br />
review<strong>in</strong>g all studies <strong>in</strong> three sessions <strong>in</strong> isolation from other data.<br />
Image quality was assessed on a scale <strong>of</strong> zero to five <strong>in</strong> terms <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>terpretability All studies were reported as high or low probability<br />
<strong>of</strong> pulmonary embolus or <strong>in</strong>determ<strong>in</strong>ate; however, for this report,<br />
only those diagnosed as a high probability <strong>of</strong> pulmonary embolus<br />
were <strong>in</strong>cluded as truly positive studies.<br />
RESULTS<br />
Thirty-n<strong>in</strong>e patients had a risk factor <strong>of</strong> prolonged<br />
bed rest or recent surgery Eleven had a past history<br />
<strong>of</strong> phlebitis or previous pulmonary embolus. Thirtyseven<br />
patients presented with dyspnea, <strong>and</strong> 32 had<br />
pleuritic chest pa<strong>in</strong>. There were 13 smokers <strong>and</strong> 12<br />
ex-smokers. Electrocardiograms were normal <strong>in</strong> 27<br />
patients <strong>and</strong> showed s<strong>in</strong>us tachycardia <strong>in</strong> 19. The chest<br />
x-ray film was normal <strong>in</strong> 14 patients <strong>and</strong> showed<br />
pleural effusions <strong>in</strong> 15 <strong>and</strong> atelectasis <strong>in</strong> six. Blood gas<br />
analysis showed an oxygen pressure <strong>of</strong> less than 80<br />
mm Hg <strong>in</strong> 37 patients, <strong>and</strong> 19 had an FEV1 <strong>of</strong> less<br />
than 1.20 L.<br />
Ten patients were diagnosed as hav<strong>in</strong>g a high<br />
probability <strong>of</strong> pulmonary embolism by the criterion <strong>of</strong><br />
the PIOPED trial.8 Diffuse match<strong>in</strong>g defects thought<br />
to be consistent with COPD were visible <strong>in</strong> 13 patients.<br />
Diagnostic images with <strong>Technegas</strong> were obta<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong><br />
49 patients. One patient showed marked central airway<br />
deposition with poor visualization <strong>of</strong> the peripheral<br />
areas <strong>of</strong> the lungs. This was due to technical problems<br />
with the prototype equipment.<br />
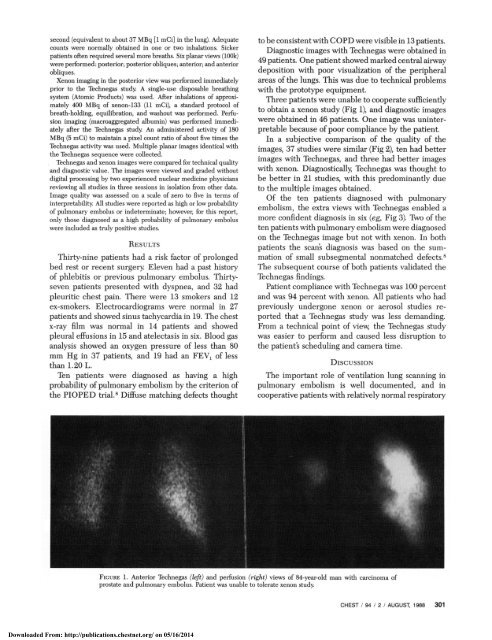
Three patients were unable to cooperate sufficiently<br />
to obta<strong>in</strong> a xenon study (Fig 1), <strong>and</strong> diagnostic images<br />
were obta<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> 46 patients. One image was un<strong>in</strong>terpretable<br />
because <strong>of</strong> poor compliance by the patient.<br />
In a subjective comparison <strong>of</strong> the quality <strong>of</strong> the<br />
images, 37 studies were similar (Fig 2), ten had better<br />
images with <strong>Technegas</strong>, <strong>and</strong> three had better images<br />
with xenon. Diagnostically, <strong>Technegas</strong> was thought to<br />
be better <strong>in</strong> 21 studies, with this predom<strong>in</strong>antly due<br />
to the multiple images obta<strong>in</strong>ed.<br />
Of the ten patients diagnosed with pulmonary<br />
embolism, the extra views with <strong>Technegas</strong> enabled a<br />
more confident diagnosis <strong>in</strong> six (eg, Fig 3). Two <strong>of</strong> the<br />
ten patients with pulmonary embolism were diagnosed<br />
on the <strong>Technegas</strong> image but not with xenon. In both<br />
patients the scan's diagnosis was based on the summation<br />
<strong>of</strong> small subsegmental nonmatched defects.8<br />
The subsequent course <strong>of</strong> both patients validated the<br />
<strong>Technegas</strong> f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
Patient compliance with <strong>Technegas</strong> was 100 percent<br />
<strong>and</strong> was 94 percent with xenon. All patients who had<br />
previously undergone xenon or aerosol studies reported<br />
that a <strong>Technegas</strong> study was less dem<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>g.<br />
From a technical po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> view, the <strong>Technegas</strong> study<br />
was easier to perform <strong>and</strong> caused less disruption to<br />
the patient's schedul<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> camera time.<br />
DiscusSION<br />
The important role <strong>of</strong> ventilation lung scann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong><br />
pulmonary embolism is well documented, <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong><br />
cooperative patients with relatively normal respiratory<br />
FicuRE 1. Anterior <strong>Technegas</strong> (left) <strong>and</strong> perfusion (right) views <strong>of</strong> 84-year-old man with carc<strong>in</strong>oma <strong>of</strong><br />
prostate <strong>and</strong> pulmonary embolus. Patient was unable to tolerate xenon study<br />
CHEST / 94 / 2 / AUGUST 1988 301<br />
Downloaded From: http://publications.chestnet.org/ on 05/16/2014