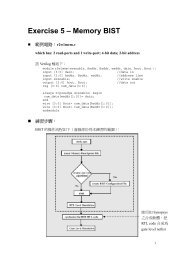
36~chapter 04 atpg.pdf
36~chapter 04 atpg.pdf
36~chapter 04 atpg.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
fault-effect from<br />
FF<br />
i<br />
is masked with the fault site for fault<br />
f j<br />
.<br />
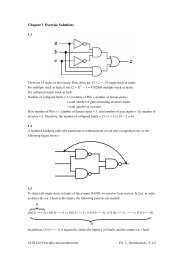
4.31 (Path-Delay ATPG)<br />
(a) There are 14 paths in the circuit:<br />
↑ afgj, ↓ afgj, ↑ bgj, ↓ bgj, ↑ befgj, ↓ befgj, ↑ cefgj, ↓ cefgj, ↑ chj,<br />
↓ chj, ↑ dhj, ↓ dhj,↑ ij, ↓ ij.<br />
(c) Both ↑ afgj and ↓ afgj are unsensitizable.<br />
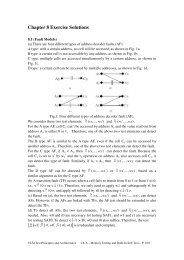
4.32 (Path-Delay ATPG)<br />
Any path that requires a=1 and b=0 as a necessary condition would be<br />
unsensitizable.<br />
4.34 (Path-Del<br />
Delay ATPG)<br />
If the untestable path-delay fault is longer than the testable critical<br />
path, then incidental detection could lead to yield loss.<br />
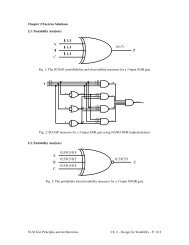
4.36 (Bridging Faults)<br />
The largest current is drawn from Vdd to Ground if the resistance between<br />
them is minimal. So any test that can turn on parallel transisters at a<br />
same time in both the AND and OR gates such that a conduction occurs from<br />
Vdd to Ground would induce the largest current.<br />
VLSI Test Principles and Architectures Ch. 4 – Test Generation – P. 8/8