View - Sandra Kalil Bussadori
View - Sandra Kalil Bussadori
View - Sandra Kalil Bussadori
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ML<br />
b<br />
ML<br />
ML<br />
H<br />
<br />
a<br />
ML<br />
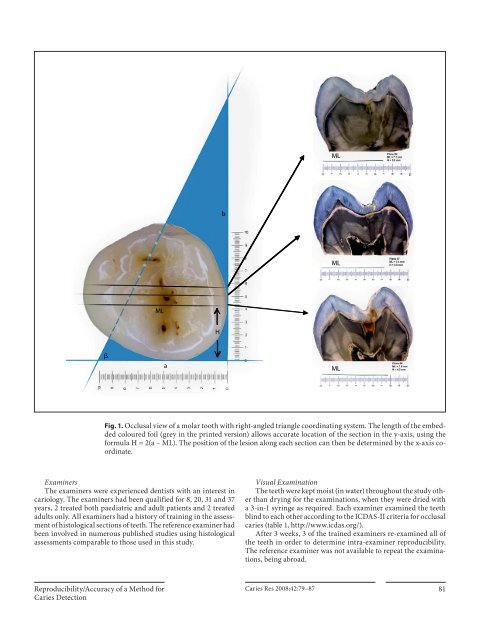
Fig. 1. Occlusal view of a molar tooth with right-angled triangle coordinating system. The length of the embedded<br />
coloured foil (grey in the printed version) allows accurate location of the section in the y-axis, using the<br />
formula H = 2(a – ML). The position of the lesion along each section can then be determined by the x-axis coordinate.<br />
Examiners<br />
The examiners were experienced dentists with an interest in<br />
cariology. The examiners had been qualified for 8, 20, 31 and 37<br />
years, 2 treated both paediatric and adult patients and 2 treated<br />
adults only. All examiners had a history of training in the assessment<br />
of histological sections of teeth. The reference examiner had<br />
been involved in numerous published studies using histological<br />
assessments comparable to those used in this study.<br />
Visual Examination<br />
The teeth were kept moist (in water) throughout the study other<br />
than drying for the examinations, when they were dried with<br />
a 3-in-1 syringe as required. Each examiner examined the teeth<br />
blind to each other according to the ICDAS-II criteria for occlusal<br />
caries ( table 1 , http://www.icdas.org/).<br />
After 3 weeks, 3 of the trained examiners re-examined all of<br />
the teeth in order to determine intra-examiner reproducibility.<br />
The reference examiner was not available to repeat the examinations,<br />
being abroad.<br />
Reproducibility/Accuracy of a Method for<br />
Caries Detection<br />
Caries Res 2008;42:79–87 81